Advanced Date/Time Handling with PHP
- 1. Welcome! Advanced Date/Time Handling ZendCon - Santa Clara, US - Nov 2nd, 2010 Derick Rethans - derick@php.net - twitter: @derickr http://derickrethans.nl/talks.html http://joind.in/2232
- 2. About Me Derick Rethans ¡ñ Dutchman living in London ¡ñ PHP development ¡ñ Author of the mcrypt, input_filter, dbus, translit and date/time extensions ¡ñ Author of Xdebug ¡ñ Contributor to the Apache Zeta Components Incubator project (formerly eZ Components) ¡ñ Freelancer doing PHP (internals) development
- 3. Problems Timezones ¡ñ Most places have whole-hour timezone offsets ¡ñ Some places change timezones during the year ¡ñ One identifier can mean different zones: PST: Pacific Standard Time, Pakistan Standard Time EST: Eastern Standard Time (USA), Eastern Standard Time (Australia) and Eastern Brazil Standard Time
- 4. Timezone Support ¡ñ Bundled timezone database with 564 zones ¡ñ Not dependent on timezone abbreviations ¡ñ Timezones have the format: Continent/Location or Continent/Location/Sublocation - Like: Europe/Amsterdam, America/Indiana/Knox
- 5. Changing Timezone Definitions ¡ñ An updated database is released about 20 times a year. ¡ñ Some of the changes are very sudden. ¡ñ PHP releases will therefore often have an outdated version. ¡ñ The PECL extension timezonedb provides a drop in replacement for the timezone database. ¡ñ pecl install timezonedb
- 6. Default Timezones Setting a default timezone: <?php date_default_timezone_set("Europe/Oslo"); $ts = new DateTime("1978-12-22 09:15"); echo $ts->format("e"); ?> Getting a default timezone: <?php $default_identifier = date_default_timezone_get(); echo $default_identifier; ?> Default timezone is 'guessed' in the following order: ¡ñ date_default_timezone_set() value ¡ñ TZ environment variable ¡ñ php.ini's date.timezone setting ¡ñ System's rendering of timezone abbreviation
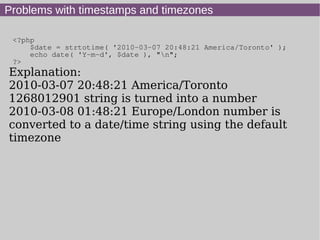
- 7. Problems with timestamps and timezones <?php $date = strtotime( '2010-03-07 20:48:21 America/Toronto' ); echo date( 'Y-m-d', $date ), "n"; ?> Explanation: 2010-03-07 20:48:21 America/Toronto 1268012901 string is turned into a number 2010-03-08 01:48:21 Europe/London number is converted to a date/time string using the default timezone
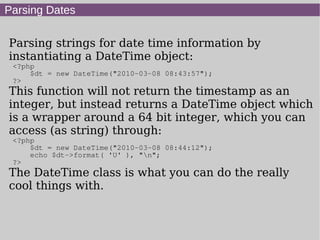
- 8. Parsing Dates Parsing strings for date time information by instantiating a DateTime object: <?php $dt = new DateTime("2010-03-08 08:43:57"); ?> This function will not return the timestamp as an integer, but instead returns a DateTime object which is a wrapper around a 64 bit integer, which you can access (as string) through: <?php $dt = new DateTime("2010-03-08 08:44:12"); echo $dt->format( 'U' ), "n"; ?> The DateTime class is what you can do the really cool things with.
- 9. Parsing Dates "22apr2006 8:36:14 #^ Europe/Oslo CEST" "22apr2006 8:36:14 #^ Europe/Oslo CEST" "22apr2006 8:36:14 Europe/Oslo CEST" "22apr2006 8:36:14 Europe/Oslo CEST" Parsing strings with the date_parse() function: <?php $date = "22apr2006 8:36:14.43 #^ Europe/Oslo CEST"; $t = date_parse( $date ); echo $t['year'], '-', $t['month'], '-', $t['day'], " "; echo $t['hour'], ':', $t['minute'], ':', $t['second'] + $t['fraction'], " "; echo $t['tz_id'], "n"; if ( $t['warning_count'] ) echo "Warnings:n"; foreach( $t['warnings'] as $pos => $message ) echo "- $message @$posn"; if ( $t['error_count'] ) echo "Errors:n"; foreach( $t['errors'] as $pos => $message ) echo "- $message @$posn";
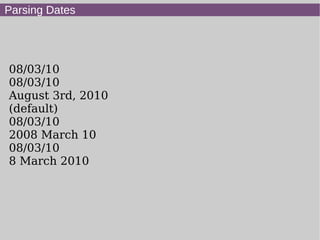
- 10. Parsing Dates 08/03/10 08/03/10 August 3rd, 2010 (default) 08/03/10 2008 March 10 08/03/10 8 March 2010
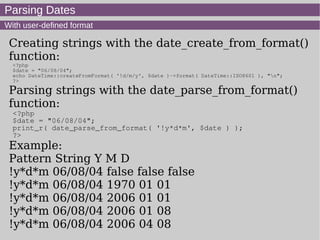
- 11. Parsing Dates With user-defined format Creating strings with the date_create_from_format() function: <?php $date = "06/08/04"; echo DateTime::createFromFormat( '!d/m/y', $date )->format( DateTime::ISO8601 ), "n"; ?> Parsing strings with the date_parse_from_format() function: <?php $date = "06/08/04"; print_r( date_parse_from_format( '!y*d*m', $date ) ); ?> Example: Pattern String Y M D !y*d*m 06/08/04 false false false !y*d*m 06/08/04 1970 01 01 !y*d*m 06/08/04 2006 01 01 !y*d*m 06/08/04 2006 01 08 !y*d*m 06/08/04 2006 04 08
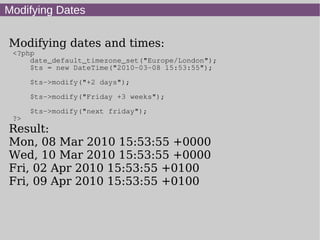
- 12. Modifying Dates Modifying dates and times: <?php date_default_timezone_set("Europe/London"); $ts = new DateTime("2010-03-08 15:53:55"); $ts->modify("+2 days"); $ts->modify("Friday +3 weeks"); $ts->modify("next friday"); ?> Result: Mon, 08 Mar 2010 15:53:55 +0000 Wed, 10 Mar 2010 15:53:55 +0000 Fri, 02 Apr 2010 15:53:55 +0100 Fri, 09 Apr 2010 15:53:55 +0100
- 13. Using Timezones The Timezone Object Creating a timezone resource: <?php $tz = new DateTimeZone("Asia/Singapore"); ?> Using the timezone when parsing a string with a date representation: <?php $tz = new DateTimeZone("Pacific/Honolulu"); $ts = new DateTime("1978-12-22 09:15", $tz); ?> A passed timezone object does not override a parsed timezone: <?php $tz = new DateTimeZone("Pacific/Honolulu"); $ts2 = new DateTime("1978-12-22 09:15 Europe/London", $tz); echo $ts2->format( DateTime::RFC2822 ); ?>
- 14. Using Timezones Changing timezones Using the timezone when parsing a string with a date representation: <?php $tz1 = new DateTimeZone("Pacific/Honolulu"); $tz2 = new DateTimeZone("Australia/Melbourne"); $ts = new DateTime("1978-12-22 09:15", $tz1); echo $ts->getTimezone()->getName(), ': ', $ts->format(DateTime::RFC2822), "<br/>"; $ts->setTimezone($tz2); echo $ts->getTimezone()->getName(), ': ', $ts->format(DateTime::RFC2822), "<br/>"; ?>
- 15. Timezones Utilities Transition Times and Location Information <?php $tz = new DateTimeZone("Europe/Berlin"); $trs = $tz->getTransitions( strtotime('1938-01-01 UTC'), strtotime('1948-01-01 UTC') ); foreach ($trs as $tr) { printf("%20s %7d %d %sn", $tr['time'], $tr['offset'], $tr['isdst'], $tr['abbr']); } $loc = $tz->getLocation(); echo 'Info: ', join( ' - ', $loc ), "n";
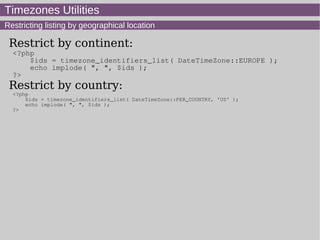
- 16. Timezones Utilities Restricting listing by geographical location Restrict by continent: <?php $ids = timezone_identifiers_list( DateTimeZone::EUROPE ); echo implode( ", ", $ids ); ?> Restrict by country: <?php $ids = timezone_identifiers_list( DateTimeZone::PER_COUNTRY, 'US' ); echo implode( ", ", $ids ); ?>
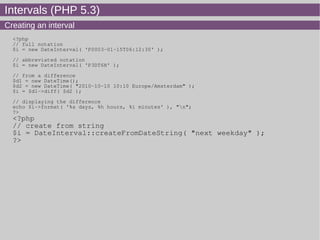
- 17. Intervals (PHP 5.3) Creating an interval <?php // full notation $i = new DateInterval( 'P0003-01-15T06:12:30' ); // abbreviated notation $i = new DateInterval( 'P3DT6H' ); // from a difference $d1 = new DateTime(); $d2 = new DateTime( "2010-10-10 10:10 Europe/Amsterdam" ); $i = $d1->diff( $d2 ); // displaying the difference echo $i->format( '%a days, %h hours, %i minutes' ), "n"; ?> <?php // create from string $i = DateInterval::createFromDateString( "next weekday" ); ?>
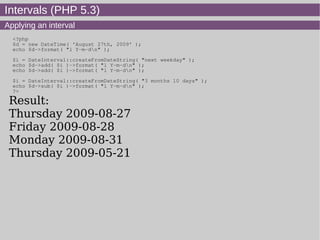
- 18. Intervals (PHP 5.3) Applying an interval <?php $d = new DateTime( 'August 27th, 2009' ); echo $d->format( "l Y-m-dn" ); $i = DateInterval::createFromDateString( "next weekday" ); echo $d->add( $i )->format( "l Y-m-dn" ); echo $d->add( $i )->format( "l Y-m-dn" ); $i = DateInterval::createFromDateString( "3 months 10 days" ); echo $d->sub( $i )->format( "l Y-m-dn" ); ?> Result: Thursday 2009-08-27 Friday 2009-08-28 Monday 2009-08-31 Thursday 2009-05-21
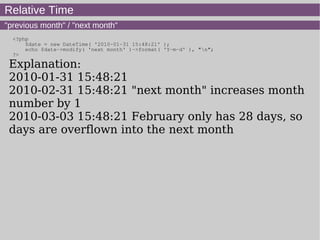
- 19. Relative Time "previous month" / "next month" <?php $date = new DateTime( '2010-01-31 15:48:21' ); echo $date->modify( 'next month' )->format( 'Y-m-d' ), "n"; ?> Explanation: 2010-01-31 15:48:21 2010-02-31 15:48:21 "next month" increases month number by 1 2010-03-03 15:48:21 February only has 28 days, so days are overflown into the next month
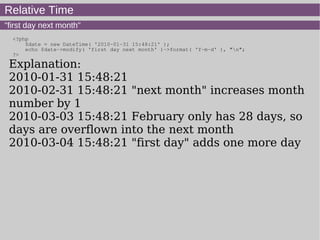
- 20. Relative Time "first day next month" <?php $date = new DateTime( '2010-01-31 15:48:21' ); echo $date->modify( 'first day next month' )->format( 'Y-m-d' ), "n"; ?> Explanation: 2010-01-31 15:48:21 2010-02-31 15:48:21 "next month" increases month number by 1 2010-03-03 15:48:21 February only has 28 days, so days are overflown into the next month 2010-03-04 15:48:21 "first day" adds one more day
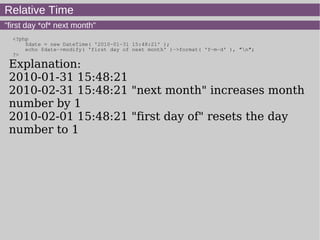
- 21. Relative Time "first day *of* next month" <?php $date = new DateTime( '2010-01-31 15:48:21' ); echo $date->modify( 'first day of next month' )->format( 'Y-m-d' ), "n"; ?> Explanation: 2010-01-31 15:48:21 2010-02-31 15:48:21 "next month" increases month number by 1 2010-02-01 15:48:21 "first day of" resets the day number to 1
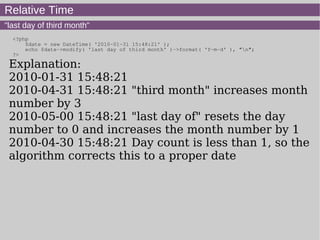
- 22. Relative Time "last day of third month" <?php $date = new DateTime( '2010-01-31 15:48:21' ); echo $date->modify( 'last day of third month' )->format( 'Y-m-d' ), "n"; ?> Explanation: 2010-01-31 15:48:21 2010-04-31 15:48:21 "third month" increases month number by 3 2010-05-00 15:48:21 "last day of" resets the day number to 0 and increases the month number by 1 2010-04-30 15:48:21 Day count is less than 1, so the algorithm corrects this to a proper date
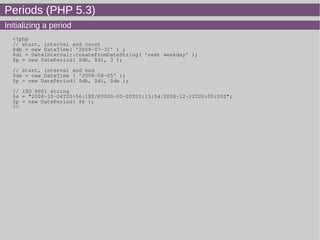
- 23. Periods (PHP 5.3) Initializing a period <?php // start, interval and count $db = new DateTime( '2008-07-31' ) ; $di = DateInterval::createFromDateString( 'next weekday' ); $p = new DatePeriod( $db, $di, 3 ); // start, interval and end $de = new DateTime ( '2008-08-05' ); $p = new DatePeriod( $db, $di, $de ); // ISO 8601 string $s = "2008-10-04T20:56:18Z/P0000-00-20T03:15:54/2008-12-22T00:00:00Z"; $p = new DatePeriod( $s ); ?>
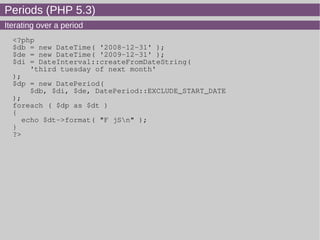
- 24. Periods (PHP 5.3) Iterating over a period <?php $db = new DateTime( '2008-12-31' ); $de = new DateTime( '2009-12-31' ); $di = DateInterval::createFromDateString( 'third tuesday of next month' ); $dp = new DatePeriod( $db, $di, $de, DatePeriod::EXCLUDE_START_DATE ); foreach ( $dp as $dt ) { echo $dt->format( "F jSn" ); } ?>
- 25. php|architect's guide to Date/Time handling
- 26. Resources ¡ñ This presentation: http://derickrethans.nl/talks.html ¡ñ World timezones: http://www.worldtimezone.com/index24.php ¡ñ Geonames: http://www.geonames.org/ ¡ñ Questions?: derick@php.net
- 27. Thanks! Derick Rethans - derick@php.net - twitter: @derickr http://derickrethans.nl/talks.html http://joind.in/2232






![Parsing Dates
"22apr2006 8:36:14 #^ Europe/Oslo CEST"
"22apr2006 8:36:14 #^ Europe/Oslo CEST"
"22apr2006 8:36:14 Europe/Oslo CEST"
"22apr2006 8:36:14 Europe/Oslo CEST"
Parsing strings with the date_parse() function:
<?php
$date = "22apr2006 8:36:14.43 #^ Europe/Oslo CEST";
$t = date_parse( $date );
echo $t['year'], '-', $t['month'], '-', $t['day'], " ";
echo $t['hour'], ':', $t['minute'], ':', $t['second'] + $t['fraction'], " ";
echo $t['tz_id'], "n";
if ( $t['warning_count'] )
echo "Warnings:n";
foreach( $t['warnings'] as $pos => $message )
echo "- $message @$posn";
if ( $t['error_count'] )
echo "Errors:n";
foreach( $t['errors'] as $pos => $message )
echo "- $message @$posn";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/time-zendcon10-101103064351-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Date-Time-Handling-with-PHP-9-320.jpg)


![Timezones Utilities
Transition Times and Location Information
<?php
$tz = new DateTimeZone("Europe/Berlin");
$trs = $tz->getTransitions(
strtotime('1938-01-01 UTC'), strtotime('1948-01-01 UTC')
);
foreach ($trs as $tr) {
printf("%20s %7d %d %sn",
$tr['time'], $tr['offset'], $tr['isdst'], $tr['abbr']);
}
$loc = $tz->getLocation();
echo 'Info: ', join( ' - ', $loc ), "n";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/time-zendcon10-101103064351-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Date-Time-Handling-with-PHP-15-320.jpg)