Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Mongolia
- 1. For International Conference ŌĆ£Tick-Borne Encephalitis and Other Tick-Borne InfectionsŌĆØ Dedicated to the 75th Anniversary of the Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Discovery MOLECULAR DETECTION OF ZOONOTIC ANAPLASMA IN VECTOR TICK IN MONGOLIA Javkhlan G.1, Enkhtaivan B1., Baigalmaa B.2 , Enkhtogtoh B. 1, Bolorchimeg B.3, Battur B. 1, Tuvshintulga B. 1, Undraa B2., Battsetseg B. 1 Irkutsk, Russia-2012 1 Laboratory of Molecular Genetics, IVM, 2 National Center for Infectious Diseases with Natural Foci , 3 National Center for Infectious Diseases with Natural Foci, Selenge province╠²
- 2. Introduction Anaplasma phagocytophilum is a Gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium, which have long been recognized as worldwide tick-borne agents for several species of wild and domesticated mammals, and human. The disease usually presents as an acute febrile illness characterized by headache, chill, myalgias, arthralgia, malaise, and hematological abnormalities, such as thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and elevated hepatic aminotransferase levels.
- 3. Basis of the study ’ü¼ In Mongolia: ’ü¼ Anaplasma ovis and Anaplasma marginale detected in reindeer by microscopic examination (Purevsuren, 1981) and PCR (Nansalmaa, 2012). ’ü¼ Anaplasma phagocytophilum antibody found in human by IFAT (Walder et al., 2006). ’ü¼ The tick vectors unknown. Therefore, we completed this study for detect Anaplasma phagocytophilum in tick vectors.
- 4. Aim of the study - Identification of collected tick species from study area - Detection Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection in tick vector using specific gene fragments by molecular biological assay -Sequencing and analyzing A.phagocytophilum groEL gene fragment partially
- 5. Methods and Results Methods and results
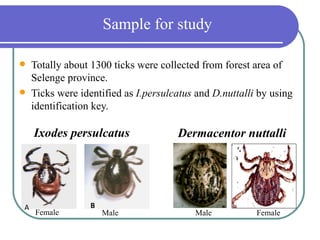
- 6. Sample for study ’ü¼ Totally about 1300 ticks were collected from forest area of Selenge province. ’ü¼ Ticks were identified as I.persulcatus and D.nuttalli by using identification key. Ixodes persulcatus Dermacentor nuttalli A B Female Male Male Female
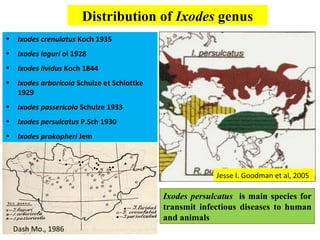
- 7. Distribution of Ixodes genus ŌĆó Ixodes crenulatus Koch 1935 ŌĆó Ixodes laguri ol 1928 ŌĆó Ixodes lividus Koch 1844 ŌĆó Ixodes arboricola Schulze et Schlottke 1929 ŌĆó Ixodes passericola Schulze 1933 ŌĆó Ixodes persulcatus P.Sch 1930 ŌĆó Ixodes prokopheri Jem Jesse I. Goodman et al, 2005 Ixodes persulcatus is main species for transmit infectious diseases to human and animals Dash Mo., 1986
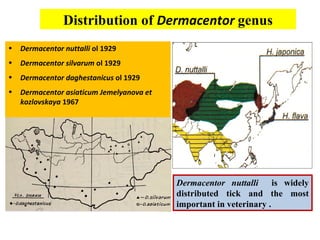
- 8. Distribution of Dermacentor genus ŌĆó Dermacentor nuttalli ol 1929 ŌĆó Dermacentor silvarum ol 1929 ŌĆó Dermacentor daghestanicus ol 1929 ŌĆó Dermacentor asiaticum Jemelyanova et kozlovskaya 1967 Dermacentor nuttalli is widely distributed tick and the most important in veterinary .
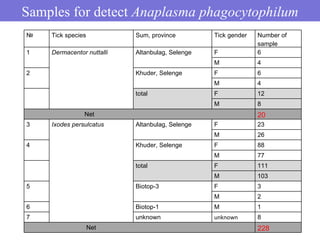
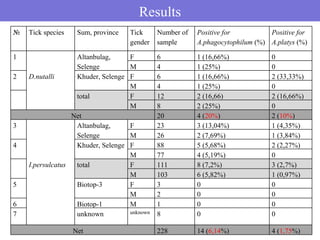
- 9. Samples for detect Anaplasma phagocytophilum Ōä¢ Tick╠²species Sum,╠²province Tick╠²gender Number╠²of╠² sample 1 Dermacentor nuttalli Altanbulag,╠²Selenge F 6 M╠² 4 2 Khuder,╠²Selenge F 6 M 4 total╠² F 12 M 8 ╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²Net╠² 20 3 Ixodes persulcatus Altanbulag,╠²Selenge F 23 M 26 4 Khuder,╠²Selenge F 88 M 77 total F 111 M 103 5 Biotop-3 F 3 M 2 6 Biotop-1 M 1 7 unknown unknown 8 ╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²╠²Net 228
- 10. Extract tick genomic DNA G-spin genomic DNA extraction kit Extract DNA from ticks after ticks were freezed and mashed by liquid nitrogen are performed through G-spin genomic DNA extraction kit protocol.
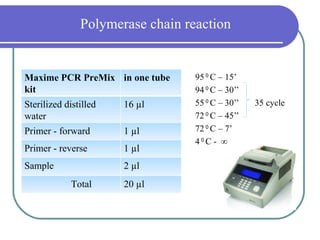
- 11. Polymerase chain reaction Maxime PCR PreMix in one tube 95╠²0╠²ąĪ ŌĆō 15ŌĆÖ kit 94╠²0╠²ąĪ ŌĆō 30ŌĆÖŌĆÖ Sterilized distilled 16 ┬Ąl 55╠²0╠²ąĪ ŌĆō 30ŌĆÖŌĆÖ 35 cycle water 72╠²0╠²ąĪ ŌĆō 45ŌĆÖŌĆÖ Primer - forward 1 ┬Ąl 72╠²0╠²ąĪ ŌĆō 7ŌĆÖ 4╠²0╠²ąĪ - Ōł× Primer - reverse 1 ┬Ąl Sample 2 ┬Ąl Total 20 ┬Ąl
- 12. Primers ’ü¼ Primers: - EphplgroEL(569)F (5ŌĆÖ-ATGGTATGCAGTTTGATCGC-3ŌĆÖ) - EphplgroEL(1193)R (5ŌĆÖ-TCTACTCTGTCTTTGCGTTC-3ŌĆÖ) ’ü¼ The primers anneal to nucleotide strings conserved in A. phagocytophilum and A. platys and were designed to selectively amplify, 624 bp of the groEL gene of both species from samples.
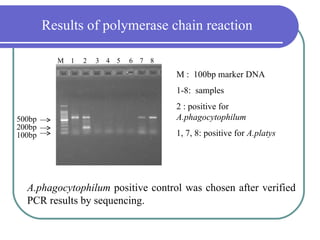
- 13. Results of polymerase chain reaction M 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 M : 100bp marker DNA 1-8: samples 2 : positive for 500bp A.phagocytophilum 200bp 100bp 1, 7, 8: positive for A.platys A.phagocytophilum positive control was chosen after verified PCR results by sequencing.
- 14. Results Ōä¢ Tick species Sum, province Tick Number of Positive for Positive for gender sample A.phagocytophilum (%) A.platys (%) 1 Altanbulag, F 6 1 (16,66%) 0 Selenge M 4 1 (25%) 0 2 D.nutalli Khuder, Selenge F 6 1 (16,66%) 2 (33,33%) M 4 1 (25%) 0 total F 12 2 (16,66) 2 (16,66%) M 8 2 (25%) 0 Net 20 4 (20%) 2 (10%) 3 Altanbulag, F 23 3 (13,04%) 1 (4,35%) Selenge M 26 2 (7,69%) 1 (3,84%) 4 Khuder, Selenge F 88 5 (5,68%) 2 (2,27%) M 77 4 (5,19%) 0 I.persulcatus total F 111 8 (7,2%) 3 (2,7%) M 103 6 (5,82%) 1 (0,97%) 5 Biotop-3 F 3 0 0 M 2 0 0 6 Biotop-1 M 1 0 0 7 unknown unknown 8 0 0 Net 228 14 (6,14%) 4 (1,75%)
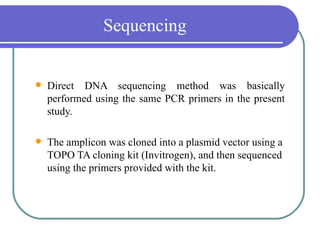
- 15. Sequencing ’ü¼ Direct DNA sequencing method was basically performed using the same PCR primers in the present study. ’ü¼ The amplicon was cloned into a plasmid vector using a TOPO TA cloning kit (Invitrogen), and then sequenced using the primers provided with the kit.
- 16. Sequence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum groEL gene, partial CGAGCGTCTT GCATGCTCCG GCCGCCATGG CCGCGGGATT ATGGTATGCA GTTTGATCGC GGATATCTTT CGCCTTACTT TGTTACAAAT GCTGAAAAAA TGCTGGTGGA ATTTGAAAAT CCATACATAT TCCTTACTGA AAAGAAGATT AATCTTGTAC AAAGCATTTT ACCAATATTA GAAAACGTTG CGAGAGCTGG CAGACCATTG CTCATCATAG CTGAAGATGT TGAAGGTGAA GCTCTGAGCA CGCTTGTACT CAATAAGCTC CGTGGTGGGC TCCAAGTTGC TGCTGTAAAG GCGCCTGGTT TCGGTGACAG AAGAAAAGAC ATGCTAGGCG ATATTGCCGT AATAGTAGGC GCTAAGTATG TAGTAAATGA CGAGCTTGCT GTTAAGATGG AAGATATCGC TCTAAGCGAT CTGGGTACTG CTAAGAGCGT GCGCATCACA AAAGACGCAA CTACTATCAT AGGTAGCGTT GATAGCAGTT CTGAAAGCAT AGCTAGCAGG ACTAATCAAA TCAAAGCTCA GATAGAAAAC TCTAGTTCTG ATTATGACAA GGAAAAGCTT AGAGAACGTT TAGCGAAGCT TTCCGGTGGC GTTGCTGTAC TCAAGGTTGG TGGATCCAGC GAAGTTGAGG TGAAGGAACG CAAAGACAGA GTAGAAATCA CTAGTGCGGC CGCCTGCAGG TCGACCATAT GGGAGAGCTC CCAACGCGTT GGATGCATAG CTTGAGTATT CTATAGTGTC ACCTAAATAG CTTGGCGTAA TCATGGTCAT AGCTGTTTCC TGTGTGAAAT TGTTATCCGC TCACAATTCC ACACAACATA CGAGCCGGAA GCATAAAGTG TAAAGCCTGG GGTGCCTAAT GAGTGAGCTA ACTCACATTA ATTGCGTTGC GCTCACTGCC CGCTTTCCAG TCGGGAAACC TGTCGTGCCA GCTGCATTAA TGAATCGGCC AACGCGCGGG GAGAGGCGGG TTTGCGTATT GGGCGCTCTT Insert (red): 625 bp
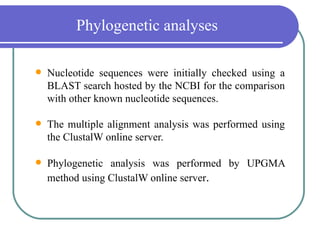
- 17. Phylogenetic analyses ’ü¼ Nucleotide sequences were initially checked using a BLAST search hosted by the NCBI for the comparison with other known nucleotide sequences. ’ü¼ The multiple alignment analysis was performed using the ClustalW online server. ’ü¼ Phylogenetic analysis was performed by UPGMA method using ClustalW online server.
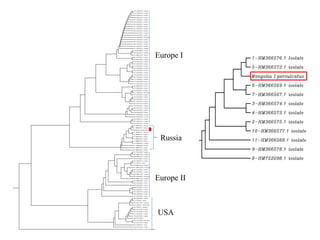
- 18. Europe I Russia Europe II USA
- 19. Conclusion l All samples were studied by using tick identification key, and identified as Dermacentor nuttalli and Ixodes persulcatus. Ixodes persulcatus (91.9%) is dominant tick species in this local area. l groEL gene fragments amplified in 26.14% of all tick DNA samples for Anaplasma phagocytophilium and in 11.75% for ąÉnaplasma platys. l In this study, 6.14% of I.persulcatus was positive for A. phagocytophilium and 1.75% was positive for A.platys. 20% of D.nuttalli was positive for A. phagocytophilium and 10% was positive for A.platys. These ticks play role to transmit the agents in nature.
- 20. Conclusion 4. ąÉ.platys groEL gene fragment is detected in this study, and this become new information in Mongolia for further study. 5. Detected Anaplasma phagocytophilium and ąÉnaplasma platys groEL gene fragments were sequenced and analyzed for verification. 6. A. phagocytophilum 625bp of groEL gene partially sequenced and performed phylogenetic analysis. Mongolian A. phagocytophilum groEL gene is in Russian group. 7. Further studies for understanding of the basic molecular mechanisms of transmission mechanism, particularly the process of stored in tick organs, is required for the development of preventive measure against anaplasmosis.
- 21. Aknowledgements ŌĆó Organizers of International Conference ŌĆ£Tick-Borne Encephalitis and Other Tick-Borne InfectionsŌĆØ Dedicated to the 75th Anniversary of the Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Discovery ŌĆó WHO Representative Office in Mongolia ŌĆó Workers of local stations for infectious diseases with Natural Foci ŌĆó Researchers of Laboratory of Molecular Genetics, Institute of Veterinary Medicine, Mongolia ŌĆóOther researchers and organizations
- 22. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION e_mail: bata07@gmail.com Laboratory of Molecular Genetics, Institute of Veterinary Medicine, Zaisan-210153, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia