Anatomy of kidney (Animals)
- 1. Kidney and its Functional unit M. FARAN YOUSAF 2018-DVMN-038 KBCMA College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Narowal
- 2. Outline: âĒ Introduction. âĒ Shape of kidney. âĒ Physiology of Kidney. âĒ Histological features of kidney. âĒ Its Structure(calyx, sinus, pelvis, hilus) âĒ Nephron âĒ References.
- 3. Introduction: âĒ Kidneys are paired structures forming urine. âĒ Mostly bean shaped in all species. âĒ Maintain the composition of the body fluids. âĒ Removes the end products of the metabolism and excrete substances from the blood. âĒ Reddish Brown in colour. âĒ Present retroperitoneally on either side of vertebral column.
- 4. Shape: âĒ Varies among species. âĒ Mostly bean shaped. âĒ Right kidney in Equines is VALENTINE heart shaped. âĒ Bovines has fissured (lobulated) outer surface and is oval shaped.
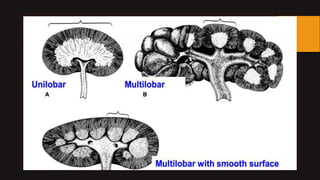
- 5. Shape: âĒ Kidney ,mainly, is of 3 types regarding papillae or lobes: a) Unilobular b) Multilobular c) Multilobular with smooth surface
- 7. âĒ Goat,Cat,Sheep,Dog,Horse has unilobular kidney. âĒ Multilobular kidney with lobulated outer surface is present in large ruminants. âĒ Multi-papillar kidney with outer smooth surface is present in humans, pigs.
- 8. Kidney of Dog Kidney of Pig Kidney of Ox
- 9. Physiology of Kidney: âĒ Formation of urine through the process of Filtration, Reabsorption and secretion. âĒ Secretion of Hormones. âĒ Maintenance of body fluids. âĒ Homeostasis. âĒ Production of Erythropoietin. âĒ Maintenance of Blood Pressure.
- 10. Histology of Kidney: âĒ It is covered with thick C.T covering called capsule. âĒ It has 2 portions: a) Cortex b) Medulla âĒ Cortex has PCT and DCT while collecting ducts and Loop of Henle are part of Medulla. âĒ Renal corpuscles are the part of renal cortex. âĒ Cortex has cortical labyrinth and medullary rays.
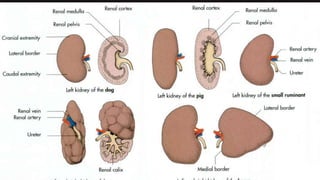
- 12. Surface Topography: The kidney has: âĒ 2 Surfaces(Dorsal and Ventral) âĒ 2 Borders(Medial and Lateral) âĒ 2 Extremities(Cranial and Caudal)
- 14. Structural points: âĒ Renal hilus:Identation in Med. Border forms through which nerves, vessels and ureter pass. At the hilus, the renal artery is dorsal, the vein in the middle, and the ureter ventral. âĒ Renal Pelvis: The renal pelvis is the dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. The renal pelvis functions as a funnel for urine flowing to the ureter. âĒ Renal Calyces: The renal calyces are chambers of the kidney through which urine passes. These are cup shaped structures surrounding the apex of pyramids. The minor calyces surround the apex of the renal pyramids. Minor calyces open into major calyces which opens then into ureter.
- 16. âĒ Renal Crest: It is present in unilobular kidney.Pelvis is elongated to form crest. âĒ Renal Column: The renal column is a medullary extension of the renal cortex in between the renal pyramids.It allows the cortex to be better anchored. Each column consists of lines of blood vessels and fibrous material. âĒ Renal Sinuses: The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat.
- 17. ïRenal Racess: âĒ Only present in Equines. âĒ Functions in collecting urine from the sides. âĒ Extensions of Pelvis.
- 20. Nephron: âĒ Functional unit of kidney. âĒ Has 2 main portions: ïRenal corpuscle: i. Glomerulus ii. Bowmanâs capsule ïRenal tubule: i. Proximal convoluted tubule ii. Loop of Henle iii. Distal convoluted tubule
- 21. âĒ 0.4 million nephrons in kidney of dog. âĒ 0.5 million nephrons in cat. âĒ 1 million in pig âĒ 2.7 million in horse âĒ 4 million in ox
- 22. Types of Nephrons: âĒ Cortical âĒ Juxtamedullary May also be called : âĒ Short looped âĒ Long looped
- 24. References: âĒ Veterinary anatomy of domestic mammals by KONIG and LIEBICH. âĒ Sissonâs Anatomy. âĒ Google.
- 25. Any Questions?
- 26. Thank You.