Angkor Wat (A heritage wonder)
- 1. Angkor wat
- 2. Angkor wat ’éŚ Name: Angkor wat ’éŚ Country : Cambodia ’éŚ City: Angkor ’éŚ Area of about 500 acres (200 hectares) ’éŚ Architectural style: Khmer ’éŚ Dated: 1186 AD ’éŚ Creator: Jayavarman IV ’éŚ Edit to world heritage site by UNECSO in 1992 ’éŚ Materials: polished marble, laid without mortar
- 3. Angkor wat Built between roughly A.D. 1113 and 1150. Angkor Wat is one of the largest religious monuments ever constructed. Its name means ŌĆ£temple city.ŌĆØOriginally built as a Hindu temple dedicated to the god Vishnu, it was converted into a Buddhist temple in the 14th century, and statues of Buddha were added to its already rich artwork. Its 213-foot-tall (65 meters) central tower is surrounded by four smaller towers and a series of enclosure walls, a layout that recreates the image of Mount Meru, a legendary place in Hindu mythology that is said to lie beyond the Himalayas and be the home of the gods.
- 4. It was easily the largest city in the world until the industrial revolution. The temple is surrounded by a 650-foot-wide (200 meters) moat that encompasses a perimeter of more than 3 miles (5 km). This moat is 13 feet deep (4 meters) and would have helped stabilize the templeŌĆÖs foundation, preventing groundwater from rising too high or falling too low. Angkor WatŌĆÖs main entrance was to the west (a direction associated with Vishnu) across a stone causeway, with guardian lions marking the way. To the east of the temple was a second, more modest, entrance. The heart of the temple was the central tower, entered by way of a steep staircase, a statue of Vishnu at top.
- 5. A n g k o r w a t Temples this one does look different. The shape is like a glimpse of a huge pyramid. What this temple is very broad. Along the path that leads to the entrance there is a giant snake- shaped fence. This is believed to be a symbol of fertility. This temple consists of a tall building and a smaller building in the vicinity.
- 6. The temples were first discovered by French missionaries in 1860. Henri Mahout, a French botanist started intensive research and restoration programs. These research efforts continued until 1968, when the Vietnam war disrupted the studies. Angkor Wat is the highest achievement of Khmer temple architecture, and is today the "flagship" of the temples at Angkor.
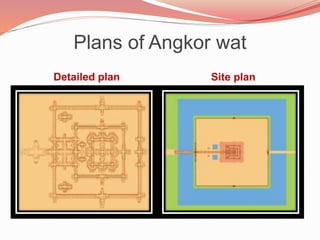
- 7. Plans of Angkor wat Detailed plan Site plan
- 8. The stones, as smooth as polished marble, were laid without mortar with very tight joints that were sometimes hard to find. The blocks were held together by mortise and tenon joints in some cases, while in others they used dovetails and gravity. The blocks were presumably put in place by a combination of elephants, coir ropes, pulleys and bamboo scaffolding.
- 9. The trees growing out of the ruins are perhaps the most distinctive feature of Ta Prohm, and "have prompted more writers to descriptive excess than any other feature of Angkor." Two species predominate, but sources disagree on their identification: the larger is either the silk (Ceiba pentandra) or thitpok Tetrameles nudiflora, and the smaller is either the strangler fig (Ficus gibbosa) or Gold Apple (Diospyros decandra).
- 10. Heritage Angkor wat Ta Prohm has been left in much the same condition in which it was found: the photogenic and atmospheric combination of trees growing out of the ruins and the jungle surroundings have made it one of Angkor's most popular temples with visitors. UNESCO inscribed Ta Prohm on the World Heritage List in 1992. Today, it is one of the most visited complexes in CambodiaŌĆÖs Angkor region. The conservation and restoration of Ta Prohm is a partnership project of the Archaeological Survey of India and the APSARA (Authority for the Protection and Management of Angkor and the Region of Siem Reap).
- 11. Arial view of Angkor wat
- 13. The Government of Italy has granted 565,000 USD to the UNESCO/Italy Funds-in-Trust, for Safeguarding of the Angkor Wat Temple-Phase I (June 2008- September 2011), while the APSARA National Authority provided materials such as sandstones, laterite and other necessary chemical products which is equivalent to 50,000 USD.
- 14. Dr. M. S. Nagaraja Rao, India's former director general of archeology, who has been in charge of the project. Armed with chemical cleaners, preservatives and experience, a team of Indian archeologists has begun restoring Angkor Wat, the vast and ancient capital of Cambodia. The Indians plan to begin with the restoration of the main entrance to the enormous complex of temples, chapels and corridors Angkor, in CambodiaŌĆÖs Northern Province of Siem Reap, is one of the most important archaeological sites of Southeast Asia.
- 15. Some glorious views of great Angkor wat
- 21. Tehreem saher Cms id: 18395 Semester : v