Algorithm and Flowcharts
- 2. Goals By the end of this lecture you should âĶ ïUnderstand the role of a computer as a tool in Computer Science. ïUnderstand the study of algorithms. ïBe able to identify how algorithms are developed & evaluated. ïFlowcharts
- 3. The Computer as a Tool ïMuch like the microscope does not define biology or the test tube does not define chemistry, the computer doesn't define Computer Science. ïThe computer is a tool by which Computer Scientists accomplish their goals â to solve problems.
- 4. What is Computer Science? ïNOT about coding or hardware or software! ïComputer Science is about PROBLEM SOLVING ïComputer Science is about DEVELOPING ALGORITHMS to solve complex problems
- 6. What is an Algorithm? ïAn algorithm is a well-developed, organized approach to solving a complex problem. ïIt refers to the logic of the program . ïIt is step by step solution to given problem.
- 7. Now a Create Algorithm!! ïProblem: Dad said you to buy books from a shop 10km from your house. ïStep 1: GET THE NAME OF BOOK ïSTEP2: GET MONEY FROM DAD ïSTEP 3: GET THE ADDRESS OF THE SHOP ïSTEP4: TAKE BUS TO SHOP ïSTEP 5: SEARCH FOR THE BOOK IN SHOP ïSTEP 6: BUY THE BOOK FROM SHOPKEEPER ïSTEP 7: COME BACK TO HOME
- 8. Algorithm Characteristics ïPrecise and unambiguous ïEach instruction should be executed in finite time. ïShould not repeat loop for infinite. ïCorrect output.
- 9. Developing an Algorithm 1. Identify inputs to the system. 2. Identify output of the system. 3. Identify the process. 4. Break the solution to steps.
- 10. 1. Identify the Inputs ïWhat data do I need? ïHow will I get the data? ïIn what format will the data be?
- 11. 2. Identify the Outputs ïWhat outputs do I need to return to the user? ïWhat format should the outputs take?
- 12. 3. Identify the Processes ïHow can I manipulate data to produce meaningful results? ïData vs. Information
- 13. 4. Break the Solution to steps. ïBy breaking the solution to the steps we can easily understand the logic of program
- 14. Create a program to get name and roll number from user and print it! ïStep 1: Initialize name as character and roll number as integer ïStep2: Display message âENTER NAME:â on screen ïStep 3: GET NAME FROM USER ïSTEP 4: Display message âENTER R.NO:â ïStep 5: GET Roll number from USER ïSTEP 6: CLEAR THE SCREEN ïSTEP 7: PRINT NAME on SCREEN ïSTEP 8: PRINT ROLL NUMBER on SCREEN ïSTEP 9: STOP
- 15. NOW WHAT IS FLOW CHART??
- 16. Flow Chart ïFlow Chart is pictorial representation of an algorithm. ïWhatever we have done in algorithm we can represent it in picture. ïIt is easy to understand. ïShows the flow of the instruction
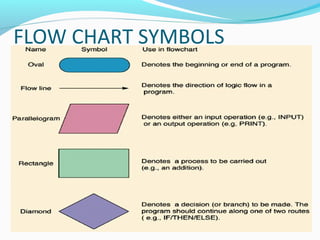
- 17. FLOW CHART SYMBOLS /output operations
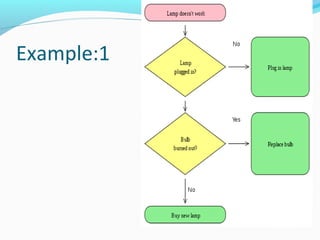
- 18. Example:1
- 19. Example 2: ADD 2 INTEGERS START INPUT VALUE OF A and B SUM=A+B PRINT :SUM STOP
- 20. Any questions?
- 21. Thank You