Antifungal drugs ppt.pptx
Download as pptx, pdf1 like185 views
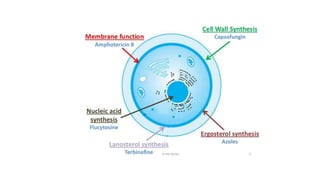
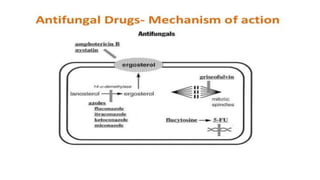
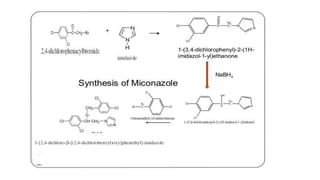
Miconazole is an antifungal drug used to treat candidal skin infections. It works by selectively disrupting fungal cell membranes, which contain high levels of ergosterol that differentiate them from mammalian cell membranes.
1 of 22
Download to read offline









![Miconazole
IUPAC Name:
1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]ethyl]imidazole](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antifungaldrugsppt-220425091801/85/Antifungal-drugs-ppt-pptx-14-320.jpg)






Ad
Recommended
Introduction to Ion Exchange Chromatography .pptx
Introduction to Ion Exchange Chromatography .pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Ion exchange chromatography is a separation technique for ions and polar molecules based on interactions with an inert matrix, using either cationic or anionic exchangers. This method relies on the reversible exchange of ions between the sample and ion exchangers, often performed in column chromatography. It efficiently separates a wide range of charged particles, including large proteins and small nucleotides, and is versatile for both analytical and preparative laboratory uses.High Performance Liquid Chromatography.pptx
High Performance Liquid Chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
The document discusses high performance liquid chromatography presented by Dr. Nidhi Gupta, an assistant professor in India. It outlines the mission and vision of MMCP, emphasizing the development of technically competent pharmacy professionals and effective pharmacists who can contribute to the healthcare system. Additionally, it highlights the promotion of research for national and global societal development.MASS SPECTROMETRY.pptx
MASS SPECTROMETRY.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of molecules to determine molecular weights and identify unknown chemical compounds. It works by first ionizing molecules, then separating the ions by mass in the mass analyzer, and detecting the ions to produce a mass spectrum. The spectrum shows the masses of molecules in a sample and can be used to quantify known compounds and study molecular structure and properties.Structural Isomerism.PPT
Structural Isomerism.PPTNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document discusses different types of isomerism including structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Structural isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Types of structural isomerism include chain isomerism, positional isomerism, and functional group isomerism. Chain isomerism involves compounds having the same molecular formula but different carbon chain structures. Positional isomerism involves compounds having functional groups at different positions. Functional group isomerism involves compounds having different functional groups. Stereoisomerism occurs when compounds have the same connectivity of atoms but different arrangements in space.Unit-5 Combinatorial Synthesis.pptx
Unit-5 Combinatorial Synthesis.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Combinatorial synthesis is a technique used in organic chemistry and materials science to efficiently generate and study large numbers of structurally similar compounds. The document is authored by Dr. Nidhi Gupta of M.M. College of Pharmacy at Maharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed to be University) in Mullana, Ambala, Haryana, India and likely discusses her work in the field of combinatorial synthesis.HPLC.pptx
HPLC.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
High Performance Liquid Chromatography is a document by Dr. Nidhi Gupta about the topic of high performance liquid chromatography. Dr. Nidhi Gupta is an assistant professor at MMCP in Mullana, Ambala, India. The document provides information about high performance liquid chromatography but does not include any specific details.Ion Exchange Chromatography.pptx
Ion Exchange Chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Ion exchange chromatography is a separation process based on the reversible exchange of ions between a sample solution and an inert matrix containing cationic or anionic exchangers. Cationic exchangers attract positively charged cations, while anionic exchangers attract negatively charged anions, and this method is primarily performed through column chromatography. Its advantages include high efficiency in separating charged molecules, applicability to various charged species, and utility for both analytical and preparative laboratory purposes.carboxylic acids.ppt
carboxylic acids.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document provides information on qualitative tests and structures and uses of various carboxylic acids. It describes litmus, sodium hydrogen carbonate, and ester tests to identify carboxylic acids. It also provides the structures and common uses of acetic acid, lactic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, succinic acid, oxalic acid, salicylic acid, benzoic acid, benzyl benzoate, dimethyl phthalate, methyl salicylate, and acetyl salicylic acid. The uses described include industrial, medical, food/beverage, and other applications.Chemical reactions_alcohols.pptx
Chemical reactions_alcohols.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. They can undergo oxidation reactions where the alcohol is converted to an aldehyde or ketone with the loss of hydrogen atoms. Substitution reactions on alcohols involve replacing the hydroxyl hydrogen with another group like a halide to form alkyl halides.Methods of preparation_aldehyde and ketones.pptx
Methods of preparation_aldehyde and ketones.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbon-oxygen double bond. They are prepared through oxidation reactions of primary alcohols to form aldehydes and secondary alcohols to form ketones. The author thanks the reader for their time.Chemical reactions_aldehyde and ketones.pptx
Chemical reactions_aldehyde and ketones.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
The document discusses carbonyl compound reactions, specifically the benzoin condensation and Perkin condensation. The benzoin condensation involves the dimerization of two aromatic aldehydes using a cyanide ion catalyst to form an aromatic acyloin compound like benzoin. The reaction mechanism involves nucleophilic addition of the cyanide ion to one aldehyde, followed by rearrangement and addition to the second aldehyde producing benzoin after proton transfer and cyanide elimination. The Perkin condensation is also discussed but no details are provided.Str and Uses_aldehyde and ketones.pptx
Str and Uses_aldehyde and ketones.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
The document summarizes the structures and uses of various carbonyl compounds including aldehydes and ketones. It describes 8 compounds - benzaldehyde, vanillin, cinnamaldehyde, formaldehyde, paraldehyde, acetone, chloral hydrate, and hexamine. For each compound, it provides the chemical structure and lists their main uses which range from use as flavoring agents and precursors to other chemicals to applications in cosmetics, plastics, paints, and medicine.Hybridisation and Method of preparation of alkenes.ppt
Hybridisation and Method of preparation of alkenes.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond functional group. Ethylene (C2H4) is an example alkene. The carbon atoms in alkenes adopt sp2 hybridization, resulting in a flat structure with 120 degree bond angles between atoms. An alkene's double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond between the carbon atoms, restricting rotation about the double bond.Method of Preparation of Amines.ppt
Method of Preparation of Amines.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document discusses the preparation and properties of amines. It describes four types of amines based on the number of carbons bonded to the nitrogen atom. Amines can be prepared through ammonolysis reactions, where an amine or ammonia displaces a halide on a primary or methyl halide. This produces primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary amines depending on the starting material. Amines have relatively high melting and boiling points due to hydrogen bonding between molecules. They are basic and can turn litmus blue, with solubility in water depending on the carbon chain length.Chemical Reactions of Amines.ppt
Chemical Reactions of Amines.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Primary amines react with alkyl halides to form secondary amines. Primary and secondary amines react with acyl halides and anhydrides to form amides through nucleophilic attack of the amine on the carbonyl group. Benzenesulphonyl chloride reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides. Primary amines react with nitrous acid to form alcohols, while secondary amines form oily nitrosoamines through the Libermann reaction. Tertiary amines form salts with nitrous acid. Amphetamine is a phenylethylamine used to treat ADHD, narcolepsy, and obesity.Str and Uses of alkyl halides.pptx
Str and Uses of alkyl halides.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document summarizes information about various alkyl halides. It discusses the chemical structures, properties and uses of ethyl chloride, chloroform, tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, tetrachloromethane, dichloromethane and iodoform. Many of these compounds are or were used as solvents, refrigerants, degreasers, paint strippers, dry cleaning fluids and disinfectants due to their volatility and ability to dissolve organic materials.Structure and Uses of different carboxylic acids.pptx
Structure and Uses of different carboxylic acids.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document discusses the structures and uses of various carboxylic acids, including acetic acid, lactic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, succinic acid, oxalic acid, salicylic acid, benzoic acid, benzyl benzoate, dimethyl phthalate, methyl salicylate, and acetyl salicylic acid. It outlines key industrial, medical, and household applications for each acid such as use in food/beverage production, pharmaceuticals, cleaning products, and agriculture.Chemical Reactions of Alkenes.pptx
Chemical Reactions of Alkenes.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alkenes undergo general chemical reactions and their stability depends on the number of substituents. More substituted alkenes are more stable than less substituted ones due to a phenomenon called hyperconjugation. They also have a lower heat of hydrogenation. The stability of alkenes increases with more substituents.Chemical reactions of alkanes.pptx
Chemical reactions of alkanes.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
The document summarizes the chemical reaction of chlorination of alkanes. It describes the reaction as a chain reaction, where (1) chlorine radicals are produced from chlorine molecules through homolytic fission initiated by heat or light. (2) The chlorine radicals react with methane to form methyl radicals and HCl molecules. (3) The methyl radicals react with chlorine molecules to form methyl chloride and new chlorine radicals. This sequence propagates the chain reaction until (4)-(6) termination steps form stable products and end the reaction.Hybridisatoion and Method of Preparation of alkanes.ppt
Hybridisatoion and Method of Preparation of alkanes.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alkanes are the simplest organic compounds made of only carbon and hydrogen. They form single covalent bonds and have no functional groups. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 where n is the number of carbon atoms. Methane (CH4) is the first member and ethane (C2H6) is the second. Alkanes have sp3 hybridization giving them a tetrahedral molecular geometry. One method to prepare alkanes is through hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes which involves passing a mixture of the unsaturated hydrocarbon and hydrogen over nickel at high temperatures.IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Part-2.pptx
IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Part-2.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
1. Here are the steps to name the molecule:
1) Identify the functional group (carbonyl group) which gives the compound the name of a ketone.
2) Name the parent chain (hexane) which contains the carbonyl group.
3) Number the parent chain starting from the end that gives the carbonyl carbon the lowest number.
4) Include the position of the carbonyl group as a prefix.
The IUPAC name is therefore: 3-hexanone
2. (a) 3-ethyloctane
(b) 1,4-dibromohexane
(c) 2,3,4-trimethylheptane
(d)Classification, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds.pptx
Classification, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document provides information on the classification, nomenclature, and isomerism of organic compounds. It discusses how organic compounds are classified based on their structure as acyclic, cyclic, aromatic, etc. It also describes the IUPAC system for systematically naming organic compounds based on functional groups and molecular structure. Key points covered include naming conventions for alkanes, alkenes, alkyl halides, and other compound classes.TLC.pptx
TLC.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Thin layer chromatography is a technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures on a sheet coated with an adsorbent material like silica gel or aluminum oxide. The mixture components separate vertically as they travel different distances up the sheet at different rates depending on how strongly they interact with the stationary and mobile phases. Each component appears as a distinct spot, and its retention factor (Rf) indicates how far it traveled relative to the solvent front. Factors like the solvent system, amount of material, adsorbent, and temperature affect the separation. TLC is a simple, fast, and inexpensive chromatography method used to analyze pharmaceuticals, foods, and other chemical mixtures.Paper Chromatography.pptx
Paper Chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
1) Paper chromatography is a technique that uses paper as the stationary phase to separate dissolved chemical substances based on their different migration rates across the paper.
2) The principle involves either partition chromatography where substances partition between the water in the paper pores and a mobile phase, or adsorption chromatography where the paper acts as a solid stationary phase and the liquid mobile phase moves through it.
3) The procedure involves selecting a paper type, preparing the sample, spotting it on the paper, developing the chromatogram by immersing the paper in a mobile phase, drying the paper, and detecting spots.Fluorimetry.pptx
Fluorimetry.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
i. Fluorescence and phosphorescence are the two types of luminescence. Fluorescence emission stops when the incident light is removed, while phosphorescence emission continues even after the light is removed.
ii. A fluorimeter uses a mercury vapor lamp, filters, and a photocell to measure fluorescence. It passes light through a primary filter to select the excitation wavelength, through the sample, and then through a secondary filter to transmit the fluorescent emission to the photocell.
iii. Fluorimetry can be used to determine substances like uranium, boron, calcium, vitamins, and aromatic pollutants through measurement of their fluorescent properties. It allows both qualitative and quantitative analysis of various samples.Gas chromatography.pptx
Gas chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Gas chromatography is a technique used to separate, identify, and quantify components of a mixture. It works by selectively partitioning the components between a stationary and mobile phase inside a column. Components are then sequentially eluted from the column. First, a sample is injected into an inert gas stream and carried into a separation column. The various components interact differently with the column's stationary phase and are separated as they move through. A detector then measures the quantity of components exiting the column, allowing identification and quantification. Gas chromatography offers high separation efficiency, small sample needs, good selectivity for similar compounds, and a wide range of applications, though it is limited to analyzing volatile substances.Nepheloturbidometry.pptx
Nepheloturbidometry.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document discusses nepheloturbidometry, which uses light scattering measurements to determine the concentration of suspended particles in liquids. It can be used for both low concentrations (nephelometry) and high concentrations (turbidometry) by measuring either scattered light or transmitted light. A nepheloturbidimeter has detectors to measure both scattered light at 90 degrees and transmitted light at 180 degrees, allowing it to analyze suspensions of unknown concentration. Factors like particle properties, light source, sample cells, and detectors can affect light scattering measurements. Nepheloturbidimetry has various applications like analyzing water clarity, determining carbon dioxide, and quantifying ions at low levels.Gel Exclusion chromatography.pptx
Gel Exclusion chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Gel exclusion chromatography, also known as size exclusion chromatography, separates analytes based on their size or hydrodynamic volume. Smaller analytes have a longer retention time as they are able to penetrate the pores in the stationary phase beads, while larger analytes pass through more quickly. The principle allows for separation of a number of molecular weights within each column. Detectors are used to monitor the concentration of analytes as they elute from the column. Though useful for determining relative molecular weights, gel permeation chromatography has limitations including poor resolution of peaks for polymer samples where molecular weights are closely spaced.Congenital Vertical Talus: Clinical Presentation, Imaging, Etiology, and Mult...
Congenital Vertical Talus: Clinical Presentation, Imaging, Etiology, and Mult...Dr. Prabhat Pandey
╠²
Congenital Vertical Talus (CVT)ŌĆöalso known as Congenital Convex Pes Valgus or Teratologic Dorsolateral Dislocation of the Talocalcaneonavicular JointŌĆöis a rare but significant pediatric foot deformity, characterized by a fixed dorsal dislocation of the talonavicular joint and rigid hindfoot equinus. This unique anatomical disruption gives rise to the hallmark "rocker-bottom" deformity, often evident at birth.
In this comprehensive presentation by Dr. Prabhat Pandey, DNB Orthopedics Resident at Tata Main Hospital, we explore every crucial aspect of Congenital Vertical TalusŌĆöfrom its pathoanatomy and etiology to detailed clinical assessment and advanced management strategies. This ║▌║▌▀ŻShare is tailored for orthopedic surgeons, pediatricians, medical students, and physiotherapists engaged in pediatric musculoskeletal care.
Congenital Vertical Talus is rare, rigid, and complex
Must distinguish from positional deformities like calcaneovalgus foot
Accurate radiographic analysis is essential for diagnosis
Reverse Ponseti casting can reduce need for extensive surgery
Surgical release is often definitive but must be timed and tailored
Multidisciplinary management is crucial in syndromic casesComplete ICU Equipment List | Machine Used in ICU | Presentation by Hospitals...
Complete ICU Equipment List | Machine Used in ICU | Presentation by Hospitals...sureshkumar75935
╠²
This presentation from hospitalstore.com provides an overview of essential ICU equipment used in critical care settings. It covers key devices such as ventilators, patient monitors, infusion pumps, defibrillators, suction machines, ICU beds, and oxygen delivery systems and many more . These machines are vital for monitoring, treating, and supporting critically ill patients in intensive care units. Understanding their function helps in ensuring optimal patient care and safety.More Related Content
More from NIDHI GUPTA (20)
Chemical reactions_alcohols.pptx
Chemical reactions_alcohols.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. They can undergo oxidation reactions where the alcohol is converted to an aldehyde or ketone with the loss of hydrogen atoms. Substitution reactions on alcohols involve replacing the hydroxyl hydrogen with another group like a halide to form alkyl halides.Methods of preparation_aldehyde and ketones.pptx
Methods of preparation_aldehyde and ketones.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbon-oxygen double bond. They are prepared through oxidation reactions of primary alcohols to form aldehydes and secondary alcohols to form ketones. The author thanks the reader for their time.Chemical reactions_aldehyde and ketones.pptx
Chemical reactions_aldehyde and ketones.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
The document discusses carbonyl compound reactions, specifically the benzoin condensation and Perkin condensation. The benzoin condensation involves the dimerization of two aromatic aldehydes using a cyanide ion catalyst to form an aromatic acyloin compound like benzoin. The reaction mechanism involves nucleophilic addition of the cyanide ion to one aldehyde, followed by rearrangement and addition to the second aldehyde producing benzoin after proton transfer and cyanide elimination. The Perkin condensation is also discussed but no details are provided.Str and Uses_aldehyde and ketones.pptx
Str and Uses_aldehyde and ketones.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
The document summarizes the structures and uses of various carbonyl compounds including aldehydes and ketones. It describes 8 compounds - benzaldehyde, vanillin, cinnamaldehyde, formaldehyde, paraldehyde, acetone, chloral hydrate, and hexamine. For each compound, it provides the chemical structure and lists their main uses which range from use as flavoring agents and precursors to other chemicals to applications in cosmetics, plastics, paints, and medicine.Hybridisation and Method of preparation of alkenes.ppt
Hybridisation and Method of preparation of alkenes.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond functional group. Ethylene (C2H4) is an example alkene. The carbon atoms in alkenes adopt sp2 hybridization, resulting in a flat structure with 120 degree bond angles between atoms. An alkene's double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond between the carbon atoms, restricting rotation about the double bond.Method of Preparation of Amines.ppt
Method of Preparation of Amines.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document discusses the preparation and properties of amines. It describes four types of amines based on the number of carbons bonded to the nitrogen atom. Amines can be prepared through ammonolysis reactions, where an amine or ammonia displaces a halide on a primary or methyl halide. This produces primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary amines depending on the starting material. Amines have relatively high melting and boiling points due to hydrogen bonding between molecules. They are basic and can turn litmus blue, with solubility in water depending on the carbon chain length.Chemical Reactions of Amines.ppt
Chemical Reactions of Amines.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Primary amines react with alkyl halides to form secondary amines. Primary and secondary amines react with acyl halides and anhydrides to form amides through nucleophilic attack of the amine on the carbonyl group. Benzenesulphonyl chloride reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides. Primary amines react with nitrous acid to form alcohols, while secondary amines form oily nitrosoamines through the Libermann reaction. Tertiary amines form salts with nitrous acid. Amphetamine is a phenylethylamine used to treat ADHD, narcolepsy, and obesity.Str and Uses of alkyl halides.pptx
Str and Uses of alkyl halides.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document summarizes information about various alkyl halides. It discusses the chemical structures, properties and uses of ethyl chloride, chloroform, tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, tetrachloromethane, dichloromethane and iodoform. Many of these compounds are or were used as solvents, refrigerants, degreasers, paint strippers, dry cleaning fluids and disinfectants due to their volatility and ability to dissolve organic materials.Structure and Uses of different carboxylic acids.pptx
Structure and Uses of different carboxylic acids.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document discusses the structures and uses of various carboxylic acids, including acetic acid, lactic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, succinic acid, oxalic acid, salicylic acid, benzoic acid, benzyl benzoate, dimethyl phthalate, methyl salicylate, and acetyl salicylic acid. It outlines key industrial, medical, and household applications for each acid such as use in food/beverage production, pharmaceuticals, cleaning products, and agriculture.Chemical Reactions of Alkenes.pptx
Chemical Reactions of Alkenes.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alkenes undergo general chemical reactions and their stability depends on the number of substituents. More substituted alkenes are more stable than less substituted ones due to a phenomenon called hyperconjugation. They also have a lower heat of hydrogenation. The stability of alkenes increases with more substituents.Chemical reactions of alkanes.pptx
Chemical reactions of alkanes.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
The document summarizes the chemical reaction of chlorination of alkanes. It describes the reaction as a chain reaction, where (1) chlorine radicals are produced from chlorine molecules through homolytic fission initiated by heat or light. (2) The chlorine radicals react with methane to form methyl radicals and HCl molecules. (3) The methyl radicals react with chlorine molecules to form methyl chloride and new chlorine radicals. This sequence propagates the chain reaction until (4)-(6) termination steps form stable products and end the reaction.Hybridisatoion and Method of Preparation of alkanes.ppt
Hybridisatoion and Method of Preparation of alkanes.pptNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Alkanes are the simplest organic compounds made of only carbon and hydrogen. They form single covalent bonds and have no functional groups. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 where n is the number of carbon atoms. Methane (CH4) is the first member and ethane (C2H6) is the second. Alkanes have sp3 hybridization giving them a tetrahedral molecular geometry. One method to prepare alkanes is through hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes which involves passing a mixture of the unsaturated hydrocarbon and hydrogen over nickel at high temperatures.IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Part-2.pptx
IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Part-2.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
1. Here are the steps to name the molecule:
1) Identify the functional group (carbonyl group) which gives the compound the name of a ketone.
2) Name the parent chain (hexane) which contains the carbonyl group.
3) Number the parent chain starting from the end that gives the carbonyl carbon the lowest number.
4) Include the position of the carbonyl group as a prefix.
The IUPAC name is therefore: 3-hexanone
2. (a) 3-ethyloctane
(b) 1,4-dibromohexane
(c) 2,3,4-trimethylheptane
(d)Classification, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds.pptx
Classification, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document provides information on the classification, nomenclature, and isomerism of organic compounds. It discusses how organic compounds are classified based on their structure as acyclic, cyclic, aromatic, etc. It also describes the IUPAC system for systematically naming organic compounds based on functional groups and molecular structure. Key points covered include naming conventions for alkanes, alkenes, alkyl halides, and other compound classes.TLC.pptx
TLC.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Thin layer chromatography is a technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures on a sheet coated with an adsorbent material like silica gel or aluminum oxide. The mixture components separate vertically as they travel different distances up the sheet at different rates depending on how strongly they interact with the stationary and mobile phases. Each component appears as a distinct spot, and its retention factor (Rf) indicates how far it traveled relative to the solvent front. Factors like the solvent system, amount of material, adsorbent, and temperature affect the separation. TLC is a simple, fast, and inexpensive chromatography method used to analyze pharmaceuticals, foods, and other chemical mixtures.Paper Chromatography.pptx
Paper Chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
1) Paper chromatography is a technique that uses paper as the stationary phase to separate dissolved chemical substances based on their different migration rates across the paper.
2) The principle involves either partition chromatography where substances partition between the water in the paper pores and a mobile phase, or adsorption chromatography where the paper acts as a solid stationary phase and the liquid mobile phase moves through it.
3) The procedure involves selecting a paper type, preparing the sample, spotting it on the paper, developing the chromatogram by immersing the paper in a mobile phase, drying the paper, and detecting spots.Fluorimetry.pptx
Fluorimetry.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
i. Fluorescence and phosphorescence are the two types of luminescence. Fluorescence emission stops when the incident light is removed, while phosphorescence emission continues even after the light is removed.
ii. A fluorimeter uses a mercury vapor lamp, filters, and a photocell to measure fluorescence. It passes light through a primary filter to select the excitation wavelength, through the sample, and then through a secondary filter to transmit the fluorescent emission to the photocell.
iii. Fluorimetry can be used to determine substances like uranium, boron, calcium, vitamins, and aromatic pollutants through measurement of their fluorescent properties. It allows both qualitative and quantitative analysis of various samples.Gas chromatography.pptx
Gas chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Gas chromatography is a technique used to separate, identify, and quantify components of a mixture. It works by selectively partitioning the components between a stationary and mobile phase inside a column. Components are then sequentially eluted from the column. First, a sample is injected into an inert gas stream and carried into a separation column. The various components interact differently with the column's stationary phase and are separated as they move through. A detector then measures the quantity of components exiting the column, allowing identification and quantification. Gas chromatography offers high separation efficiency, small sample needs, good selectivity for similar compounds, and a wide range of applications, though it is limited to analyzing volatile substances.Nepheloturbidometry.pptx
Nepheloturbidometry.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
This document discusses nepheloturbidometry, which uses light scattering measurements to determine the concentration of suspended particles in liquids. It can be used for both low concentrations (nephelometry) and high concentrations (turbidometry) by measuring either scattered light or transmitted light. A nepheloturbidimeter has detectors to measure both scattered light at 90 degrees and transmitted light at 180 degrees, allowing it to analyze suspensions of unknown concentration. Factors like particle properties, light source, sample cells, and detectors can affect light scattering measurements. Nepheloturbidimetry has various applications like analyzing water clarity, determining carbon dioxide, and quantifying ions at low levels.Gel Exclusion chromatography.pptx
Gel Exclusion chromatography.pptxNIDHI GUPTA
╠²
Gel exclusion chromatography, also known as size exclusion chromatography, separates analytes based on their size or hydrodynamic volume. Smaller analytes have a longer retention time as they are able to penetrate the pores in the stationary phase beads, while larger analytes pass through more quickly. The principle allows for separation of a number of molecular weights within each column. Detectors are used to monitor the concentration of analytes as they elute from the column. Though useful for determining relative molecular weights, gel permeation chromatography has limitations including poor resolution of peaks for polymer samples where molecular weights are closely spaced.Recently uploaded (20)
Congenital Vertical Talus: Clinical Presentation, Imaging, Etiology, and Mult...
Congenital Vertical Talus: Clinical Presentation, Imaging, Etiology, and Mult...Dr. Prabhat Pandey
╠²
Congenital Vertical Talus (CVT)ŌĆöalso known as Congenital Convex Pes Valgus or Teratologic Dorsolateral Dislocation of the Talocalcaneonavicular JointŌĆöis a rare but significant pediatric foot deformity, characterized by a fixed dorsal dislocation of the talonavicular joint and rigid hindfoot equinus. This unique anatomical disruption gives rise to the hallmark "rocker-bottom" deformity, often evident at birth.
In this comprehensive presentation by Dr. Prabhat Pandey, DNB Orthopedics Resident at Tata Main Hospital, we explore every crucial aspect of Congenital Vertical TalusŌĆöfrom its pathoanatomy and etiology to detailed clinical assessment and advanced management strategies. This ║▌║▌▀ŻShare is tailored for orthopedic surgeons, pediatricians, medical students, and physiotherapists engaged in pediatric musculoskeletal care.
Congenital Vertical Talus is rare, rigid, and complex
Must distinguish from positional deformities like calcaneovalgus foot
Accurate radiographic analysis is essential for diagnosis
Reverse Ponseti casting can reduce need for extensive surgery
Surgical release is often definitive but must be timed and tailored
Multidisciplinary management is crucial in syndromic casesComplete ICU Equipment List | Machine Used in ICU | Presentation by Hospitals...
Complete ICU Equipment List | Machine Used in ICU | Presentation by Hospitals...sureshkumar75935
╠²
This presentation from hospitalstore.com provides an overview of essential ICU equipment used in critical care settings. It covers key devices such as ventilators, patient monitors, infusion pumps, defibrillators, suction machines, ICU beds, and oxygen delivery systems and many more . These machines are vital for monitoring, treating, and supporting critically ill patients in intensive care units. Understanding their function helps in ensuring optimal patient care and safety.National Health Planning Committees of India
National Health Planning Committees of IndiaAll India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna
╠²
Here we discussed about the various National Health Planning Committees of India who shaped our healthcare system as we know it today.Disability Support Services Melbourne - Comfort Support Care
Disability Support Services Melbourne - Comfort Support CareNDISProviderMelbourn
╠²
Comfort Support Care offers personalised Disability Support Services in Melbourne, helping individuals live more independently and with dignity. From daily personal care to community participation, our friendly support workers are here to assist. We focus on your goals, well-being, and NDIS plan needs, ensuring consistent and compassionate care every day.
VoyageHealing- ketamine and wellness clinic.pdf
VoyageHealing- ketamine and wellness clinic.pdfVoyage Healing
╠²
A Compassionate Ketamine and Wellness Clinic.
At Voyage, we are reimagining mental health treatment offering talk therapy, medication management, and novel tools like ketamine therapy and Spravato.
Burns types and its management .pptx
Burns types and its management .pptxRishika Rawat
╠²
Damage to the skin or deeper tissues caused by sun, hot liquids, fire, electricity or chemicals.
Most burns happen accidentally. The degree of severity of most burns is based on the size and depth of the burn. Electrical burns, however, are more difficult to diagnose because they're capable of causing significant injury beneath the skin without showing any signs of damage on the surface.Medivic Ambulance Operates Carefully to Reduce the Hurdle on Patients in Patn...
Medivic Ambulance Operates Carefully to Reduce the Hurdle on Patients in Patn...Medivic Aviation Air and Train AMbulance Services in Guwahati
╠²
Medivic Train Ambulance Service in Patna and Ranchi understands the nervousness of families and strives to reduce this through professional management and constant monitoring. We're prepared for every medical emergency and provide dedicated, convenient assistance at all times.
Web@: https://tinyurl.com/2jh9wpdu
More@: https://tinyurl.com/n9dt3vn7
Shamis Tate Shares 5 Essential Brain Health Tips.pdf
Shamis Tate Shares 5 Essential Brain Health Tips.pdfShamis Tate
╠²
Neurologist Shamis Tate shares 5 simple and effective brain health tips. Learn how good sleep, healthy food, staying active, using your mind, and connecting with others can help keep your brain strong, sharp, and healthy. Easy steps that anyone can follow to feel better and think clearer every day.What is Medical Billing, and How does it Work.pdf
What is Medical Billing, and How does it Work.pdfDevinclark22
╠²
Medical billing is the process of verifying insurance, coding procedures accurately, submitting claims, and following up on delayed payments
Cognitive Code: Integrating AI into Mental Health Practice
Cognitive Code: Integrating AI into Mental Health Practicealishbae86
╠²
Artificial Intelligence and Mental Health is a pioneering exploration of how AI technologies can transform the mental health landscape. Written by Alishba, a verified young researcher and medical student, this book blends clinical insight, psychological understanding, and cutting-edge tech innovation to envision a future where machines donŌĆÖt replace humansŌĆöbut enhance healing.
Through a thoughtful combination of case studies, research-backed analysis, and conceptual models, the book examines:
The integration of AI in early mental health screening and diagnosis
Ethical considerations and data privacy in AI-based therapy
Chatbots and virtual reality in managing anxiety, depression, and trauma.
The future of AI in destigmatizing mental illness globally
This work stands as one of the first books authored by a 21-year-old Pakistani female medical student to deeply analyze the intersections of AI and mental health in a narrative format. It's written not only for clinicians and researchers, but also for students, innovators, and policy-makers aiming to bring equity, empathy, and technology together.Trending-Now_-Ayurvedic-Bone-Regeneration-Therapies-for-AVN-_2025_.ppt
Trending-Now_-Ayurvedic-Bone-Regeneration-Therapies-for-AVN-_2025_.pptkhephioisols
╠²
Discover how Ayurvedic therapies in 2025 offer non-invasive, holistic solutions for avascular necrosis (AVN), promoting bone regeneration and improved mobilityWeight loss podcast motivation for 2025.
Weight loss podcast motivation for 2025.lalaaligujjar
╠²
Weight loss tips.weight loss.weight loss for beginners Radiological diagnosis of Gastric carcinoma
Radiological diagnosis of Gastric carcinomaabid hossain
╠²
radiological presentation of stages of gastric cancer , different modalities to identify and doagnose them Reliable Ambulance Services Saving Lives Across Cities.pdf
Reliable Ambulance Services Saving Lives Across Cities.pdfAmbulance services in delhi
╠²
Experience fast and dependable ambulance services in Prayagraj, designed to provide critical medical support during emergencies. Our well-equipped ambulances and skilled paramedics ensure safe and comfortable patient transport, available round-the-clock to assist you whenever needed. Trust us for professional and compassionate care every step of the way.Dr. James Farley Focuses on Better Health Outcomes for Every Patient
Dr. James Farley Focuses on Better Health Outcomes for Every PatientDrJamesFarley
╠²
Discover how Dr. James Farley delivers better health outcomes through his Neuro-BioMedicine Health System. With over 25,000 treatments performed, Dr. Farley specializes in chronic conditions, addiction recovery, and brain health using a science-based, patient-first approachCongenital Vertical Talus: Clinical Presentation, Imaging, Etiology, and Mult...
Congenital Vertical Talus: Clinical Presentation, Imaging, Etiology, and Mult...Dr. Prabhat Pandey
╠²
Medivic Ambulance Operates Carefully to Reduce the Hurdle on Patients in Patn...
Medivic Ambulance Operates Carefully to Reduce the Hurdle on Patients in Patn...Medivic Aviation Air and Train AMbulance Services in Guwahati
╠²
Ad
Antifungal drugs ppt.pptx
- 15. Uses of Miconazole ŌĆó Miconazole is an antifungal synthetic derivative of imidazole and used in the treatment of candidal skin infections, Miconazole selectively affects the integrity of fungal cell membranes, high in ergosterol content and different in composition from mammalian cells membranes.