Alzheimers
- 1. Alzheimer's Disease The Worst Plague of The 21st Century
- 2. What is Alzheimer's disease? Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder in which the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive decline.
- 3. Dr. Alois Alzheimer The first person to describe this disease
- 4. The first Alzheimer Patient in History Auguste Deter
- 5. The Haunting case of Auguste D. A 51 years old women, a patient who had profound memory loss, unfounded suspicions about her family, shrinkage in her brain and other worsening psychological changes like, cognitive and language deficits, auditory hallucinations, delusions, paranoia and aggressive behaviour.
- 6. What causes Alzheimer's disease Scientists donât yet fully understand what causes Alzheimerâs disease, but it is clear that it develops because of a complex series of events that take place in the brain over a long period of time. It is likely that the causes include genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Because people differ in their genetic make-up and lifestyle, the importance of these factors for preventing or delaying Alzheimerâs differs from person to person.
- 7. Signs and Symptoms Very early sign and symptoms Memory problems are typically one of the first warning signs of cognitive loss, possibly due to the development of Alzheimerâs disease. A decline in other aspects of cognition, such as word-finding, vision/spatial issues, and impaired reasoning or judgment, may also signal the very early stages of Alzheimerâs disease.
- 8. Mild Alzheimer's Disease Alzheimerâs disease progresses, memory loss worsens, and changes in other cognitive abilities which are evident.
- 9. Moderate Alzheimerâs disease In this stage, damage occurs in areas of the brain that control language, reasoning, sensory processing, and conscious thought. Memory loss and confusion grow worse, and people begin to have problems recognizing family and friends.
- 10. Severe Alzheimerâs disease By the final stage, plaques and tangles have spread throughout the brain, and brain tissue has shrunk significantly. People with severe Alzheimerâs cannot communicate and are completely dependent on others for their care. Near the end, the person may be in bed most or all of the time as the body shuts down.
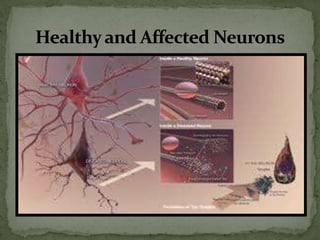
- 11. Healthy and Affected Neurons
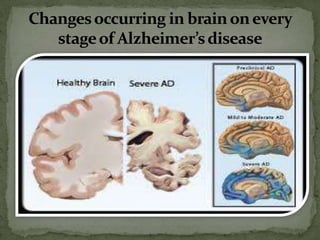
- 12. Changes occurring in brain on every stage of Alzheimerâs disease
- 14. Genetics Alzheimer's disease have a tendency to pass from generation to generation. It is a genetic disease which has maximum chances of getting inherited from parents.
- 15. Diagnosing Alzheimer's disease To diagnose Alzheimerâs, doctors may: â Ask questions about overall health, past medical problems, ability to carry out daily activities, and changes in behaviour and personality. â Conduct tests of memory, problem solving, attention, counting, and language. â Carry out standard medical tests, such as blood and urine tests, to identify other possible causes of the problem. â Perform brain scans, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to distinguish Alzheimerâs from other possible causes for symptoms, like stroke or tumor.
- 16. Treatment There is no specific treatment to cure Alzheimerâs disease completely with the prescribed medicines as it is most complex disease ever found in history. There are some prescribed medicines by U.S. food and drug administration to treat Alzheimerâs disease but canât cure it completely, it can just stabilize the memory and some brain function for limited period of time.