ann ppt , multilayer perceptron. presentation on
- 1. Machine Learning Neural Networks ║¦║¦▀ús mostly adapted from Tom Mithcell, Han and Kamber
- 2. Artificial Neural Networks ´ü¼ Computational models inspired by the human brain: ´ü¼ Algorithms that try to mimic the brain. ´ü¼ Massively parallel, distributed system, made up of simple processing units (neurons) ´ü¼ Synaptic connection strengths among neurons are used to store the acquired knowledge. ´ü¼ Knowledge is acquired by the network from its environment through a learning process
- 3. History ´ü¼ late-1800's - Neural Networks appear as an analogy to biological systems ´ü¼ 1960's and 70's ÔÇô Simple neural networks appear ´ü¼ Fall out of favor because the perceptron is not effective by itself, and there were no good algorithms for multilayer nets ´ü¼ 1986 ÔÇô Backpropagation algorithm appears ´ü¼ Neural Networks have a resurgence in popularity ´ü¼ More computationally expensive
- 4. Applications of ANNs ´ü¼ ANNs have been widely used in various domains for: ´ü¼ Pattern recognition ´ü¼ Function approximation ´ü¼ Associative memory
- 5. Properties ´ü¼ Inputs are flexible ´ü¼ any real values ´ü¼ Highly correlated or independent ´ü¼ Target function may be discrete-valued, real-valued, or vectors of discrete or real values ´ü¼ Outputs are real numbers between 0 and 1 ´ü¼ Resistant to errors in the training data ´ü¼ Long training time ´ü¼ Fast evaluation ´ü¼ The function produced can be difficult for humans to interpret
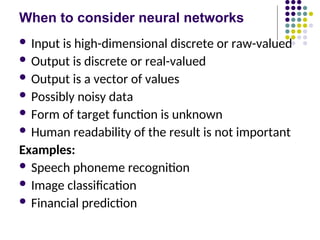
- 6. When to consider neural networks ´ü¼ Input is high-dimensional discrete or raw-valued ´ü¼ Output is discrete or real-valued ´ü¼ Output is a vector of values ´ü¼ Possibly noisy data ´ü¼ Form of target function is unknown ´ü¼ Human readability of the result is not important Examples: ´ü¼ Speech phoneme recognition ´ü¼ Image classification ´ü¼ Financial prediction
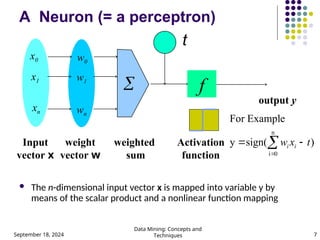
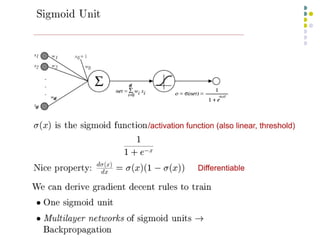
- 7. September 18, 2024 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 7 A Neuron (= a perceptron) ´ü¼ The n-dimensional input vector x is mapped into variable y by means of the scalar product and a nonlinear function mapping t - f weighted sum Input vector x output y Activation function weight vector w ´âÑ w0 w1 wn x0 x1 xn ) sign( y e For Exampl n 0 i t x w i i ´Ç¡ ´Ç¢ ´âÑ ´Ç¢
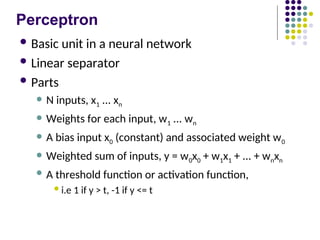
- 8. Perceptron ´ü¼ Basic unit in a neural network ´ü¼ Linear separator ´ü¼ Parts ´ü¼ N inputs, x1 ... xn ´ü¼ Weights for each input, w1 ... wn ´ü¼ A bias input x0 (constant) and associated weight w0 ´ü¼ Weighted sum of inputs, y = w0x0 + w1x1 + ... + wnxn ´ü¼ A threshold function or activation function, ´ü¼i.e 1 if y > t, -1 if y <= t
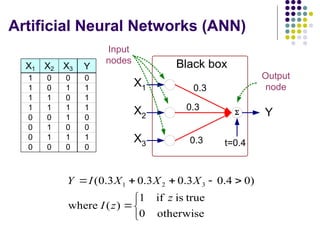
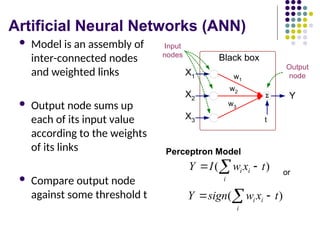
- 9. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) ´ü¼ Model is an assembly of inter-connected nodes and weighted links ´ü¼ Output node sums up each of its input value according to the weights of its links ´ü¼ Compare output node against some threshold t ´üô X1 X2 X3 Y Black box w1 t Output node Input nodes w2 w3 ) ( t x w I Y i i i ´Ç¡ ´Ç¢ ´âÑ Perceptron Model ) ( t x w sign Y i i i ´Ç¡ ´Ç¢ ´âÑ or
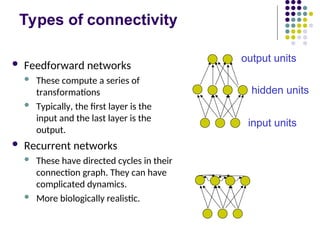
- 10. Types of connectivity ´ü¼ Feedforward networks ´ü¼ These compute a series of transformations ´ü¼ Typically, the first layer is the input and the last layer is the output. ´ü¼ Recurrent networks ´ü¼ These have directed cycles in their connection graph. They can have complicated dynamics. ´ü¼ More biologically realistic. hidden units output units input units
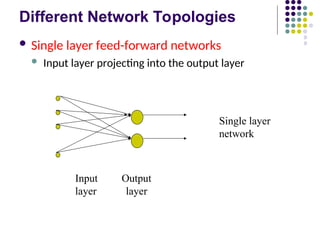
- 11. Different Network Topologies ´ü¼ Single layer feed-forward networks ´ü¼ Input layer projecting into the output layer Input Output layer layer Single layer network
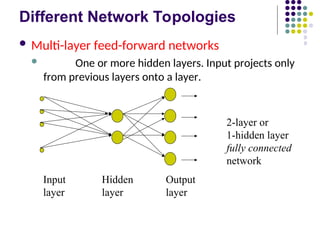
- 12. Different Network Topologies ´ü¼ Multi-layer feed-forward networks ´ü¼ One or more hidden layers. Input projects only from previous layers onto a layer. Input Hidden Output layer layer layer 2-layer or 1-hidden layer fully connected network
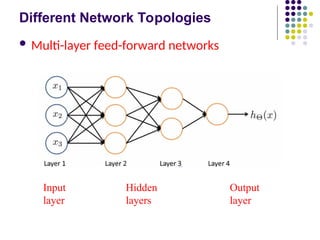
- 13. Different Network Topologies ´ü¼ Multi-layer feed-forward networks Input Hidden Output layer layers layer
- 14. Different Network Topologies ´ü¼ Recurrent networks ´ü¼ A network with feedback, where some of its inputs are connected to some of its outputs (discrete time). Input Output layer layer Recurrent network
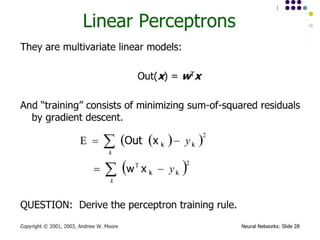
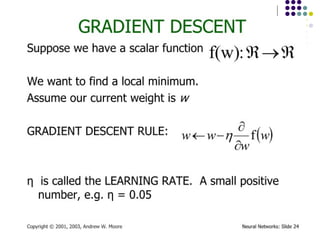
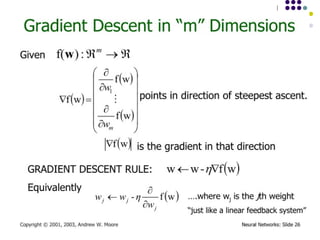
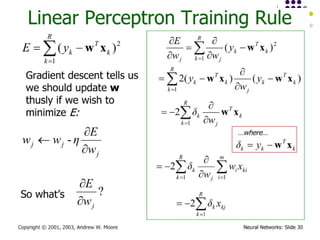
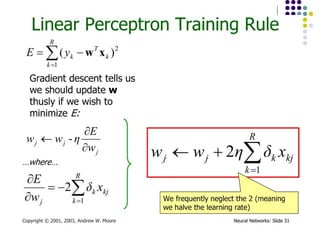
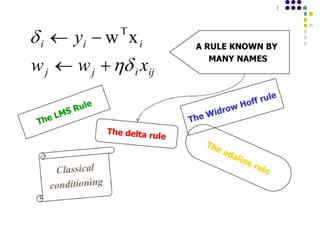
- 15. Algorithm for learning ANN ´ü¼ Initialize the weights (w0, w1, ÔǪ, wk) ´ü¼ Adjust the weights in such a way that the output of ANN is consistent with class labels of training examples ´ü¼ Error function: ´ü¼ Find the weights wiÔÇÖs that minimize the above error function ´ü¼ e.g., gradient descent, backpropagation algorithm ´üø ´üØ2 ) , ( ´âÑ ´Ç¡ ´Ç¢ i i i i X w f Y E
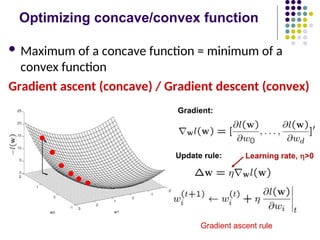
- 16. Optimizing concave/convex function ´ü¼ Maximum of a concave function = minimum of a convex function Gradient ascent (concave) / Gradient descent (convex) Gradient ascent rule
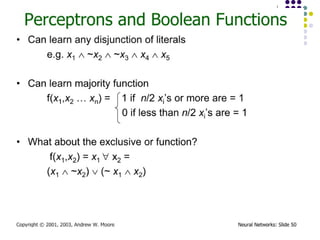
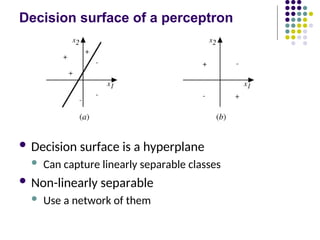
- 24. Decision surface of a perceptron ´ü¼ Decision surface is a hyperplane ´ü¼ Can capture linearly separable classes ´ü¼ Non-linearly separable ´ü¼ Use a network of them
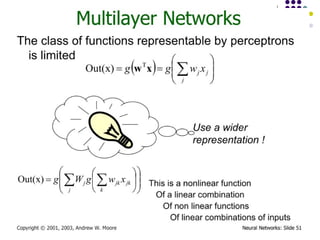
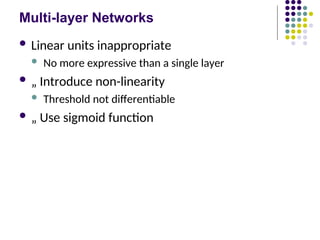
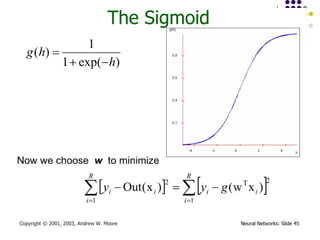
- 27. Multi-layer Networks ´ü¼ Linear units inappropriate ´ü¼ No more expressive than a single layer ´ü¼ ÔÇ× Introduce non-linearity ´ü¼ Threshold not differentiable ´ü¼ ÔÇ× Use sigmoid function
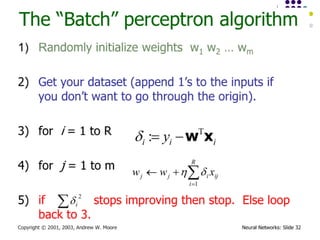
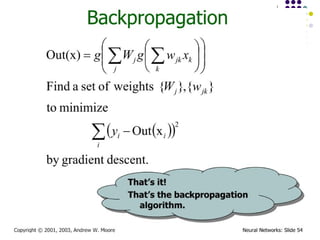
- 31. September 18, 2024 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 31 Backpropagation ´ü¼ Iteratively process a set of training tuples & compare the network's prediction with the actual known target value ´ü¼ For each training tuple, the weights are modified to minimize the mean squared error between the network's prediction and the actual target value ´ü¼ Modifications are made in the ÔÇ£backwardsÔÇØ direction: from the output layer, through each hidden layer down to the first hidden layer, hence ÔÇ£backpropagationÔÇØ ´ü¼ Steps ´ü¼ Initialize weights (to small random #s) and biases in the network ´ü¼ Propagate the inputs forward (by applying activation function) ´ü¼ Backpropagate the error (by updating weights and biases) ´ü¼ Terminating condition (when error is very small, etc.)
- 33. September 18, 2024 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 33 How A Multi-Layer Neural Network Works? ´ü¼ The inputs to the network correspond to the attributes measured for each training tuple ´ü¼ Inputs are fed simultaneously into the units making up the input layer ´ü¼ They are then weighted and fed simultaneously to a hidden layer ´ü¼ The number of hidden layers is arbitrary, although usually only one ´ü¼ The weighted outputs of the last hidden layer are input to units making up the output layer, which emits the network's prediction ´ü¼ The network is feed-forward in that none of the weights cycles back to an input unit or to an output unit of a previous layer ´ü¼ From a statistical point of view, networks perform nonlinear regression: Given enough hidden units and enough training samples, they can closely approximate any function
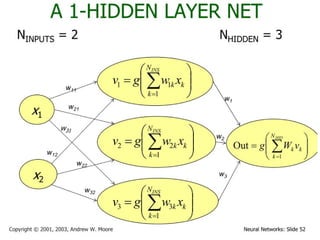
- 34. September 18, 2024 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 34 Defining a Network Topology ´ü¼ First decide the network topology: # of units in the input layer, # of hidden layers (if > 1), # of units in each hidden layer, and # of units in the output layer ´ü¼ Normalizing the input values for each attribute measured in the training tuples to [0.0ÔÇö1.0] ´ü¼ One input unit per domain value, each initialized to 0 ´ü¼ Output, if for classification and more than two classes, one output unit per class is used ´ü¼ Once a network has been trained and its accuracy is unacceptable, repeat the training process with a different network topology or a different set of initial weights
- 35. September 18, 2024 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 35 Backpropagation and Interpretability ´ü¼ Efficiency of backpropagation: Each epoch (one interation through the training set) takes O(|D| * w), with |D| tuples and w weights, but # of epochs can be exponential to n, the number of inputs, in the worst case ´ü¼ Rule extraction from networks: network pruning ´ü¼ Simplify the network structure by removing weighted links that have the least effect on the trained network ´ü¼ Then perform link, unit, or activation value clustering ´ü¼ The set of input and activation values are studied to derive rules describing the relationship between the input and hidden unit layers ´ü¼ Sensitivity analysis: assess the impact that a given input variable has on a network output. The knowledge gained from this analysis can be represented in rules
- 36. September 18, 2024 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 36 Neural Network as a Classifier ´ü¼ Weakness ´ü¼ Long training time ´ü¼ Require a number of parameters typically best determined empirically, e.g., the network topology or ÔÇ£structure.ÔÇØ ´ü¼ Poor interpretability: Difficult to interpret the symbolic meaning behind the learned weights and of ÔÇ£hidden unitsÔÇØ in the network ´ü¼ Strength ´ü¼ High tolerance to noisy data ´ü¼ Ability to classify untrained patterns ´ü¼ Well-suited for continuous-valued inputs and outputs ´ü¼ Successful on a wide array of real-world data ´ü¼ Algorithms are inherently parallel ´ü¼ Techniques have recently been developed for the extraction of rules from trained neural networks
- 38. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) X1 X2 X3 Y 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 ´üô X1 X2 X3 Y Black box 0.3 0.3 0.3 t=0.4 Output node Input nodes ´â« ´â¡ ´â¼ ´Ç¢ ´Ç¥ ´Ç¡ ´Ç½ ´Ç½ ´Ç¢ otherwise 0 true is if 1 ) ( where ) 0 4 . 0 3 . 0 3 . 0 3 . 0 ( 3 2 1 z z I X X X I Y
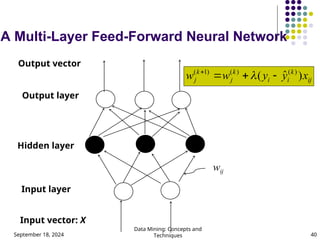
- 40. September 18, 2024 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 40 A Multi-Layer Feed-Forward Neural Network Output layer Input layer Hidden layer Output vector Input vector: X wij ij k i i k j k j x y y w w ) ╦å ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 ( ´Ç¡ ´Ç½ ´Ç¢ ´Ç½ ´ü¼
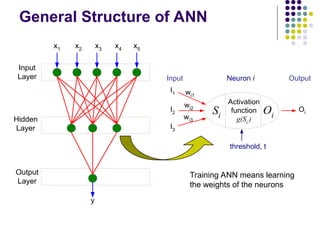
- 41. General Structure of ANN Activation function g(Si ) Si Oi I1 I2 I3 wi1 wi2 wi3 Oi Neuron i Input Output threshold, t Input Layer Hidden Layer Output Layer x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 y Training ANN means learning the weights of the neurons







![September 18, 2024
Data Mining: Concepts and
Techniques 34
Defining a Network Topology
´ü¼ First decide the network topology: # of units in the input
layer, # of hidden layers (if > 1), # of units in each hidden
layer, and # of units in the output layer
´ü¼ Normalizing the input values for each attribute measured in
the training tuples to [0.0ÔÇö1.0]
´ü¼ One input unit per domain value, each initialized to 0
´ü¼ Output, if for classification and more than two classes, one
output unit per class is used
´ü¼ Once a network has been trained and its accuracy is
unacceptable, repeat the training process with a different
network topology or a different set of initial weights](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai7-240918172806-d9070636/85/ann-ppt-multilayer-perceptron-presentation-on-34-320.jpg)