Alarms waves capnography
- 1. Capnography Monitoring By: Ahmad Amirdash MS, APRN, AG-ACNP-BC, CCRN, BBA You are Welcome to use slides but please reference my post when you do so to maintain the integrity of authorship
- 2. What do the alarms mean? Does the patient have: Clinical Assessment Considerations: ? Low RR alarms ? Decreasing RR ? Hypoventilation ? Shallow breathing ? Periods of “No Breath” or Apnea ? Check if etCO2 level is increasing ? High etCO2 alarm ? Increasing etCO2 ? Hypoventilation/CO2 accumulating ? Low RR ? Recent ingestion of carbonated beverages/antacids ? Low etCO2 alarm ? Decreasing etCO2 ? RR increasing/hyperventilating ? Shallow breathing ? No Breath or Apnea alarm ? Apnea ? Complete airway obstruction ? FilterLine needs repositioning ? Extreme shallow breathing
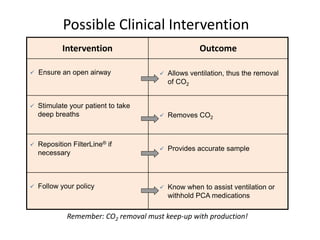
- 3. Possible Clinical Intervention Intervention Outcome ? Ensure an open airway ? Allows ventilation, thus the removal of CO2 ? Stimulate your patient to take deep breaths ? Removes CO2 ? Reposition FilterLine? if necessary ? Provides accurate sample ? Follow your policy ? Know when to assist ventilation or withhold PCA medications Remember: CO2 removal must keep-up with production!
- 4. What do I look for? ? Significant changes in the values (trends greater than 10 mmHg) ? Alarms: – etCO2 trending too high – etCO2 trending too low – RR decreasing – Periods of No Breath Detected (apnea) ? Can be any one or a combination of all
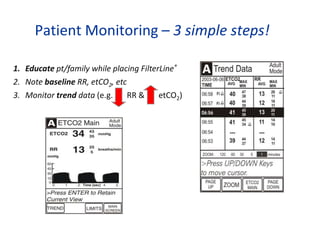
- 5. 1. Educate pt/family while placing FilterLine? 2. Note baseline RR, etCO2, etc 3. Monitor trend data (e.g. RR & etCO2) Patient Monitoring – 3 simple steps!
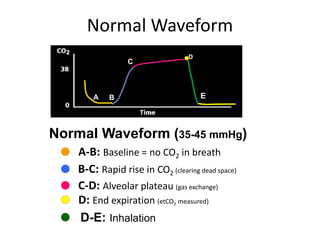
- 6. Normal Waveform (35-45 mmHg) A-B: Baseline = no CO2 in breath B-C: Rapid rise in CO2 (clearing dead space) D-E: Inhalation C-D: Alveolar plateau (gas exchange) D D: End expiration (etCO2 measured) Normal Waveform