Anatomy of file_system
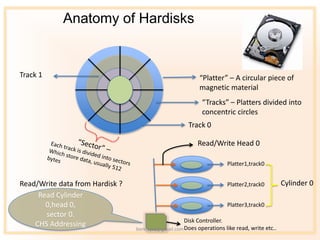
- 2. Anatomy of Hardisks Track 1 ˇ°Platterˇ± ¨C A circular piece of magnetic material ˇ°Tracksˇ± ¨C Platters divided into concentric circles Track 0 Read/Write Head 0 Platter1,track0 Read/Write data from Hardisk ? Platter2,track0 Cylinder 0 Read Cylinder 0,head 0, Platter3,track0 sector 0. Disk Controller. CHS Addressing bennojoy@gmail.com Does operations like read, write etc..
- 3. Anatomy of Communication Communication in Humans: Requirements: ? Speaker/Listener ? Voice/Language ? Medium: Air ? Addressing bennojoy@gmail.com
- 4. Communicating with your Hardisk Various communication standards exist to talk to our Harddisks: Communication Requirements SCSI Specification Speaker/Listener Initiator/Target Voice/Language SCSI Commands Medium SCSI Bus Addressing SCSI ID bennojoy@gmail.com
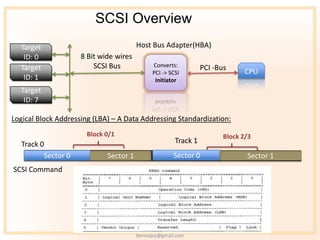
- 5. SCSI Overview Target Host Bus Adapter(HBA) ID: 0 8 Bit wide wires Target SCSI Bus Converts: PCI -Bus PCI -> SCSI CPU ID: 1 Initiator Target ID: 7 Logical Block Addressing (LBA) ¨C A Data Addressing Standardization: Block 0/1 Block 2/3 Track 0 Track 1 Sector 0 Sector 1 Sector 0 Sector 1 SCSI Command bennojoy@gmail.com
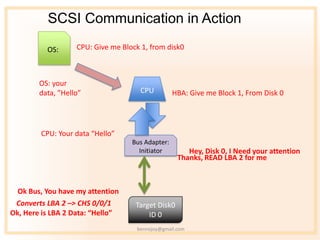
- 6. SCSI Communication in Action OS: CPU: Give me Block 1, from disk0 OS: your data, ˇ±Helloˇ± CPU HBA: Give me Block 1, From Disk 0 CPU: Your data ˇ°Helloˇ± Bus Adapter: Initiator Hey, Disk 0, I Need your attention Thanks, READ LBA 2 for me Ok Bus, You have my attention Converts LBA 2 ¨C> CHS 0/0/1 Target Disk0 Ok, Here is LBA 2 Data: ˇ°Helloˇ± ID 0 bennojoy@gmail.com
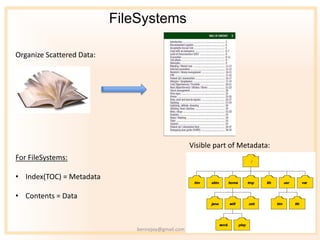
- 7. FileSystems Organize Scattered Data: Visible part of Metadata: For FileSystems: ? Index(TOC) = Metadata ? Contents = Data bennojoy@gmail.com
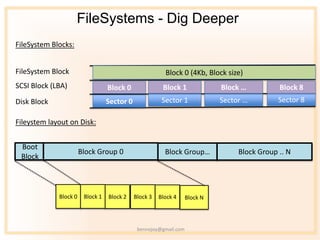
- 8. FileSystems - Dig Deeper FileSystem Blocks: FileSystem Block Block 0 (4Kb, Block size) SCSI Block (LBA) Block 0 Block 1 Block ˇ Block 8 Disk Block Sector 0 Sector 1 Sector ˇ Sector 8 Fileystem layout on Disk: Boot Block Group 0 Block Groupˇ Block Group .. N Block Block 0 Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Block 4 Block N bennojoy@gmail.com
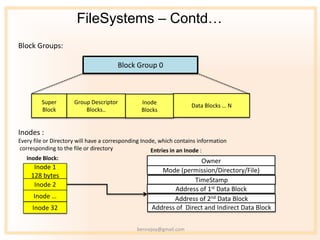
- 9. FileSystems ¨C Contdˇ Block Groups: Block Group 0 Super Group Descriptor Inode Data Blocks ˇ N Block Blocks.. Blocks Inodes : Every file or Directory will have a corresponding Inode, which contains information corresponding to the file or directory Entries in an Inode : Inode Block: Owner Inode 1 Mode (permission/Directory/File) 128 bytes TimeStamp Inode 2 Address of 1st Data Block Inode ˇ Address of 2nd Data Block Inode 32 Address of Direct and Indirect Data Block bennojoy@gmail.com
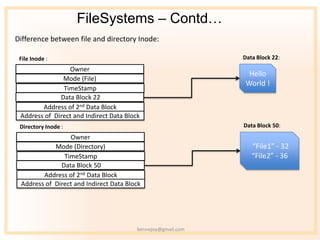
- 10. FileSystems ¨C Contdˇ Difference between file and directory Inode: File Inode : Data Block 22: Owner Hello Mode (File) World ! TimeStamp Data Block 22 Address of 2nd Data Block Address of Direct and Indirect Data Block Directory Inode : Data Block 50: Owner Mode (Directory) ˇ°File1ˇ± - 32 TimeStamp ˇ°File2ˇ± - 36 Data Block 50 Address of 2nd Data Block Address of Direct and Indirect Data Block bennojoy@gmail.com
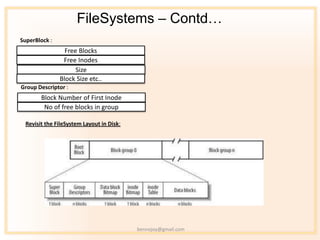
- 11. FileSystems ¨C Contdˇ SuperBlock : Free Blocks Free Inodes Size Block Size etc.. Group Descriptor : Block Number of First Inode No of free blocks in group Revisit the FileSystem Layout in Disk: bennojoy@gmail.com
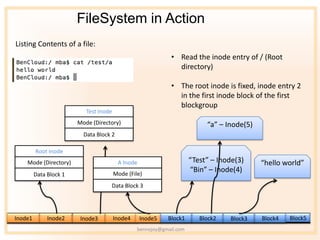
- 12. FileSystem in Action Listing Contents of a file: ? Read the inode entry of / (Root directory) ? The root inode is fixed, inode entry 2 in the first inode block of the first blockgroup Test Inode Mode (Directory) ˇ°aˇ± ¨C Inode(5) Data Block 2 Root Inode Mode (Directory) A Inode ˇ°Testˇ± ¨C Inode(3) ˇ°hello worldˇ± Mode (File) ˇ°Binˇ± ¨C Inode(4) Data Block 1 Data Block 3 Inode1 Inode2 Inode3 Inode4 Inode5 Block1 Block2 Block3 Block4 Block5 bennojoy@gmail.com
- 13. Thank Youˇ Email: bennojoy@gmail.com bennojoy@gmail.com