Adrenal Glands Anatomy
- 1. ANATOMY OF ADRENAL GLANDS By- Dr. Geeta Dolli Associate Professor
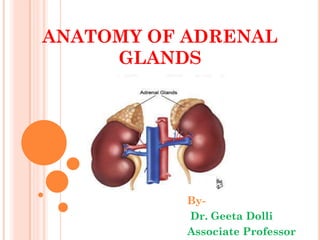
- 2. ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLAND Adrenal glands are a pair of important Endocrine glands situated on the posterior abdominal wall over the upper pole of kidneys behind the peritoneum.
- 3.  LOCATION; Epigastrium, at the upper pole of kidney. Infront of the crus of the diaphragm,opposite the vertibral end of the11th intercostal space and12th rib. SIZE, SHAPE AND WEIGHT Length-50mm Bredth-30mm Thickness-10mm and Weight-5g Rt-Triangular or Pyramidal Lt-Semilunar SHEATHS: Areolar tissue+fat, perirenal fascia
- 5. RIGHT ADRENAL GLAND  The Right Adrenal Gland is triangular in shape Apex- Bare area of liver  Base- Upper pole of right kidney  Surfaces 2 in Number • Anterior surface- Inferior vena cava, Right lobe of liver, duodenum • Posterior surface- Right crus of diaphragm  Borders 3 in number • Anterior- hilum, suprarenal vein • Medial- Right coeliac ganglion, right inferior phrenic artery • Lateral- Liver
- 6. LEFT ADRENAL GLAND  The Left Adrenal Gland is semi- circular in shape  2 Ends  Upper- Posterior end of spleen  Lower- Hilum, left suprarenal vein  2 Surfaces  Anterior- stomach,splenic artery, pancreas  Posterior- Kidney, Left crus of diaphragm  2 Borders  Medial- Left coeliac ganglion, left inferior phrenic artery,left gastric artery  Lateral- Stomach
- 7. STRUCTURE OF ADRENAL GLAND  ANATOMY OF ADRENAL GLANDS  The adrenal glands are paired bodies lying cranial to the kidneys within the retroperitoneal space.  The glands consist of two layers; I. cortex II. medulla
- 9. The adrenal cortex is red to light brown in colour and is composed of three zones. From the outer to inner, the layers are; 1. zonaglomerulosa 2. zonafasciculata 3. zonareticularis The adrenal cortex represents 80- 90% of the adrenal gland. The adrenal medulla represents only 10-20% of the adrenal gland.
- 10. • The adrenal glands are firm, and their capsule is easily fractured on flexion. The cortex on appearance is yellow and radially striated, whilst the medulla is darker with a more uniform appearance. • The zonaglomerulosa is narrow and the cells are in a whorled pattern. • The zonafasiculata is wide and the cells lie in columns and the zonareticularis is more randomly organised.
- 11. Cortex Medulla Catecholamine Zona reticularis Sex hormones Zona fesciculata Glucocorticoids Zona glomerulosa Mineralocorticoids
- 12. BLOOD SUPPLY Arteries • Superior suprarenal artery • Middle suprarenal artery • Inferior suprarenal artery Veins • Right suprarenal vein • Left suprarenal vein
- 13. LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AND NERVE SUPPLY Lymphatic drainage • Lumbar lymph nodes Nerve supply • Preganglionic sympathetic fibers • Postganglionic sympathetic fibers- chromaffin cells
- 14. APPLIED ANATOMY Addison’s disease Cushing’s syndrom Adrenogenital syndrom Adrenalectomy Phaeochromocytoma Ectopic sites Masculinisation/ Feminisation