Anti parkinsons drugs
- 2. Parkinsoniasm ŌĆó Defination:- It is an extrapyramidal disorder related to dysfunction of the basal ganglia.It results in disturbance of movement and posture without significant paralysis. Normally, equilibrium exists between accetycholine an d dopamine. With dopamine deficiency,there is acetylcholine hyperactivity; this may be a mechanism for parkinsonian symptoms. OR A disorder of the central nervous system that affects movement, often including tremors. Nerve cell damage in the brain causes dopamine levels to drop, leading to the symptoms of parkinsonŌĆÖs. OR Tremors(shaking) more on one side ,disappear if patient attempts to hold something. Expressionies face and monotonous speech.
- 3. Dopamine Receptors ŌĆó D1 and D5(excitatory):-Occurs in the brain cortex, limbic system, striatum and cardiovascular system and acting through increase cAMP and increase Phospholipase C. ŌĆó D2, D3 and D4(inhibitory):-Occurs in the brain cortex, limbic system,striatum, pituitary and cardiovascular system and acting through decrease cAMP, K+ channel increase and Ca2+ channel decrease.
- 4. Anti Parkinsonian drugs 1. Drugs affect brain dopaminergic system: a) Dopamine precursor: Levodopa b) Dopamine decarboxylase inhibitors: Carbidopa,Beneserazide c) Dopaminergic agonist: Bromcriptin, Ropinirpole, Piribedil, Pramipixole,Cabergoline d) *MAO B inhibitors: Selegiline,Rasagiline e) ** COMT inhibitors: Talca pone f) Dopamine facilitators: Amantadine 2. Central acting anticholinergics: Trihexphenidyl, Procyclidine,Biperiden 3. Antihisaminics: Orphenadrine,Promethazine *=Mono amino oxidase **= catechol-o-methyl transferase
- 5. Mode of actions Levodopa: It is the precursor and producing of dopamine After the decarboxylation converts into dopamine in the peripheral tissue as well as brain neuron Peripheral generated dopamine (responsible many side effects.) MAO:After the penetration,levodopa converts into dopamine which acts on D1 and D2 receptor Resolve bradykinesia, rigidty and tremor Smoothening the muscular movements.
- 6. Mode of actions Dopaminergic agonist: D1 and D2 agonist action. Dopamine facilitators: Enhance the presynaptic synthesis Release of dopamine.
- 7. Mode of actions Dopamine decarboxylase inhibitors: These drugs inhibits, dopa decarboxylase in the peripheral tissue These donot penetrate in brain Donot inhibit conversion of levodopa in brain Only prevents the peripheral degradation of levodopa and potentiation of anti parkinson action.
- 10. Adverse Effects ŌĆó Levodopa: i) Postural hypotension, ii) Nausea, iii) Vomiting, iv) Arrhythmia ŌĆó Bromcriptin: i)Vomiting ii) Hallucination iii) Hypotension ŌĆó Ropinirpole & Pramipixole: i) Nausea ii) Hallucination iii) Hypotension ŌĆó Selegiline: i) Postural hypotension ii) Nausea iii) Confusion ŌĆó Amantadine: i) Insomnia ii) Nightmares
- 11. Treatment A) Younger age group(50-60 yrs): When life expectancy is more,keep levodopa reserved for use in later years. 1. If predominant Tremors: Give anti-cholinergic Eg:- Orphenadrine, Trihexphenidyl 2. If predominant Rigidity: Give Dopamine agonist Eg:- Bromcriptin, Piribedil 3. If not controlled with both drugs,add Eg:- i) Selegiline ii) Amantadine iii) When symptoms are severe enough to interfere with daily routine, in spite of above drugs, add Levodopa.
- 12. Treatment B) Older age group(>65-70 yrs): a)Start with Levodopa. b) Avoid anti-cholinergic,as CNS side effects are more in elderly. 1) i) Levodopa ii) Levodopa+Carbidopa 2) i) If symptoms are not controlled, as happens with the progress of the disease, ii) Add Selegiline, then Bromcriptin. iii) Give Levodopa in small divided doses every 4 hrs for continuous action.
- 13. Types, Drug, Dose TYPE N O DRUG TAB/CAPSULE INJ. SYRUP DOSE COMBINATION WITH Atropine-like drug 1 Biperiden 2 mg tab. 5 mg in 1 ml inj. 1 tab 2 times per day To 2 tabs 3-4 times per day 2 Orphenadrine 50 mg tab. 50 mg 3 times per day upto 400 mg per day Paracetamol 3 Procyclidine Hcl 2.5 , 5 mg tab. 2.5 mg 3 times per day upto 30 mg per day 4 Trihexphenidyl Hcl 2 mg tab. 2 mg daily upto 5 tablets per day Haloperidol, Trifluoperazine
- 14. Types, Drug, Dose TYPE N O DRUG TAB/CAPSULE INJ. SYRUP DOSE COMBINATION WITH Levodopa 1 Levodopa 500 mg tab. 250 mg daily,increase every 3 day upto 6-8 g/day 2 Levodopa+Carbidopa 250 mg:25 mg tab. 1 tab 3 times per day upto 7 tab per day i.e 1 tab 3 hrly 3 Levodopa+Beneserazide 100 mg:25 mg cap. 1 cap 2 times per day upto 4-8 cap per day
- 15. Types, Drug, Dose TYPE N O DRUG TAB/CAPSULE INJ. SYRUP DOSE COMBINATION WITH Dopamine agonist drug 1 Bromcriptin 2.5 mg tab. ┬Į tab daily with meals upto 10 mg per day 2 Piribedil 50 mg tab. 1 tab daily to 4 tab per day with meals 3 Ropinirpole 0.5,1,2 mg tab. 0.5 mg OD 4 Pramipixole 0.5,1,1.5 mg tab. 0.5 to 1.5 mg TDS 5 Cabergoline 0.25,0.5 mg tab. 0.5-1 mg per week upto 2 mg twice a week
- 16. Types, Drug, Dose TYPE N O DRUG TAB/CAPSULE INJ. SYRUP DOSE COMBINATION WITH Other drugs 1 Amantadine 100 m g cap. 1 cap daily, maximum 2 caps per day 2 Selegiline 5 mg tab. 10 mg daily(1 tab with breakfast and lunch) 3 Rasagiline 0.5 , 1 mg tab. 1 mg per day
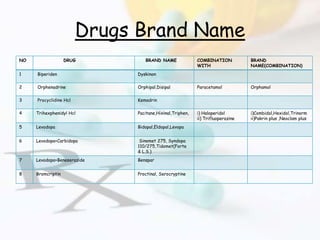
- 17. Drugs Brand Name NO DRUG BRAND NAME COMBINATION WITH BRAND NAME(COMBINATION) 1 Biperiden Dyskinon 2 Orphenadrine Orphipal,Disipal Paracetamol Orphamol 3 Procyclidine Hcl Kemadrin 4 Trihexphenidyl Hcl Pacitane,Hixinal,Triphen, i) Haloperidol ii) Trifluoperazine i)Combidol,Hexidol,Trinorm ii)Pakrin plus ,Neoclam plus 5 Levodopa Bidopal,Eldopal,Levopa 6 Levodopa+Carbidopa Sinemet 275, Syndopa 110/275,Tidomet(Forte & L.S.) 7 Levodopa+Beneserazide Benspar 8 Bromcriptin Proctinal, Serocryptine
- 18. Drugs Brand Name N O DRUG BRAND NAME COMBINATION WITH BRAND NAME(COMBINATION WITH) 1 Piribedil Trivistal L. A. 2 Ropinirpole Parkirop,Ropark,Ropitor 3 Pramipixole Parpex,Pramipex 4 Cabergoline Cabgolin,Collete, Caberlin 5 Amantadine Amantrel 6 Selegiline Jumex,Selgin,Elegelin,Selerin 7 Rasagiline Azilect,Relgin
- 19. References ŌĆó Shah Umang, Akabari Ashok, Baser Amit Kumar,Patel Ashish ŌĆ£Complete companion for GPATŌĆØ 5th edition 2020 , page number 2.37, Published by Pearson India Pvt Ltd.page number 2.37. ŌĆó Vaidya Ghanashyam ŌĆ£General PracticeŌĆØ 5th edition 2017 and reprinbt 2019, published by bhalani publication.page number 49 & 291. ŌĆó Aminoff MJ, Greenberg DA, Simon RP (2005). "Chapter 7: Movement disorders". Clinical Neurology (6th ed.). Lange: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 241ŌĆō45. ISBN 978-0-07-142360-1. ŌĆó Connolly BS, Lange AE (2014): Pharmacological Treatment of Parkinson Disease. A Review. JAMA. 311(16):1670-1683. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3654. ŌĆó ŌĆ£Pharmacologic Management of Parkinsonism & Other Movement DisordersŌĆØ (Chapter 28). In: Katzung BG: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 13e. Katzung BG, Masters SB, Trevor AJ (Editors). McGraw-Hill / Lange. ŌĆó Jankovic J (2015): Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson disease.
- 20. THANK YOU