Anatomy of Urinary System.pptx
- 1. Anatomy of Urinary System By Shemsedin A.
- 2. Learning Outcomes 30-2 .1 Describe the structure, location, and functions of the kidney. .2 Define the term nephron and describe its structure. .3 Explain how nephrons filter blood and form urine. .4 List substances normally found in urine. 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 3. Learning Outcomes (cont.) 30-3 .5 Describe the locations, structures, and functions of the ureters, bladder, and urethra. .6 Explain how urination is controlled. .7 Describe the causes, signs and symptoms, and treatments of various diseases and disorders of the urinary system. 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 4. Introduction 30-4 ’éŚ System functions to remove waste products from the blood ’éŚ Main functional units of the kidneys are the nephrons ’éŚ Nephrons filter the blood and form the urine Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 5. The Kidneys 30-5 Functions Remove metabolic waste products from the blood Secrete the hormone erythropoietin, which stimulates bone marrow to produce red blood cells Secrete the hormone renin, which helps regulate blood pressure Description The kidneys are bean-shaped organs that lie behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal) on either side of the vertebral column. 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 6. The Kidneys (cont.) 30-6 ’éŚ Renal sinus ŌĆō concave depression of the surface of the kidney ’éŚ Hilum ŌĆō point of entry for the renal artery, renal vein, and ureter ’éŚ Renal pelvis ŌĆō expansion of the ureter that further divides into calyces ’éŚ Renal cortex ŌĆō outermost portion of the kidney that covers the pyramids and dips down between them ’éŚ Renal medulla ŌĆō middle portion that also divides into renal pyramids ’éŚ Renal column ŌĆō portion of the cortex between pyramids Kidney 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 7. The Kidneys: Nephrons 30-8 ’éŚ Removes waste products from the blood ’éŚ Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons ’éŚ Made of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule Renal Corpuscles ’ü» Composed of a group of capillaries called a glomerulus ’ü» Glomerulus is surrounded by BowmanŌĆÖs capsule ’ü» Blood filtration occurs in corpuscle ’ü» Extend from the BowmanŌĆÖs capsule of a nephron ’ü» Consist of three parts: ’āś Proximal convoluted tubule ’āś Loop of Henle ’āś Distal convoluted tubule Renal Tubules Glomerulus 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 8. The Kidneys ŌĆō Nephrons (cont.) 30-10 Veins of the Kidney Afferent Arteriole Glomerulus Efferent Arteriole Peritubular Capillaries ’āś Afferent arterioles deliver blood to the glomeruli ’āś Efferent arterioles carry blood from the glomeruli to peritubular capillaries 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 9. 30-11 Apply Your Knowledge What are the functions of the kidney? ANSWER: The kidney removes metabolic waste products from the blood, secretes erythropoietin to help regulate RBC production, and secretes renin to help regulate the BP. Correct! 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 10. Urine Formation: Glomerular Filtration ’éŚ First process occurs in renal corpuscles ’éŚ Fluid part of the blood is forced from glomerulous into BowmanŌĆÖs capsule ’éŚ Becomes glomerular filtrate 30-12 Glomerulus
- 11. Urine Formation: Glomerular Filtration (cont.) ’éŚ Factors affecting glomerular filtration ’éŚ Filtration pressure ŌĆō amount of pressure that forces filtrate from the glomerulus into BowmanŌĆÖs capsule. ’éŚ Determined by blood pressure ’éŚ Rate of filtration ŌĆō sympathetic nervous system control ’éŚ Constriction of afferent arterioles decreases filtration pressure 30-13
- 12. Urine Formation: Tubular Reabsorption 30-14 ’éŚ Second process in urine formation ’éŚ Glomerular filtrate ’āĀ proximal convoluted tubule ’éŚ Nutrients, water, and ions pass through the walls of the renal tubule into the peritubular capillaries ’éŚ Water reabsorption depends on hormones ’éŚ Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) ’éŚ Aldosterone ’éŚ Both increase water reabsorption, which decreases urine production Tubular Reabsorption 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 13. Urine Formation: Tubular Secretion 30-15 ’éŚ Third process of urine formation ’éŚ Substances move from blood in the peritubular capillaries into the renal tubules ’éŚ Secreted substances ’éŚ Drugs ’éŚ Hydrogen ions ’éŚ Waste products Tubular Secretion 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 14. Urine Formation (cont.) 30-17 ’éŚ Urine composition ’éŚ Mostly water ’éŚ Urea and uric acid ’éŚ Formed by the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids ’éŚ Trace amounts of amino acids and various ions ’éŚ Secretion of waste products helps maintain the acid-base balance 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 15. 30-18 Apply Your Knowledge Match the following: ___ Second process in urine formation A. Glomerular filtration ___ Substances move from blood into renal tubules B. Tubular reabsorption ___ Depends on filtration pressure C. Tubular secretion ___ Third process of urine formation ___ First process of urine formation ___ Filtrate flows into the proximal convoluted tubule C C B A A B ANSWER: Nice Job! 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 16. Ureters, Urinary Bladder, and Urethra (cont.) 30-20 ’éŚ Urinary bladder ’éŚ Expandable muscular organ ’éŚ Stores up to 600 ml urine on average ’éŚ Detrusor muscle ŌĆō smooth muscle in wall of bladder ’éŚ Trigone ŌĆō triangle on internal floor of bladder formed by urethra and ureters ’éŚ Micturation ’éŚ Process of urination ’éŚ Stretching of bladder triggers process ’éŚ Approximately 150cc of urine Bladder 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 17. Ureters, Urinary Bladder, and Urethra (cont.) 30-21 ’éŚ Urination ’éŚ External urethral sphincter relaxes ’éŚ Micturation reflex ŌĆō impulses from pons and hypothalamus ’éŚ Detrusor muscle contracts ’éŚ Urine expelled Impulses to contract urethra; inhibit micturition impulse until ready to urinate Bladder distends Stretch receptors Spinal cord Parasympathetic nerves stimulate detrusor muscle Brain stem and cerebral cortex 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 18. Ureters, Urinary Bladder, and Urethra (cont.) 30-22 ’éŚ Urethra ’éŚ Tube that moves urine from the bladder to the outside world ’éŚ Shorter in females ŌĆō patient education ’éŚ Urinate when urge occurs ’éŚ Drink adequate clear fluids ’éŚ Wipe front to back ’éŚ Urinate after intercourse 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 19. Apply Your Knowledge 30-23 True or False: ___ Ureters move urine by peristalsis. ___ The detrusor is formed by the openings of the ureters and urethra. ___ The process of micturition is triggered when the bladder contains about 150 ml urine. ___ The urethra move urine from the kidney to the bladder. ___ The urethra is longer in females. ___ Contraction of the detrusor muscle pushes urine from the bladder. F F T F T trigone males ureters T ANSWER: 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
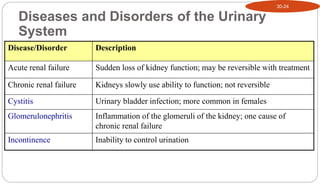
- 20. Diseases and Disorders of the Urinary System Disease/Disorder Description Acute renal failure Sudden loss of kidney function; may be reversible with treatment Chronic renal failure Kidneys slowly use ability to function; not reversible Cystitis Urinary bladder infection; more common in females Glomerulonephritis Inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidney; one cause of chronic renal failure Incontinence Inability to control urination 30-24
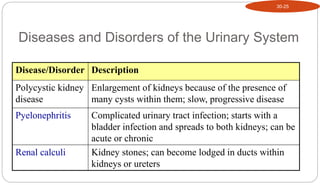
- 21. Diseases and Disorders of the Urinary System Disease/Disorder Description Polycystic kidney disease Enlargement of kidneys because of the presence of many cysts within them; slow, progressive disease Pyelonephritis Complicated urinary tract infection; starts with a bladder infection and spreads to both kidneys; can be acute or chronic Renal calculi Kidney stones; can become lodged in ducts within kidneys or ureters 30-25
- 22. 30-26 Apply Your Knowledge Matching: ___ Complicated urinary tract infection A. Pyelonephritis ___ Inability to control urination B. Glomerulonephritis ___ Kidney stones C. Incontinence ___ Slow loss of kidney function D. Chronic renal failure ___ Bladder infection E. Renal calculi ___ Inflammation of the glomeruli F. Cystitis ___ Kidney enlargement due to cysts G. Acute renal failure ___ Sudden loss of kidney function H. Polycystic kidney disease H G F E D C B A ANSWER: GOOD JOB ! 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 23. In Summary 30-27 ’éŚ The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra ’éŚ The kidneys remove metabolic waste products from the blood and secrete erythropoietin and renin ’éŚ Urine travels through the ureters to the bladder ’éŚ Stretching of the bladder triggers micturition reflex ’éŚ Urine travels from the bladder through the urethra to the outside world 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.
- 24. 30-28 This too shall passŌĆö just like a kidney stone. ~ 1/9/2024 By Shemsedin A.