Advanced ventricular assist device ppt
- 2. What is a Ventricular Assist Device (VAD)? Mechanical circulatory device that is used to replace the pumping action of a failing human heart. Left ventricular failure is primarily treated using a VAD.
- 3. Need of Ventricular Assist Device ’ü« 5 million people suffer from Congestive heart failure (CHF). ’ü« 2,50,000 patients are in advanced stage of CHF. ’ü« 50,000 deaths are caused due to ventricular failure alone.
- 4. Classification of Ventricular Assist Devices ’āś On the basis of period of use: a) Temporary, b) Permanent ’āś On the basis of impaired ventricle: a) LVAD, b) RVAD, c) Bi-VAD ’āś On the basis of Pumping mechanism: a) Pulsatile b) Non pulsatile
- 5. ’āś On the basis of suspension of rotors: a) Bearing suspension b) Electromagnetic or Hydrodynamic suspension.
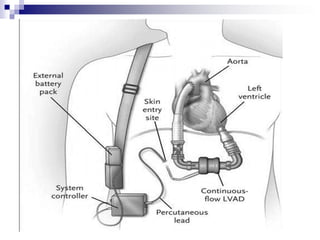
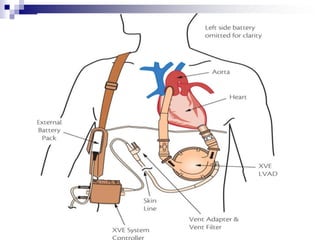
- 6. Advanced Ventricular Assist Device Termed as ŌĆ£Non pulsatile VADŌĆØ because the main difference between the pulsatile (earlier version of VADs) and non pulsatile ones is the pumping mechanism. Pulsatile VADs emulated the real contraction phenomenon of ventricles while Advanced VADs use continuous flow mechanisms.
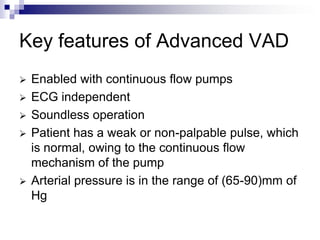
- 7. Key features of Advanced VAD ’āś Enabled with continuous flow pumps ’āś ECG independent ’āś Soundless operation ’āś Patient has a weak or non-palpable pulse, which is normal, owing to the continuous flow mechanism of the pump ’āś Arterial pressure is in the range of (65-90)mm of Hg
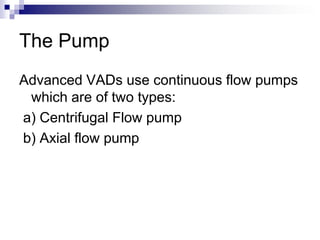
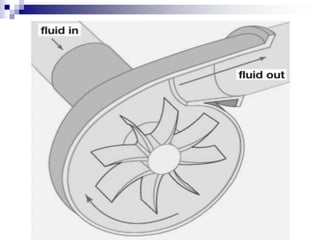
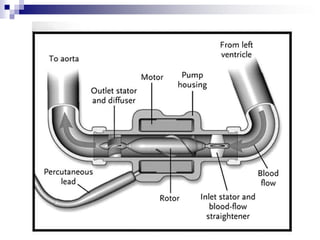
- 10. The Pump Advanced VADs use continuous flow pumps which are of two types: a) Centrifugal Flow pump b) Axial flow pump
- 13. Key Features of Continuous flow pumps ’āś Flow: Measured in liters per minute (lpm): 3 to 10 lpm Flow is directly proportional to pump speed. ’āś Speed: Measured in rpm: 8000 to 15000rpm ’āś Power:
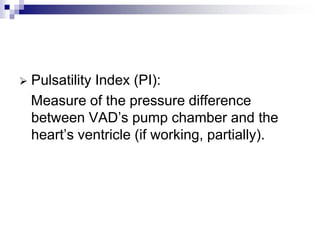
- 14. ’āś Pulsatility Index (PI): Measure of the pressure difference between VADŌĆÖs pump chamber and the heartŌĆÖs ventricle (if working, partially).
- 15. Shortcomings ’āś Coagulation and Thrombosis ’āś Haemolysis ’āś Infection ’āś Portability
- 16. Conclusion It has been a boon for cardiac patients. Future of VADs look bright as newer technologies and methods are being experimented to make the device better, lighter and easily portable.
- 17. Thank you