Altered expression of the klf4 in colorectal cancers
- 1. Altered expression of the KLF4 in colorectal cancers Byung Joon Choi et. al.,2006 By Avinash tiwari M. Tech 1st year 201710902010002
- 2. Introduction: ŌĆó The mammalian gastrointestinal epithelium is a dynamic system in which cell proliferation is coupled to differentiation. ŌĆó Aberrations in this process frequently lead to colorectal cancer. ŌĆó colorectal cancer is one of the leading primary cancers
- 3. cause Minor reason (inherited predisposition) Hereditary non-polyposis c.c. familial adenomatous polyposis Major reason Somatic mutation or Altered expression of tumor- associated protein
- 4. KLF-4 in colorectal cancer: ŌĆó Kru┬©ppel-like factor 4 (KLF-4) is family of zinc finger containing transcription factor ŌĆó Highly expressed in epithelial of gastrointestinal tract, skin and vascular endothelial cells. ŌĆó Play a important roll during the differentiation of gut epithelial cell. ŌĆó KLF4 activates the promoter of the negative cell-cycle-regulatory cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF/Cip1 gene in a p53- dependent manner
- 5. ŌĆó Induces cell cycle arrest at the transition from G1 to S phase ŌĆó Altered expression of KLF4 may be involved in the tumorigenesis of several kinds of human cancers, including colon, breast, gastric, esophageal, and bladder cancers. ŌĆó the level of KLF4 and the KLF4 mRNA expression is significantly decreased in colonic adenomas & in sporadic colonic adenomas and carcinoma patients with familial adenomatous polyposis when compared with normal colonic tissues
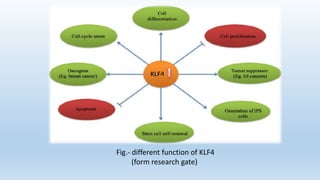
- 6. Fig.- different function of KLF4 (form research gate)
- 7. Material and method: Method & material Tissue samples Immunohistochemistry for the KLF4:
- 8. A. Tissue samples 1. ŌĆó Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded samples were obtained from surgical resections of 123 colorectal cancers 2. ŌĆó Classification of tumor according DukeŌĆÖs criteria. 3. ŌĆó There were 12, 47, 56, and 8 cases with stage A, B, C, and D, respectively.
- 9. Tissue samples cont. 4. ŌĆó Screened the histological sections and selected areas of the representative tumor cells. 5. ŌĆó Tissue cores were taken from each tumor sample and placed in a paraffin block using a commercially available microarray instrument 6. ŌĆó One cylinder of normal colonic mucosa adjacent to each tumor was also transferred to the recipient block.
- 10. B. Immunohistochemistry for the KLF4: 1. ŌĆó 2 mm sections were cut the day before use and stained according to standard protocols. 2. ŌĆó To maximize the signal on immunohistochemistry, two strategies were used = ŌĆó antigen retrieval in citrate buffer ŌĆó Signal amplification with biotinylated tyramide
- 11. 3. ŌĆó heat-induced epitope retrieval was conducted in citrate buffer (pH 6.0) and boiling the buffer for 30 min and cool 4. ŌĆó rinsing with PBS, the slides were treated with 1% H2O2 in PBS for 15 min at room temperature to abolish endogenous peroxidase activity. 5. ŌĆó washing with TNT buffer (0.1 mol/L Tris-HCl, pH for 20 min the slides were treated with TNB buffer. 6. ŌĆó incubated overnight at 4 degree C with the antibody (1/100 dilution) for KLF4 protein
- 12. 7. ŌĆó detection was carried out using biotinylated goat anti-rabbit antibody, followed by incubation with peroxidase-linked avidinŌĆōbiotin complex. 8. ŌĆó Diaminobenzidine was used as chromogen, and the slide was counterstained with MayerŌĆÖs hematoxylin. 9. ŌĆó As negative controls, the slide was treated by replacement of primary antibody with non-immune serum.
- 13. Results: Immunohistochemistry for the KLF4: ŌĆó In immunohistochemistry, normal colonic mucosa showed moderate to strong expression of KLF4 protein mainly in the nucleus of the glandular epithelial cells. ŌĆó Inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes in lamina propria of colonic mucosa, also Demonstrated focal, weakly positive staining Colorectal normal cells
- 14. ŌĆó Expression of KLF4 in tumor cells shows Moderate to strong immunopositivity for KLF4 protein was clearly marked on the nucleus of colorectal tumor cells compared with normal colonic mucosa. ŌĆó Colorectal cancer, well differentiated adenocarcinoma, displayed moderate to strong immunostaining in nucleus of cancer cells. Colorectal cancer stage B
- 15. ŌĆó Another cancer showed immunonegativity for the KLF4 protein in the nucleus of the cancer cells ŌĆó KLF4 protein was detected in 30 (24.4%) of 123 colorectal cancers Colorectal cancer stage C
- 16. ŌĆó KLF4 protein was detected in 30 (24.4%) of 123 colorectal cancers ŌĆó KLF4 expression was detected in 100% (6/6),73.2% (82/112), and 100% (5/5) of well, moderately,and poorly differentiated colorectal cancers ŌĆó In this classification, the expression of the KLF4 protein was not associated with the differentiation of tumor cells (w2 test, P40.05). ŌĆó Loss of KLF4 expression was seen in 4 (33.3%) of 12 cases corresponding to stage A, 9 (19.1%) of 47 to stage B, 16 (28.6%) of 56 to stage C, and 1 (12.5%) of 8 to stage D. ŌĆó In addition, KLF4 expression was lost in 16 (27.1%) of 59 cases with lymph node metastasis. ŌĆó There was a tendency that loss of KLF4 expression was more common in left-sided colon cancer (27.5%) than in right-sided colon cancer (12%).
Editor's Notes
- #5: KLF 4 is also known as the gut enriched KLF of epithelial zinc finger Post mitotic terminally differentiated cellsŌĆ”..reported in middle layer to upper region of the crypt