algebraic expression class VIII
- 1. Model Lesson Plan (Mathematics) Class VIII Topic Algebraic Expressions and Identities Sub Topic Identities TIME DURATION-45 MINUTES
- 2. Prepared & Presented By Ms. Sushma Singh (TGT Maths) RPVV Rohini Delhi
- 3. 1. Objectives:- In Algebraic Expressions & Identities 1. The child will know about the identities in algebraic expression and will be able to represent it geometrically. 2. He will be able to know the relationship between algebra, geometry and arithmetic. 3. He will also understand the relationship between the algebraic expressions 4. From the exercises based on pictures and numericals he will generalise the algebraic expression. 5. He will be able to use it in daily life etc...
- 4. 2. Teaching Method:- 1) Art Integrated Learning (AIL) This process involves learning through integrating various subjects with different modules of art such as painting, drawing, clay modelling, paper-cutting, theatre, dance etc... 2) Interactive method Presentation based learning, video modules,etcŌĆ”
- 5. 3. Material Required:- Pencil, geometry box, notebook, pen glaze paper, scissors, pasting material, learning kit, power ppt etc.
- 6. 4. Previous Knowledge:- Children have studied mathematics up to class 7th and they are aware about variables, constants and algebraic expressions.
- 7. 5. Introduction:- Hi Students! Today in this class of mathematics we are going to study about use Identities in algebraic expressions .
- 8. ŌĆó Before we start I want to ask you one Interesting question. Have you ever learnt algebra, when you were very small kid? ŌĆó Your Simple flat answer is NO.
- 9. ŌĆó But I say yes, you have learnt algebra when you were a small baby and your mother started calling you chikki, duggu. Do you know from where these names came? Duggu! Where r u?
- 10. ŌĆó Since you were unnamed that time and your mother wanted to interact with you, she needed some variable to address you and she started calling you by these names. You learnt that it was your name and started giving response to mother with smile.
- 11. Similarly in mathematics when we represent numbers 2, 3, 4 with some other names like a, b, c these are called variables. Variables and constants form a term and terms are added to form algebraic expressions. Your name is a variable which you learnt when you were kid.
- 12. 6. Content:- ŌĆó Let us see how we can represent different numbers and algebraic expressions geometrically.
- 13. This is what we call geometrical expression of algebraic expression. When we use variables to represent certain values we deal with algebra.
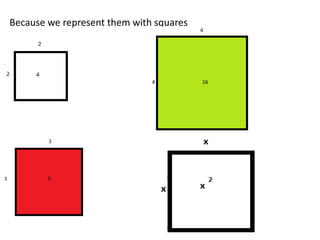
- 14. So I must assume that you know algebra. Let us perform one activity: But before that one more question for you Why 4, 9, and 16 are called squared numbers?
- 15. Because we represent them with squares
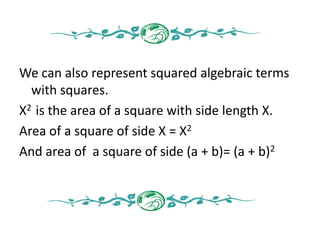
- 16. We can also represent squared algebraic terms with squares. X2 is the area of a square with side length X. Area of a square of side X = X2 And area of a square of side (a + b)= (a + b)2
- 17. ACTIVITY-1 a2 + ab + ab +b2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
- 18. Did U know? You can apply the algebraic identity to work out arithmetic problems IDENTITY TAKEN:- (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 Example: (17)2 = (10 + 7 )2 = 102 + 2(10) (7) + 72 = 100 + 140 + 49 = 289
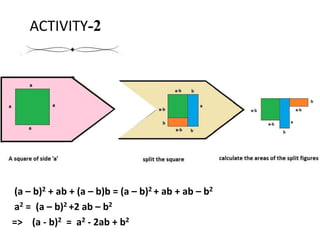
- 19. ACTIVITY-2 (a ŌĆō b)2 + ab + (a ŌĆō b)b = (a ŌĆō b)2 + ab + ab ŌĆō b2 a2 = (a ŌĆō b)2 +2 ab ŌĆō b2 => (a - b)2 = a2 - 2ab + b2
- 20. You can also apply the algebraic identity to work out arithmetic problems IDENTITY TAKEN:- (a - b)2 = a2 - 2ab + b2 Example: (17)2 = (20 - 3 )2 = 202 - 2(20) (3) + 32 = 400 - 120 + 9 = 289
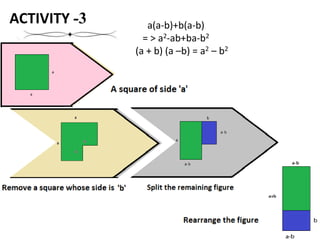
- 21. ACTIVITY -3 a(a-b)+b(a-b) = > a2-ab+ba-b2 (a + b) (a ŌĆōb) = a2 ŌĆō b2
- 22. You can also apply the algebraic identity to work out arithmetic problems IDENTITY TAKEN:- (a + b) (a ŌĆōb) = a2 ŌĆō b2 Example: (17 X 23) = (20 - 3) (20 +3) = 202 - 32 = 400 ŌĆō 9 = 391
- 23. What is an identity? Consider the equality, (a+1)(a+2)=a2 +3a+2 For a=2 We can show LHS=RHS, (2+1)(2+2)=22 + 3(2)+2 12=12 Let us now take a=-3 Then also, (-3+1)(-3+2)=(-3)2+3(-3)+2 2=2 Such an equality, true for every value of variable in it, is called IDENTITY
- 24. 7. What have we learnt? An identity is equality, which is true for all values of the variables in the equality. The following are the standard identities: (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 -------------------------(1) (a - b)2 = a2 - 2ab + b2 -------------------------(11) (a + b) (a ŌĆōb) = a2 ŌĆō b2 --------------------- (111) The above identities are useful in carrying out squares and products of algebraic expressions. They also allow easy alternative methods to calculate products of numbers
- 25. 8. Now try these questions:- 1) Using the identity (1) find (i) (2x + 3y)2 (ii) 1032 2) Using the identity (11) find (i) (4p - 3q)2 (ii) (4.9)2 3) Using the identity (111) find (i) (3/2 m + 2/3 n) (3/2 m ŌĆō 2/3 n) (ii) 9832 - 172 (iii) 194 X 206
- 26. 9. Try at Home:- 1. Represent the identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 by taking the value of a =3 and b = 4 geometrically. 2. Using identity find the value of the arithmetic problem (104)2. 3. Find the product of 104 X 96 by using the algebraic identity.
- 27. Thank you ’üŖ