Ammonium phosphate
- 1. AMMONIUM PHOSPHATE Prepared by- Mr. Vishal B. Thakare (M.Tech, Chemical, SVNIT Surat) Assistant Professor, PARUL UNIVERSITY Vadodara vishalbt88@gmail.com
- 2. AMMONIUM PHOSPHATE ïķAmmonium phosphate ((NH4)3PO4) also known as ammonium orthophosphate is the salt of ammonia and phosphoric acid. It consists of ammonium cations and phosphate anion. It is water soluble and the aqueous solution on boiling losses ammonia. ïķThere are two major types of ammonium phosphate which are monoammonium phosphate (MAP, NH4H2PO4) and diammonium phosphate (DAP, (NH4)2HPO4)
- 3. 1. Monoammonium phosphate (MAP) Anhydrous ammonia added to liquid phosphoric acid gives monoammonium phosphate (MAP). It is a fertilizer or fertilizer intermediate with high P2O5 content of about 55% and nitrogen content 11-12%. 2. Diammonium phosphate (DAP) With more ammonia, technical grade diammonium phosphate (DAP) containing 16 to 18% nitrogen and 20 to 21 % phosphorus (46% P2O5) is formed.
- 4. Raw Materials Basis: 1000kg of Diammonium phosphate Ammonia = 200kg Phosphoric acid = 465kg Reactions NH3 + H3PO4 NH4H2PO4 Ammonia Phosphoric acid Monoammonium Phosphate NH3 + NH4H2PO4 (NH4)2HPO4 Ammonia Monoammonium Phosphate Diammonium phosphate
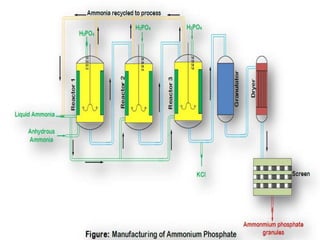
- 6. ïķQuantities of phosphoric acid and ammonia in the neutralization step are different form mono ammonium phosphate (MAP) and diammonium phosphate (DAP). ïķTo manufacture mono ammonium phosphate, ammonia to phosphoric acid ratio is 0.6 in the neutralizer and then 1.0 in the granulator. While for diammonium phosphate, the ratios are 1.4 and 1.0 in the neutralizer and granulator respectively. ïķPhosphoric and ammonia are added to the first of three continuous mixed reactors, anhydrous ammonia is added beneath the slurry level in the first neutralizer in an amount equivalent to 80% neutralization. ïķFurther ammonia is added in the 2nd and 3rd tanks to obtain conversion to the diammonium salt if a higher nitrogen containing fertilizer is needed. (DAP)
- 7. ïķThe exothermic reaction heats the slurry nearly to the boiling point (130°C). Unreacted and excess NH3 vapor is collected from the top of each tank and recharged below the liquid level for reducing NH3 losses (less than 3%). ïķSlurry from the third neutralized is mixed with KCl and absorbed in a bed of dry recycle fertilizer moving through a rotating drum granulator. ïķA rotary adiabatic drier reduces the moisture to less than 1%, with 10 minute contact time with air initially at 1500oC ïķDried product is separated into three fractions on a double deck screen. A portion of the product from the deck of the lower screen is sent to bagging operations.