Airpressureback
- 1. Air Pressure & AirAir Pressure & Air circulationcirculation The answer is blowinâ in the windThe answer is blowinâ in the wind
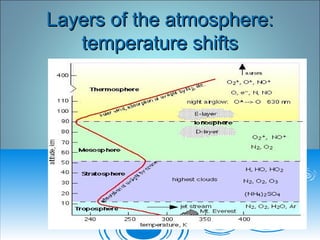
- 2. Layers of the atmosphere:Layers of the atmosphere: temperature shiftstemperature shifts
- 3. Pressure/ measurementPressure/ measurement ï Sea level average= 15 lbs per sq inch orSea level average= 15 lbs per sq inch or ï 1013mb1013mb ï 101,320 pascals101,320 pascals ï Barometer- mercury or aneroidBarometer- mercury or aneroid ï Wind direction â wind vanesWind direction â wind vanes ï Directional arrows/ speedDirectional arrows/ speed
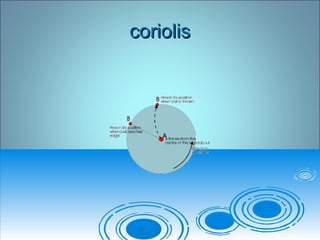
- 4. Birth of the windsBirth of the winds ï Weather systems travel with windWeather systems travel with wind movements:movements: ï A. Surface level air movements:A. Surface level air movements: ï 1. Pressure gradients1. Pressure gradients ï 2. coriolis force2. coriolis force ï 3. Friction3. Friction ï Isobars â curved lines outlining pressureIsobars â curved lines outlining pressure regionsregions ï B. Upper level winds - geostrophic ( noB. Upper level winds - geostrophic ( no
- 7. Friction: only with surfaceFriction: only with surface windswinds ï Friction bends the surface winds from aFriction bends the surface winds from a straight path, and a diagonal path isstraight path, and a diagonal path is formedformed High low
- 8. Cyclones are patterns of windCyclones are patterns of wind flowflow ï Cyclonic circulation Pattern: upward andCyclonic circulation Pattern: upward and inward in the Northern Hemisphere (LOW)inward in the Northern Hemisphere (LOW) ï Anticyclonic: Downward and outward inAnticyclonic: Downward and outward in the Northern Hemisphere (HIGH)the Northern Hemisphere (HIGH) ï Reversed in the Southern HemisphereReversed in the Southern Hemisphere
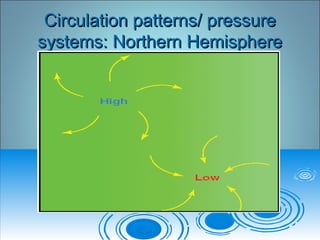
- 9. Circulation patterns/ pressureCirculation patterns/ pressure systems: Northern Hemispheresystems: Northern Hemisphere
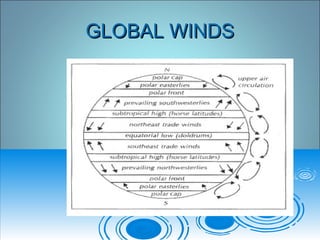
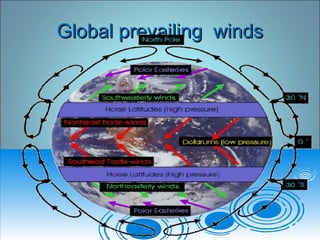
- 11. Global scale winds:Global scale winds: World wind & pressure beltsWorld wind & pressure belts ï World wind & pressure belts:World wind & pressure belts: ï zones âzones â ï natural: Equatorial low, (ITCZ)natural: Equatorial low, (ITCZ) subtropical highs, subpolar lowssubtropical highs, subpolar lows ( outbreak) & Polar Highs( outbreak) & Polar Highs ï Induced zones â products of the naturalInduced zones â products of the natural beltsbelts
- 13. Global prevailing windsGlobal prevailing winds
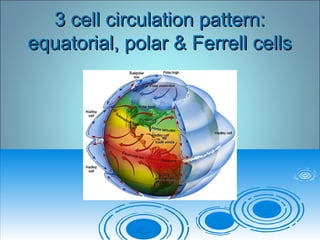
- 14. 3 cell circulation pattern:3 cell circulation pattern: equatorial, polar & Ferrell cellsequatorial, polar & Ferrell cells
- 15. Global flows - continuedGlobal flows - continued ï Hadley ( Equatorial) cells & world wind beltsHadley ( Equatorial) cells & world wind belts (polar & mid latitude)(polar & mid latitude) ï Modifiers:Modifiers: Surface winds â convective: valley,Surface winds â convective: valley, Mountain,Mountain, ï Upper level wind systems â Rossby waves, &Upper level wind systems â Rossby waves, & ï jet streams (polar ( ~250 mph) westerlyjet streams (polar ( ~250 mph) westerly ï ----subtropical jet ( westerly winds)----subtropical jet ( westerly winds) ï Tropical easterly jet ( summer in N.Tropical easterly jet ( summer in N. Hemisphere)Hemisphere)
- 17. Polar Jet StreamPolar Jet Stream
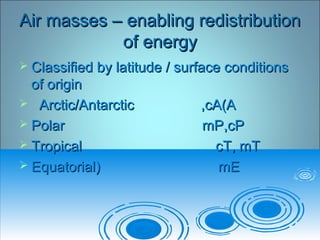
- 18. Air masses â enabling redistributionAir masses â enabling redistribution of energyof energy ï Classified by latitude / surface conditionsClassified by latitude / surface conditions of originof origin ï Arctic/Antarctic ,cA(AArctic/Antarctic ,cA(A ï Polar mP,cPPolar mP,cP ï Tropical cT, mTTropical cT, mT ï Equatorial) mEEquatorial) mE
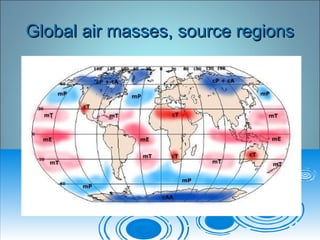
- 19. Global air masses, source regionsGlobal air masses, source regions
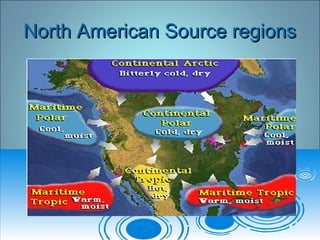
- 20. North American Source regionsNorth American Source regions
- 21. Wind / pressure systemsWind / pressure systems ï Global pressure belts â High & lowGlobal pressure belts â High & low pressure air masses give rise to windpressure air masses give rise to wind systems: global circulation.systems: global circulation. ï Regional pressure belts give rise toRegional pressure belts give rise to regional wind systems: (Mistral, Bora,regional wind systems: (Mistral, Bora, chinook), Santa Anachinook), Santa Ana
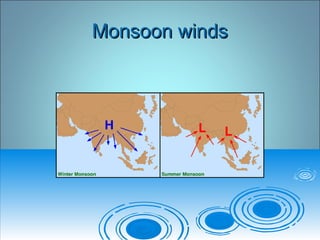
- 22. Monsoons & monsoonal typeMonsoons & monsoonal type windswinds ï Monsoons - SEASONAL CHANGES IN PRESSURE &Monsoons - SEASONAL CHANGES IN PRESSURE & WINDSWINDS ï California coastal pressure changes,California coastal pressure changes, ï El Nino- not a wind system per se, just generates them.El Nino- not a wind system per se, just generates them. ï Monsoonal winds ( seasonal, shifting),Monsoonal winds ( seasonal, shifting), ï SEASONAL CHANGES BY LATITUDE: winter â highSEASONAL CHANGES BY LATITUDE: winter â high pressure in high latitude lands, creates cool dry northerlypressure in high latitude lands, creates cool dry northerly windswinds ï summer â STH over the oceans, low latitudes- bringssummer â STH over the oceans, low latitudes- brings rains to the east coasts of continents, dry air to the westrains to the east coasts of continents, dry air to the west coast of continents.coast of continents.
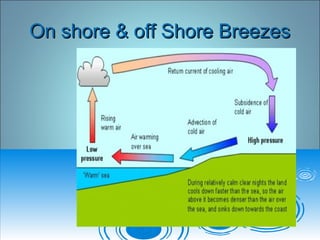
- 25. Local windsLocal winds ï Convectional flows ( on-shore, off-shore)Convectional flows ( on-shore, off-shore) ï Mountain/valley breezes ( also known as)Mountain/valley breezes ( also known as) ï drainage winds : Mountain, valleydrainage winds : Mountain, valley ï ( Katabiatic-( Katabiatic- ï ---Chinook (Foehn - Switzerland),---Chinook (Foehn - Switzerland), (Mistral France),( Bora â Adriatic (Croatia)(Mistral France),( Bora â Adriatic (Croatia) ï Santa Ana ( Western U.S.)Santa Ana ( Western U.S.)
- 26. On shore & off Shore BreezesOn shore & off Shore Breezes
- 27. Indications of wind directionIndications of wind direction
- 28. Seasonal shift of pressure/windSeasonal shift of pressure/wind patternspatterns ï ASIA Pacific N.Amer. Atl. EurASIA Pacific N.Amer. Atl. Eur ï Winter: Icel.LWinter: Icel.L ï Siberian H Aleutian L HawiianHSiberian H Aleutian L HawiianH ï Summer:Summer: ï Asiatic L Hawaiian H Azores HAsiatic L Hawaiian H Azores H
- 29. January: Northern HemisphereJanuary: Northern Hemisphere pressure systems Enc.pressure systems Enc. BritannicaBritannica
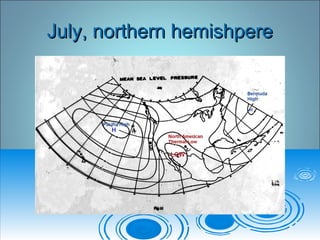
- 30. July, northern hemishpereJuly, northern hemishpere
- 31. Southern hemisphereSouthern hemisphere ï Variations are less extreme because ofVariations are less extreme because of the dominance of water in the hemispherethe dominance of water in the hemisphere
- 32. RECAP: Additional wind flows-RECAP: Additional wind flows- override prevailing winds for a timeoverride prevailing winds for a time ï Surface winds â convective: valley,Surface winds â convective: valley, Mountain, Upper level â Rossby waves,Mountain, Upper level â Rossby waves, ï jet streams (polar ( -250 mph) westerlyjet streams (polar ( -250 mph) westerly ï ----subtropical jet ( westerly winds)----subtropical jet ( westerly winds) ï Tropical easterly jet ( summer in N.Tropical easterly jet ( summer in N. Hemisphere)Hemisphere) ï GIVE VARIETY TO LOCAL WEATHERGIVE VARIETY TO LOCAL WEATHER PATTERNSPATTERNS