An Introduction to MongoDB
- 1. Presented by Chamodi Adikaram (179333J)
- 2. content ŌĆó introduction ŌĆó cap theorem ŌĆó terminology ŌĆó structure ŌĆó key features ŌĆó crud operations ŌĆó best use cases
- 3. introduction ŌĆó mongoDB was founded in 2007 by Dwight Merriman, Eliot Horowitz and Kevin Ryan (10gen) ŌĆó mongo comes from the term humongous. ŌĆó it is a free and open-source cross-platform document-oriented NoSQL database program
- 4. cap theorem availability consistency partition tolerance ca cp ap
- 5. cap theorem cntdŌĆ” consistency: ŌĆó all replicas contain the same version of the data partition tolerance: ŌĆó multiple entry points ŌĆó system remains operational on system split ŌĆó single master architecture to have consistency over availability
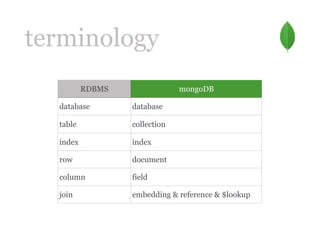
- 6. terminology RDBMS mongoDB database database table collection index index row document column field join embedding & reference & $lookup
- 7. structure
- 8. structure ŌĆó documents in BSON (binary JSON): JSON like structure
- 9. key features 1. schema less ŌĆó application tracks the schema and mapping ŌĆó you can have different fields in every document ŌĆó no Data Definition Language ŌĆó keys are a basic data type but in reality stored as strings ŌĆó document Identifiers (_id) will be created for each document, field name reserved by system ŌĆó results in lot of flexibility
- 10. key features cntdŌĆ” 2. replication sets ŌĆó single master architecture ŌĆó maintaining backup copies of your database instance ŌĆó secondaries can elect a new primary within seconds if your primary goes down
- 11. key features cntdŌĆ” 3. auto- sharding ŌĆó for big data ŌĆó distributes a single logical database system across a cluster of machines ŌĆó ranges of some indexed value you specify are assigned to different replica sets ŌĆó can be turned on off per collection ŌĆó facilitates built in horizontal scaling
- 12. key features cntdŌĆ” 4. querying ŌĆó mongo shell ŌĆó you can write scripts for the mongo shell in javascript that manipulate data in mongoDB or perform administrative operation ŌĆó alternative to shell robomongo
- 13. key features cntdŌĆ” 5. fast in-place updates ŌĆó the database does not have to allocate and write a full new copy of the object ŌĆó this can be highly performant for frequent update use cases ŌĆó mongoDB disk writes are lazy
- 14. key features cntdŌĆ” 6. aggregated functionality ŌĆó provides SQL-like aggregation functionality ŌĆó expressions produce output documents based on calculations performed on input documents ŌĆó db.parts.aggregate ( {$group : {_id: type, totalquantity : {$sum:quanity}} }) ŌĆ©
- 15. key features cntdŌĆ” 7. map/reduce functionality ŌĆó can perform map reduce operations without hadoop ŌĆó file system: gridFS ŌĆó performs complex aggregator functions given a collection of keys, value pairs ŌĆó db.collection.mapReduce( <mapfunction>, <reducefunction>, { out: <collection>, query: <document>, sort: <document>, limit: <number>, finalize: <function>, scope: <document>, jsMode: <boolean>, verbose: <boolean> } )
- 16. crud operations ŌĆó createŌĆ© db.restaurants.insert({borough : 'Colombo',cuisine : 'Chinese',name: 'Fab',restaurant_id : '41704627'}); ŌĆó readŌĆ© db.restaurants.find({cuisine : 'Chinese'}); ŌĆó updateŌĆ© db.restaurants.update({restaurant_id : '41704627'},{$set: {name:'Fabulous'}}); ŌĆó deleteŌĆ© db.restaurants.remove({restaurant_id : '41704627'});
- 17. best use cases
- 18. best use cases cntdŌĆ” ŌĆó suitable for high volume and scaling data such as: ŌĆó blog posts ŌĆó comments ŌĆó digital content management ŌĆó not suitable for highly transactional, business intelligence related instances
- 19. Q&A Thank you!