ALCOHOLIC LIVER DISEASE
- 1. ALCOHOLIC LIVER DISEASE Dr. Rakesh Kumar . Adi (D.M.) Gastroenterology Osmania General Hospital
- 2. PARADOX Why does cirrhosis develop in only a small fraction of alcoholics ? What is the pathogenesis of sev. ALD ? What are the most effective treatments for patients with adv. disease ?
- 3. Background Spectrum of ALD Alcoholic hepatitis Presentations Management Prognosis
- 4. India : alcohol The prevalence of use of alcohol ranges from a low of 7% in Gujarat , to 75% in Arunachal Pradesh. The per capita consumption is 4 lit/adult /year It accounts for 50% of CLD ALD cause of mortality M: 11/100000 F: 6/100000
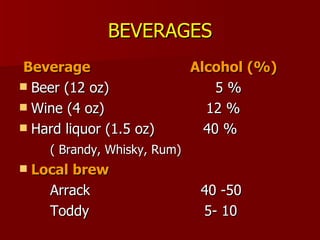
- 5. BEVERAGES Beverage Alcohol (%) Beer (12 oz) 5 % Wine (4 oz) 12 % Hard liquor (1.5 oz) 40 % ( Brandy, Whisky, Rum) Local brew Arrack 40 -50 Toddy 5- 10
- 6. Standard drink ( 12 gms abs.alcohol ) 4 4 One beer wine hard liqour 1 ounce = 30 ml
- 7. Simple conversion BEER : ml / 25 WINE : ml / 10 HARD LIQOUR : ml/ 3 } Gms of alcohol
- 8. Risk for the development of ALD. Time to develop ALD = to amount of alcohol consumed Men : 60-80 gm/day for 10 years Women : 20-40 gm/day for 10 years Alcoholic cirrhosis , develops ONLY in 10 to 20% of those who are chronically heavy drinkers.
- 9. Risk of liver disease Amount of alcohol consumed, Genetic factors Female sex Obesity Chronic viral hepatitis Nutritional impairment and Drugs
- 10. Alcohol Abuse vs. Alcohol Dependence Alcohol abusers as those who drink despite recurrent social, interpersonal, and legal problems Dependence - presence of 3 or more symptoms a) tolerance b) withdrawal symptoms c) loss of control over drinking d) strong desire to drink e) drinking despite harm
- 11. DETECTION OF ALCOHOL ABUSE CAGE ( C ut down, A nnoyed by criticism, G uilty about drinking , E ye-opener in the morning) AUDIT ( A lcohol U se D isorders I dentification T est) 10-item questionnaire
- 12. Laboratory markers GGT MCV CDT : Elevated levels of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin Combined MCV and GGT detects 70% of the alcohol-dependent population. CDT may be more sensitive in evaluating drinking
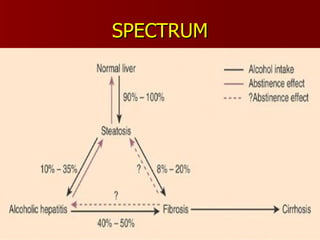
- 13. Spectrum of disease ALD comprises an overlapping spectrum of pathological processes Steatosis (alcoholic fatty liver) Alcoholic hepatitis Alcoholic cirrhosis.
- 14. SPECTRUM
- 15. Spectrum
- 16. ALCOHOLIC HEPATITIS It is a form of hepatic injury that carries a significant morbidity and exceptional high short term mortality .
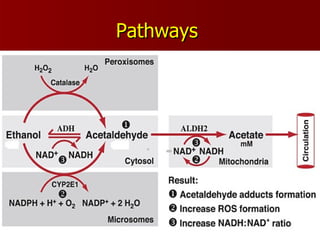
- 17. Ethanol Metabolism Ethanol is metabolized by three major systems in the liver: Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADHs), Cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1), Catalase
- 18. Pathways
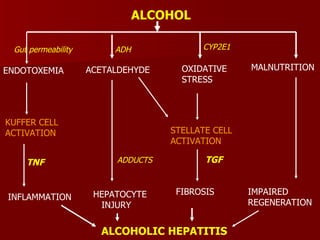
- 19. Pathogenesis Genetic factors ( ADH2 ,ALDH2 ) Toxic metabolites of ALDH ( adducts ) Free radicals and oxidative stress ( ROS ) Role of immune system Hypermetabolic state of hepatocyte Cytokines ( TNF ,TGF ) Malnutrition
- 20. ALCOHOL ENDOTOXEMIA ACETALDEHYDE OXIDATIVE STRESS MALNUTRITION KUFFER CELL ACTIVATION INFLAMMATION HEPATOCYTE INJURY STELLATE CELL ACTIVATION FIBROSIS IMPAIRED REGENERATION ALCOHOLIC HEPATITIS Gut permeability ADH CYP2E1 TNF ADDUCTS TGF
- 21. PATHOLOGY Steatosis Ballooning necrosis Malloryâs hyaline bodies Neutrofilic cellular infiltration Fibrosis
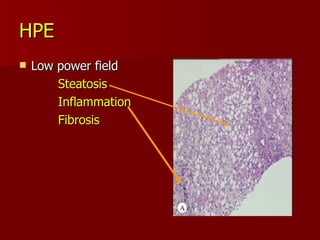
- 22. HPE Low power field Steatosis Inflammation Fibrosis
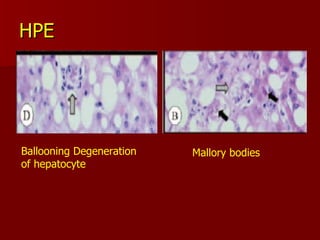
- 23. HPE Ballooning Degeneration of hepatocyte Mallory bodies
- 24. Presentations Asymptomatic (majority of cases) Hepatomegaly Biochemistry mildly abnormal Needs histology for confirmation Symptomatic (minority of cases) Liver failure
- 25. Clincal Features Symptoms Jaundice Fatigue Anorexia Weight loss Fever Pain in RHC Physical examination Stigma of CLD Tender hepatomegaly Hepatic decompensation- Ascites, Eso. varies Encephalopathy.
- 26. Lab Both AST and ALT are INC. , < 300 IU/mL AST>ALT of 2 ( 80% ) Inc in GGT Macocytosis with anemia Thrombocytopenia Leukocytosis- correlates with degree of injury. Increasing Bilrubin And PT correlate with severity of liver disease
- 27. OthersâĶ.. High CDT High gamma globulin (IgA) High uric acid High serum lactate Low albumin High triglycerides
- 28. Prognosis of AH: Why Score it? To identify patients at greatest risk of death To decide when to offer second line treatment (Steroids/ pentoxifylline) Design of clinical studies for Rx of AH
- 29. Prognostic Scores for AH Discriminant function (Modified DF) Glasgow Alcoholic Hepatitis Score MELD CTP
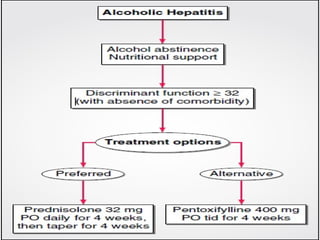
- 30. Maddrey Discriminant Function 4.6 x (prolongation of PT) + Bilrubin If < 32 1 month mortality 10 % If > 32, 1 month mortality is 35% ; 45 % + encephalopathy. 75 % + HRS
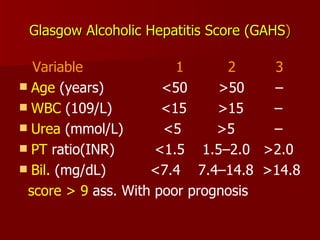
- 31. Glasgow Alcoholic Hepatitis Score (GAHS ) Variable 1 2 3 Age (years) <50 >50 â WBC (109/L) <15 >15 â Urea (mmol/L) <5 >5 â PT ratio(INR) <1.5 1.5â2.0 >2.0 Bil. (mg/dL) <7.4 7.4â14.8 >14.8 score > 9 ass. With poor prognosis
- 32. A prognostic model (the ââLilleââ model ) At day 0 : Presence of encephalopathy mDF , creatinine and an early change in bil.( DAY 7) Score >> 0.5 predicted nearly 80% of the deaths at 6 months
- 33. MANAGEMENT Life style Modification Nutrition Therapy Drugs
- 34. Life style Modification EtOH intake : 80% survival rate in those who abstain Smoking : Cigarette smoking is an independent risk factor for cirrhosis in ALD Am J Epi. 1994 Obesity
- 35. Nutrition Therapy Nutritional supplement improves hepatic function, and outcome in AH . Patients consuming > 3000 kcal/d had virtually no mortality, whereas those consuming < 1000 kcal/d had > 80% 6-month mortality Alcohol Clin Exp 1995
- 36. DRUGS
- 37. Ėý
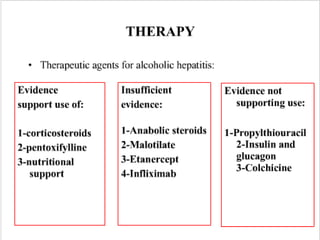
- 38. Corticosteroids Decrease the immune response Anti inflammatory Antifibrotic Increase production of albumin Improve ascites. Improve caloric intake by improving appetite
- 39. Prednisolone : 32 mg PO for 4 weeks followed by taper Active form prednisolone, rather than the inactive precursor prednisone, is preferred NO long term survival benefits
- 40. The ASG recommends use of steroids for sev. AH Ideal patient has 1) MDF > 32 with 2)Spontaneous encephalopathy 4)No contraindications such as active GI bleeding, HRS ,sepsis, AVH Carithers, Ann Int Med, 1989 Mendenhall, NEJM, 1984
- 41. Pentoxifylline It attenuates TNF-a release and action Exerts an antifibrinogenic action lower portal hypertension Decreases blood viscosity Improve organ microcirculation Tissue oxygenation
- 42. Side-effects : Epigastric pain, vomiting, and dyspepsia Dose : 400 mg TID Improvement in short-term (4-week) survival Decrease in the rate of development of hepatorenal syndrome Akriviadis, Gastroenterology, 2000
- 43. Specific AntiâTNF Therapy Infliximab (anti-TNF antibody Etanercept , a TNF receptor antagonist, Until more data are available, specific anti-TNF therapy should be used only in the context of a clinical trial.
- 44. Antioxidants S-adenosylmethionine : Benefits of SAM in ALD include roles as an Antioxidant Critical methyl donor Decreasing TNF levels, and Glutathionine
- 45. Propylthiouracil : No significant effects of PTU vs placebo on mortality, complications of liver disease . Cochrane review of 6RCT Colchicine : NO beneficial effect on overall mortality . Morgan, Gastroenterology, 2002
- 46. Newer Approaches Polyenylphosphatidylcholine N-acetyl cysteine Combination therapy Liver transplantation : OLT for alcoholic hepatitis is not currently recommended . LAG Guidelines 2006
- 47. Ėý
- 48. Thank q
- 49. Women : alcohol Women alcoholics begin drinking later, and drink less alcohol per day than men Women drink for fewer years than men . Yet , Women die of ALD at a 10 year earlier age than men.
- 50. More pronounced fatty liver Less induction of fatty acid binding protein (higher FFA) Increased plasma endotoxin levels Increased CD 13 More severe pericentral hypoxia More marked activation of NfkB Womenâs Risk of ALD