Affix
- 1. Roots and Affixes How words are created?
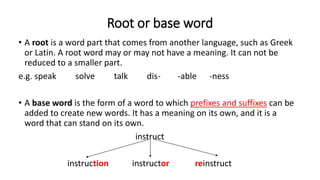
- 2. Root or base word âĒ A root is a word part that comes from another language, such as Greek or Latin. A root word may or may not have a meaning. It can not be reduced to a smaller part. e.g. speak solve talk dis- -able -ness âĒ A base word is the form of a word to which prefixes and suffixes can be added to create new words. It has a meaning on its own, and it is a word that can stand on its own. instruct instruction instructor reinstruct
- 3. Differences of root and base word âĒ New words can be formed using root words and base words by adding suffixes or prefixes, and several affixes can be added to root words to have a meaning. âĒ A root word is the basic linguistic unit, and it is the original form of a word while a base word is a word in its simplest form. E.g. They repainted the old car. re + paint + ed prefix base suffix
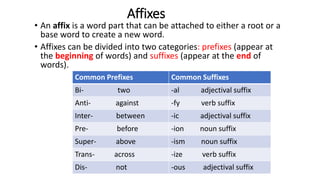
- 4. Affixes âĒ An affix is a word part that can be attached to either a root or a base word to create a new word. âĒ Affixes can be divided into two categories: prefixes (appear at the beginning of words) and suffixes (appear at the end of words). Common Prefixes Common Suffixes Bi- two -al adjectival suffix Anti- against -fy verb suffix Inter- between -ic adjectival suffix Pre- before -ion noun suffix Super- above -ism noun suffix Trans- across -ize verb suffix Dis- not -ous adjectival suffix
- 5. Apply âĒ For example one could analyze the word intangible, using the chart shown previously. âĒ First break the word into its parts: Prefix Root suffix English word In- + tang + -ible = intangible Tang is a latin root meaning âtouchâ In- is a prefix meaning ânotâ -ible is a suffix meaning âable toâ
- 6. Derivation and inflection âĒ Derivation: by adding a prefix or suffix, such as -ness or un-. For example, happiness and unhappy derive from the base word happy. âĒ Inflection: refers to modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, aspect, person, number, gender, and mood.
- 7. Derivation âĒ adjective-to-noun: -ness (slow â slowness) âĒ adjective-to-verb: -ise (modern â modernise) or -ize (final â finalize) âĒ adjective-to-adjective: -ish (red â reddish) âĒ adjective-to-adverb: -ly (personal â personally) âĒ noun-to-adjective: -al (recreation â recreational) âĒ noun-to-verb: -fy (glory â glorify) âĒ verb-to-adjective: -able (drink â drinkable) âĒ verb-to-noun (abstract): -ance (deliver â deliverance) âĒ verb-to-noun (agent): -er (write â writer)
- 8. Inflection