AEFI in Immunization
- 1. For More Health Information Log On To My Website www.vdcure.com AEFI Adverse Events Following Immunization
- 2. The vaccinators and the supervisors at the vaccination site will provide primary management for AEFIs. All sub centers should be prepare for facing any kind of AEFI with AEFI treatment kit.
- 3. Serious AEFIs: Refer immediately to the nearest health facility/AEFI management centre, and reported to the appropriate authority. Transportation costs will be borne through untied funds with Village Health and Sanitation Committee (VHSC).
- 6. Drugs Inj. Adrenalin (1:1000) solution – 2 ampoules Inj. Hydrocortisone (100 mg) – 1 vial I/V fluids (Ringer lactate/Normal Saline): 1 unit I/V fluids (5% Dextrose): 1 unit Tab Paracetamol (500 mg/125mg) - 10 tabs/Syp
- 7. Equipment Disposable Syringe (insulin type) having 0.01 ml graduations and 26G IM needle – 2 sets Disposable Syringe (5 ml) and 24/26G IM needle – 2 sets Scalp vein set – 2 sets IV drip set: 1 set Cotton wool + adhesive tape : 1 each At hospital setting, Oxygen support and airway intubation facility should be available.
- 8. Info/reports/Records: Label showing: Date of inspection, Expiry date of Inj. Adrenaline and shortest expiry date of any of the components Drug dosage tables for Inj Adrenaline and Hydrocortisone
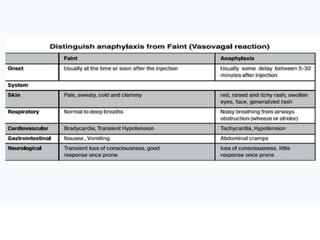
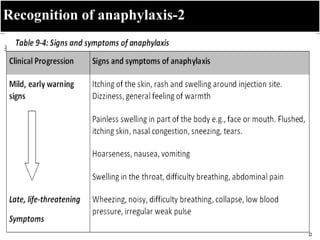
- 9. Management of a case of anaphylaxis Recognition of anaphylaxis-1 • Anaphylaxis ( a very rare at ~1/one million doses of measles vaccine given) but severe and potentially fatal allergic reaction, • When anaphylaxis occurs, the patient must be diagnosed properly, treated, and managed urgently by trained staff and transferred to a hospital setting, • The vaccinators, paramedics and physicians should be adequately trained – to able to distinguish anaphylaxis from fainting (Vasovagal syncope), anxiety and breath-holding spells, which are common benign reactions. – During fainting, individual suddenly becomes pale, loses consciousness and collapses to the ground. Fainting requires no specific treatment or investigation.
- 10. Recognition of anaphylaxis-2 – Bullet points – Bullet Points
- 11. Management of anaphylaxis • Once diagnosis is made, consider patient being in a potentially fatal condition, regardless of the severity of the current symptoms. • Begin treatment immediately, • In addition, make plans to transfer the patient immediately to the hospital (if not already in a hospital setting). • As described earlier, make easy availability of AEFI treatment kit
- 12. Steps in managAenamphyelanxist? of anaphylaxis Assess ABC: Airway/Breathing/Circulation Diagnosis: Look for Acute onset of illness/Life threatening problems with A-B-C/Skin changes Call for help/Lie patient flat/Raise patient’s legs/Keep airway clear/If necessary give CPR Inj. Adrenaline IM (1:1000 solution) Per dosage chart Inj Hydrocortisone [see dosage chart] Refer to next level, as needed In hospital settings: Establish airway/High flow oxygen/IV fluids
- 13. Management of anaphylaxis • Give adrenaline 1:1000 (age appropriate dose) by deep i/m injection into opposite limb, Give an additional half dose around the injection site (to delay antigen absorption). • If no improvement, repeat within 10-20 minutes of the first injection, up to a maximum of three doses, in total. • Give Inj. Hydrocortisone IM or slow IV per dosage • If patient conscious after adrenaline is given, place his/her head lower than the feet and keep the patient warm. • Give oxygen by face mask, if available. • Mark the immunization card clearly to prevent future repeat dose of offending vaccine. • Report anaphylaxis to the appropriate officer
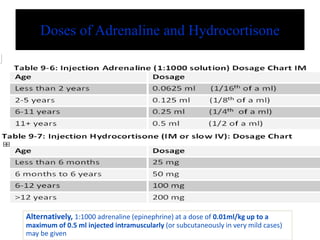
- 14. Doses of Adrenaline and Hydrocortisone Alternatively, 1:1000 adrenaline (epinephrine) at a dose of 0.01ml/kg up to a maximum of 0.5 ml injected intramuscularly (or subcutaneously in very mild cases) may be given
- 15. Note on Adrenaline dosage • 1 in 1000 solution means – 1g of adrenaline in 1000 ml of solution – 1000 mg of adrenaline in 1000 ml of solution – Or, 1 mg of adrenaline in 1 ml of solution – Or 0.01 mg of adrenaline in 0.01 ml of solution • Adrenaline dosage is 0.01 ml/kg of body weight • For a syringe which has 1 ml divided into 100 small divisions, each small division = 0.01 ml – So adrenaline dosage is easy to calculate and administer with such a syringe • Example: A child with body weight 12 Kg will need 0.12 ml of adrenaline = 12 small divisions of the syringe.
- 17. Summary • Measles vaccine is a safe and effective vaccine. • AEFI due to programme errors must be prevented at all costs, • Very rarely, measles vaccine can cause serious AEFI (e.g. anaphylaxis), which must be treated promptly, • All Govt. facilities ( PHC upwards) will function as AEFI management centres with designated medical officers, • All AEFI management centres must be fully equipped with AEFI treatment kits and protocols, prominently displayed. • The standard guidelines should be followed in all cases.
- 18. For More Health Information Log On To Thank My Website You www.vdcure.com










![Steps in managAenamphyelanxist? of anaphylaxis
Assess ABC: Airway/Breathing/Circulation
Diagnosis: Look for Acute onset of illness/Life
threatening problems with A-B-C/Skin
changes
Call for help/Lie patient flat/Raise patient’s
legs/Keep airway clear/If necessary give CPR
Inj. Adrenaline IM (1:1000 solution)
Per dosage chart
Inj Hydrocortisone [see dosage chart]
Refer to next level, as needed
In hospital settings: Establish airway/High flow
oxygen/IV fluids](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aefi-141212081748-conversion-gate01/85/AEFI-in-Immunization-12-320.jpg)