Anexo proteĂnas
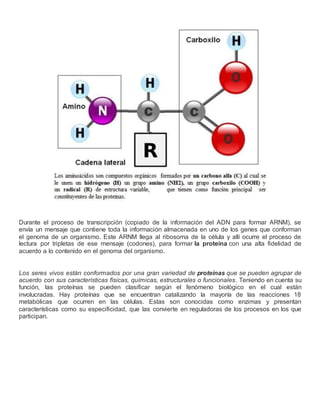
- 1. COLEGIO DE LA PRESENTACIĂN TUNJA LAS PROTEĂNAS Las proteĂnas son polĂmeros lineales de Îą-aminoĂĄcidos que se organizan aleatoriamente para formar asociaciones estructuralmente diferentes, con diversas funciones biolĂłgicas. Los aminoĂĄcidos son compuestos orgĂĄnicos que se caracterizan por tener una estructura bĂĄsica de un grupo carboxilo, unido a un grupo amino por medio de un carbono tetramĂŠrico (C Îą) que, ademĂĄs de unirse al grupo carboxilo y al grupo amino, se une a un hidrĂłgeno a travĂŠs de su tercer enlace y, a travĂŠs de su cuarto enlace, a una cadena variable que da origen a la diversidad de Îą-aminoĂĄcidos que constituyen las proteĂnas. A pesar de que se conocen mĂĄs de quinientos aminoĂĄcidos, solo son veinte los que se encuentran, mayoritariamente, en las proteĂnas y los que dan origen a la diversidad funcional y estructural de las mismas. Para que los aminoĂĄcidos se unan entre sĂ y puedan formar estructuras estables, se realiza un enlace covalente entre el grupo amino de un aminoĂĄcido y el grupo carboxilo del siguiente, estableciĂŠndose un enlace tipo amida que posee caracterĂsticas especiales y se denomina enlace peptĂdico. Las proteĂnas se sintetizan constantemente y, para que eso ocurra, la informaciĂłn de su estructura se encuentra almacenada en una molĂŠcula completamente diferente, el ADN. Para que se forme una proteĂna nueva, se requiere que se activen una serie de procesos que involucran varias estructuras celulares, y otros, mĂĄs complejos: de copiado de informaciĂłn a partir de un gen (ADN), la generaciĂłn de una molĂŠcula mensajera que lleve la informaciĂłn desde el ADN hasta el ribosoma (ARN) y la lectura y traducciĂłn de dicha informaciĂłn para que el mensaje que viene codificado en un lenguaje de cuatro componentes en el ARN sea traducido en un lenguaje de veinte componentes en la proteĂna.
- 2. Durante el proceso de transcripciĂłn (copiado de la informaciĂłn del ADN para formar ARNM), se envĂa un mensaje que contiene toda la informaciĂłn almacenada en uno de los genes que conforman el genoma de un organismo. Este ARNM llega al ribosoma de la cĂŠlula y allĂ ocurre el proceso de lectura por tripletas de ese mensaje (codones), para formar la proteĂna con una alta fidelidad de acuerdo a lo contenido en el genoma del organismo. Los seres vivos estĂĄn conformados por una gran variedad de proteĂnas que se pueden agrupar de acuerdo con sus caracterĂsticas fĂsicas, quĂmicas, estructurales o funcionales. Teniendo en cuenta su funciĂłn, las proteĂnas se pueden clasificar segĂşn el fenĂłmeno biolĂłgico en el cual estĂĄn involucradas. Hay proteĂnas que se encuentran catalizando la mayorĂa de las reacciones 18 metabĂłlicas que ocurren en las cĂŠlulas. Estas son conocidas como enzimas y presentan caracterĂsticas como su especificidad, que las convierte en reguladoras de los procesos en los que participan.
- 3. Si se revisan los procesos de comunicaciĂłn celular, se encontrarĂĄ que en todos ellos hay proteĂnas involucradas. Ejemplos de estas proteĂnas son los receptores de hormonas y los receptores de neurotransmisores, los cuales interactĂşan con sus ligandos por complementariedad entre sus estructuras y desencadenan respuestas celulares. Muchos de estos ligandos (hormonas y neurotransmisores) son, a su vez, de naturaleza proteica. Las molĂŠculas biolĂłgicas para transportar son, generalmente, proteĂnas, que se relacionan con cualquier tipo de transporte de molĂŠculas. Entre los que se destacan el transporte de molĂŠculas hidrofĂłbicas a travĂŠs de medios acuosos como las lipoproteĂnas en la sangre y el transporte de sustancias a travĂŠs del citoplasma por medio de una red de microtĂşbulos, como lo hace la kinesina. đŹďż˝ AsĂ mismo, las proteĂnas pueden servir de transportadores a travĂŠs de la membrana biolĂłgica ya sea participando en procesos redox, como en la membrana de la mitocondria, o como transportadoras de molĂŠculas polares a travĂŠs de la membrana, como ocurre en los canales iĂłnicos. Algunas proteĂnas pueden cumplir tambiĂŠn funciones de almacenamiento de sustancias nutritivas, como sucede en las etapas del desarrollo embrionario o con algunos iones vitales para el organismo.
- 4. Otros procesos biolĂłgicos tambiĂŠn son soportados por este tipo de molĂŠculas. La estructura y soporte de las cĂŠlulas son dadas por una compleja red de naturaleza proteica que se denomina citoesqueleto, el cual constituye un armazĂłn alrededor del que se organizan todos los componentes celulares, sirviendo como soporte para la realizaciĂłn de fenĂłmenos indispensables para la viabilidad celular como el transporte intracelular o la divisiĂłn celular. En los tejidos de sostĂŠn (conjuntivo, Ăłseo y cartilaginoso) de los vertebrados, las fibras de colĂĄgeno presentes en la matriz extracelular son las encargadas de conferir resistencia mecĂĄnica tanto a la tracciĂłn como a la compresiĂłn. La queratina (presente en cabello, plumas, uĂąas y cuernos), la fibroĂna de la seda de araĂąa y la fibrina que segregan las plaquetas para formar los coĂĄgulos sanguĂneos tambiĂŠn son proteĂnas con funciĂłn estructural. La defensa en los diferentes organismos tambiĂŠn es un proceso realizado por proteĂnas. En las bacterias, las llamadas endonucleasas de restricciĂłn se encargan de identificar y destruir molĂŠculas de ADN que no se identifican como propias y, en los vertebrados superiores, las inmunoglobulinas reconocen molĂŠculas extraĂąas y se unen a ellas para facilitar su destrucciĂłn, proceso del que se encargan las cĂŠlulas del sistema inmunitario. El control de diferentes funciones vitales de las cĂŠlulas se puede realizar a nivel gĂŠnico y, en este proceso, las proteĂnas regulan la expresiĂłn gĂŠnica, es decir, se encargan de decidir en todo momento quĂŠ genes deben ser transcritos a ARN y, por lo tanto, traducidos a proteĂna. Independientemente del tipo de proteĂna que se estĂŠ considerando, para que esta sea funcional, debe tener una estructura tridimensional estable. Para llegar a esta estabilidad, las proteĂnas presentan tres (algunas cuatro) niveles estructurales que contribuyen para alcanzar esa estabilidad.
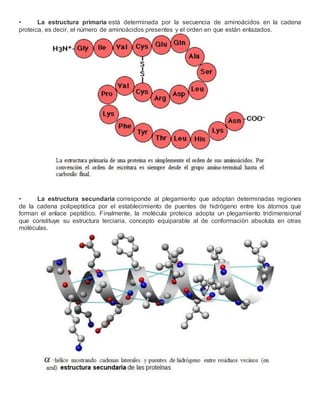
- 5. ⢠La estructura primaria estĂĄ determinada por la secuencia de aminoĂĄcidos en la cadena proteica, es decir, el nĂşmero de aminoĂĄcidos presentes y el orden en que estĂĄn enlazados. ⢠La estructura secundaria corresponde al plegamiento que adoptan determinadas regiones de la cadena polipeptĂdica por el establecimiento de puentes de hidrĂłgeno entre los ĂĄtomos que forman el enlace peptĂdico. Finalmente, la molĂŠcula proteica adopta un plegamiento tridimensional que constituye su estructura terciaria, concepto equiparable al de conformaciĂłn absoluta en otras molĂŠculas.
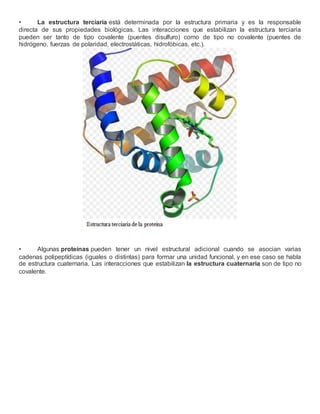
- 6. ⢠La estructura terciaria estĂĄ determinada por la estructura primaria y es la responsable directa de sus propiedades biolĂłgicas. Las interacciones que estabilizan la estructura terciaria pueden ser tanto de tipo covalente (puentes disulfuro) como de tipo no covalente (puentes de hidrĂłgeno, fuerzas de polaridad, electrostĂĄticas, hidrofĂłbicas, etc.). ⢠Algunas proteĂnas pueden tener un nivel estructural adicional cuando se asocian varias cadenas polipeptĂdicas (iguales o distintas) para formar una unidad funcional, y en ese caso se habla de estructura cuaternaria. Las interacciones que estabilizan la estructura cuaternaria son de tipo no covalente.
- 7. Las proteĂnas se asocian entre sĂ o con otra clase de biomolĂŠculas para formar asociaciones supramacromoleculares (microtĂşbulos, ribosomas, nucleosomas, virus, membranas, etc.). Las interacciones que estabilizan este nivel de estructura tambiĂŠn son de tipo no covalente. Esta organizaciĂłn se diferencia de la cuaternaria debido a que la estequiometrĂa de las estructuras formadas puede variar considerablemente. La pĂŠrdida de la estructura terciaria se denomina desnaturalizaciĂłn y va acompaĂąada de la pĂŠrdida de funcionalidad. Sin embargo, con la desnaturalizaciĂłn no desaparece la estructura primaria, ya que se mantienen los enlaces peptĂdicos. En algunos casos la desnaturalizaciĂłn es reversible. Las proteĂnas se pueden estudiar en todos sus niveles estructurales por medio de diferentes tĂŠcnicas experimentales.