Anchor Modeling GSE11 Presentation
- 1. Anchor Modeling A Technique for Information under Evolution Lars R?nnb?ck @ GSE Nordics June 7¨C9, 2011
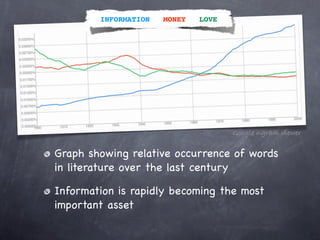
- 2. INFORMATION MONEY LOVE Google ngram viewer Graph showing relative occurrence of words in literature over the last century Information is rapidly becoming the most important asset
- 3. c litus Hera C 5 00.B ˇ°Panta rheiˇ± Everything flows
- 4. Evolving Information Changing content Changing structure Changing constraints Changing interpretation There's a big difference between saying: "This Changing origins information has a 95% reliability" and "This Changing reliability information is 100% reliable".
- 5. What is a database? The purpose of a database is to store a body of information and allow searches over it. The purpose of a temporal database is to store a body of information under evolution and allow historical searches over it. t a re no , we But e yet! ther
- 6. What is a Data Warehouse? Integrates information from many sources Keeps a history of changes Provides ˇ°one version of the truthˇ± Enables reporting, ad-hoc analysis, mining Calculates and stores new information
- 7. The dilemma Many sources and many users naturally lack of result in many tim ion adherence er at changes e ov rad g de 25% 55% Dimensional Modeling 20% Normalized Haphazard lack of adherence
- 8. Patch or Redo? Patching works initially to cope with new requirements Maintenance costs usually rise proportionally to the lifetime of the data warehouse Redoing is unavoidable at some point (and for dimensional modeling sometimes accounted for) The average lifetime is ?ve years The return of investment should and could be much better with a longer lifetime!
- 9. What is Anchor Modeling? Anchor Modeling combines normalization and emulation to provide an agile database modeling technique for evolving information that is implementable in current relational databases. Most, if not all, of what Anchor Modeling is doing in its physical (relational) representation could be "hidden" from the end-user in a true temporal database.
- 10. Technologies Entity-Relationship one- Modeling to- one Sixth Normal Form Tables Temporal Database Emulation
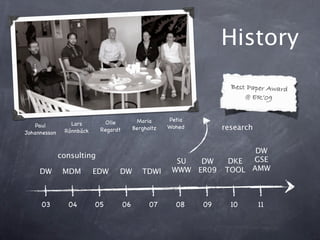
- 11. History Best Paper Award @ ERˇŻ09 Maria Petia Lars Olle Paul Bergholtz Wohed research R?nnb?ck Regardt Johannesson DW consulting SU DW DKE GSE DW MDM EDW DW TDWI WWW ER09 TOOL AMW 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11
- 12. Philosophy Make modeling free from assumptions Make modeling agile and iterative Make evolution non-destructive Do not duplicate information Do not alter existing information Decouple metadata from the model Provide a simple interface for queries
- 13. Evolutio Changing content Anchor M n in full support [6NF + time of change] odeling Changing structure full support (through extensions) [non-destructive schema evolution] Changing constraints minimal support [only primary and foreign keys] Changing interpretation achievable [explicitly modeled] Changing origins restricted support [using metadata] Changing reliability restricted support [using metadata]
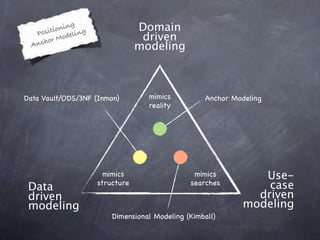
- 14. ionin g Posit odeling Domain chor M driven An modeling Data Vault/ODS/3NF (Inmon) mimics Anchor Modeling reality mimics mimics Use- Data structure searches case driven driven modeling modeling Dimensional Modeling (Kimball)
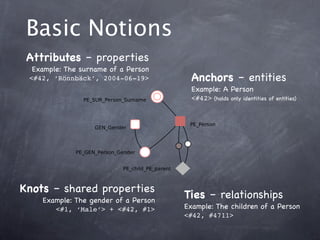
- 15. Basic Notions Attributes ¨C properties Example: The surname of a Person <#42, ˇ®R?nnb?ckˇŻ, 2004-06-19> Anchors ¨C entities Example: A Person ????????????????????? <#42> (holds only identities of entities) ????????? ?????????? ???????????????????? ?????????????????? Knots ¨C shared properties Example: The gender of a Person Ties ¨C relationships <#1, ˇ®MaleˇŻ> + <#42, #1> Example: The children of a Person <#42, #4711>
- 16. Historization <#42, ˇ®SamuelssonˇŻ, 1972-08-20> closed interval historical information <#42, ˇ®R?nnb?ckˇŻ, 2004-06-19> open interval current information Historization is done using the time of change as the start of an interval implicitly closed by another instance of Note tha t UPDAT the same identity with a later never al lowed in E is time of change. anchor databas an e
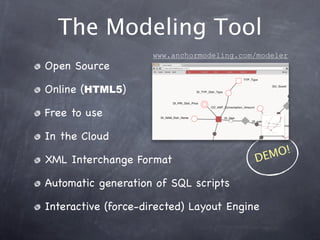
- 17. The Modeling Tool www.anchormodeling.com/modeler Open Source Online (HTML5) Free to use In the Cloud EM O! XML Interchange Format D Automatic generation of SQL scripts Interactive (force-directed) Layout Engine
- 18. Important Bene?ts Handles evolving information (keeping the integrity intact) Increases longevity (databases with long life expectancy) Simpli?es modeling concepts (less prone to error) Enables modular and iterative development Needs no translation logic to the physical layer Automates generation of scripts No downtime when upgrading databases Scans only relevant data during searches Sparse data cause no gaps (no null values)
- 19. More Information : Twitter: anchormod Homepage m eling ode ling.co w. anchorm ht tp://ww od eling Tool Tutorials . M B log . Video deling.com E -mail: lars.r onnback@anchormo LinkedIn Groups: Anchor Modeling Temporal Data Modeling Temporal Data










![Evolutio
Changing content Anchor M
n in
full support [6NF + time of change] odeling
Changing structure
full support (through extensions) [non-destructive schema evolution]
Changing constraints
minimal support [only primary and foreign keys]
Changing interpretation
achievable [explicitly modeled]
Changing origins
restricted support [using metadata]
Changing reliability
restricted support [using metadata]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anchormodelinggse-1306655706916-phpapp01-110529025958-phpapp01/85/Anchor-Modeling-GSE11-Presentation-13-320.jpg)