Ajax, rss, feeds, web service,
- 1. Presented By JM.Radhakrishnan
- 2. What is AJAX? Ajax stands for ŌĆ£ Asynchronous JavaScript and XML ŌĆØ
- 3. Ajax is a way of developing Web applications that combines
- 4. OR
- 5. AJAX is a mixture of several popular technologies put together to build the next generation of web applications, which are more responsive, more interactive and behave like their desktop counterparts
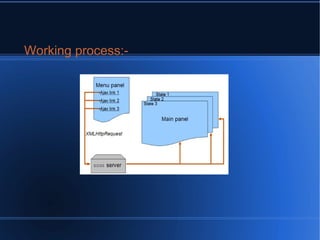
- 6. Features:- Asynchronous loading of content without page refresh
- 7. # Ajax sites has one or more pages.
- 8. # When you change anything in all your sites
- 9. pages without having to rebuild it each time.
- 10. Increased interactivity and responsiveness
- 11. Reduced loading time and server traffic
- 13. Usage:- The use of Ajax techniques has led to an increase in interactive or dynamic interfaces on web pages
- 14. Examples:- Flickr - A Yahoo! Company
- 15. Flickr is a photo storage and display program that uses AJAX.
- 16. Gmail - Google
- 17. Gmail is an AJAX powered email system.
- 18. Google Maps - Google
- 19. Google Maps uses AJAX to power it's interactive map.
- 20. RIA
- 21. What is RIA? RIA stands for ŌĆ£Rich Internet ApplicationŌĆØ .
- 22. RIAs are web application.
- 23. Typically delivered either by way of a site-specific browser, via a browser plug-in, or independently via sandboxes or virtual machines
- 24. Examples:- The most famous example of RIA is ŌĆ£FlashŌĆØ.
- 25. WEB SERVICES
- 26. What is web services:- Web services are typically application programming interfaces (API) that can be accessed over a network and executed on a remote system hosting the requested services.
- 27. (or)
- 28. A "web service" as a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network.
- 29. Features of web services:- Productivity Enhancements.
- 30. Extensibility
- 31. Performance
- 32. Commitment to Interoperability and Standards
- 33. Usage:- The comman usage of web services are clients and servers that communicate over the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) protocol used on the web.
- 34. Examples:- The best example is ŌĆ£InternetŌĆØ .
- 35. SOA
- 36. What is SOA? It stands for ŌĆ£service oriented architectureŌĆØ .
- 37. A service-oriented architecture is essentially a collection of services.
- 38. These services communicate with each other. The communication can involve either simple data passing or it could involve two or more services coordinating some activity. Some means of connecting services to each other is needed.
- 39. Features:- It features online articles, services, and product listings that can be used to develop a service-oriented architecture using Web services.
- 40. Example:- Real-Time Embedded Systems.
- 41. Improving the size of communication buffers in synchronous models with time constraints
- 42. MASH-UP
- 43. What is mash-up? A mash-up is a web page or application that uses or combines data or functionality from two or many more external sources to create a new service.
- 44. It implies easy, fast integration, frequently using open APIs and data sources to produce enriching results that were not necessarily the original reason for producing the raw source data.
- 45. Types of mashup:- Data mashups
- 46. consumer mashups
- 49. Second life maps
- 51. RSS:- It stands for ŌĆ£Really Simple Syndication" .
- 52. RSS is a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works such as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video in a standardized format.
- 53. An RSS document includes full or summarized text, plus metadata such as publishing dates and authorship
- 54. WIKI:- A wiki is a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text editor.
- 55. Wikis are typically powered by wiki software and are often used to create collaborative websites, to power community websites, for personal note taking, in corporate intranets, and in knowledge management systems.
- 56. Flash:- Flash is a vector animation software, originally designed to create animations for display on web pages.
- 57. Vector graphics are ideal for the web because they are so lightweight.
- 58. Macromedia argues that Flash is the way to go instead of HTML because of the following reasons: # . Flash movies load faster and save on download time because Flash is vector based whereas HTML is not. # . Flash intelligently ŌĆścachesŌĆÖ itŌĆÖs movies so they donŌĆÖt have to be reloaded. # . Flash gives the user a more responsive ŌĆśrich-clientŌĆÖ like experience.
- 59. Blog:- A blog is a type of website, usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material such as graphics or video.
- 60. Entries are commonly displayed in reverse-chronological order.
- 61. "Blog" can also be used as a verb, meaning to maintain or add content to a blog.
- 62. Type of Blogs:- Personal blogs
- 63. Corporate and organizational blogs
- 64. By genre
- 65. By media type
- 66. By device
- 67. Pod cast:- A podcast is a series of digital media files that are released episodically and often downloaded through web syndication.
- 68. The mode of delivery differentiates podcasting from other means of accessing media files over the Internet, such as direct download, or streamed webcasting
- 69. SOAP:- It defined as ŌĆ£Simple Object Access ProtocolŌĆØ .
- 70. Soap is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of Web Services in computer networks
- 71. The SOAP architecture consists of several layers of specifications for message format, message exchange patterns (MEP), underlying transport protocol bindings, message processing models, and protocol extensibility.
- 72. Social web:- The Social Web is currently used to describe how people socialize or interact with each other throughout the World Wide Web.
- 73. The first kind of socializing is typified by "people focus" websites such as Bebo, Facebook, and Myspace. Such sites promote the person as focus of social interaction. To do this an online identity is constructed by each user
- 74. The second kind of socializing is typified by a sort of "hobby focus" websites. For example, if one is interested in photography and wants to share this with like-minded people, then there are photography websites such as Flickr, Kodak Gallery and Photobucket.
- 75. The Social Web may also be used to refer to two different, yet related concepts.
- 76. The first is as a description of web 2.0 technologies that are focused on social interaction and community before anything else.
- 77. The second is a proposal for a future network similar to the World Wide Web.
- 78. Tagging:- In online computer systems terminology, a tag is a non-hierarchical keyword or term assigned to a piece of information. This kind of metadata helps describe an item and allows it to be found again by browsing or searching.
- 79. Tags are generally chosen informally and personally by the item's creator or by its viewer, depending on the system.
- 80. Tagging was popularized by websites associated with Web 2.0 and is an important feature of many Web 2.0 services. It is now also part of some desktop software.
- 81. Many blog systems allow authors to add free-form tags to a post, along with placing the post into categories.
- 82. For example , a post may display that it has been tagged with baseball and tickets.
- 83. Feeds:- A web feed is a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content.
- 84. Content distributors syndicate a web feed, thereby allowing users to subscribe to it.
- 85. Making a collection of web feeds accessible in one spot is known as aggregation, which is performed by an aggregator.
- 86. A web feed is also sometimes referred to as a syndicated feed.
- 87. Web feeds are operated by many news websites, weblogs, schools, and podcasters.