ANTI-LEPROTIC DRUGS.pptx
- 1. GRACE COLLEGE OF PHARMACY,PALAKKAD APPROVED BY PCI,GOVERNMENT OF KERALA AFFLIATED TO KERALA UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES ANTI-LEPROTIC DRUGS Prepared by: Mr. GOKUL J SIDDHARTH RESEARCH SCHOLAR gokulsiddu@gmail.com
- 2. ANTI-LEPROTIC DRUGS âĒLeprosy caused by Mycobacterium leprae. âĒConsidered as an incurable disease âĒChaulmoogra oil is used as anti-leprotic
- 3. Antileprotic Drugs: Sulfones âĒ Dapsone(DDS) Phenazine derivatives âĒ Clofazimine Anti-tubercular drugs âĒ Rifampin âĒ Ethionamide Other antibiotic âĒ Ofoloxacin âĒ Moxifloxacin âĒ Minocycline âĒ Clarithromycin
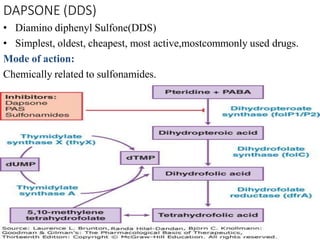
- 4. DAPSONE (DDS) âĒ Diamino diphenyl Sulfone(DDS) âĒ Simplest, oldest, cheapest, most active,mostcommonly used drugs. Mode of action: Chemically related to sulfonamides.
- 5. ADME âĒ Oral absorption. âĒ Widely distributed in the body. âĒ CSF penetration is poor. âĒ 70% plasma protein binding, more concentrated in skin, muscle, liver, kidney. âĒ Metabolized by glucoronide conjugation and sulfates conjugation. âĒ Excreted in bile and reabsorbed from intestine. âĒ Final exretion by urine Adverse effects âĒ Mild heamolytic anemia âĒ Dose related toxicity âĒ Patient with G-6-PD deficiency are more susceptible âĒ Gastric intolerance-nausea, anorexia âĒ Methaemoglobinaemia, headache, paresthesia, mental symptoms and drug fever.
- 6. âĒ Allergic rashes, phototoxicity,rarely exfoliative dermatitis âĒ Hepatitis agranulocytosis are rare. âĒ Leprae reaction,sulfone syndrome Contraindications: âĒ Dapsone should not be used in patients with severe anemia with (HbË7g/dl) and G-6-PD deficiency Uses: âĒ Leprosy âĒ Dapsone + pyrimethamine combination used for chloroquine-resistant malaria. CLOFAZIMINE: âĒ It is a dye with leprostatic and anti-inflammatory properties. Mode of action: âĒ Interfere template function of DNA in M.leprae
- 7. Resistance: âĒ Resistance produced in 1-3yrs when it is used alone ADME âĒ Orally active/absorbed âĒ Accumulates in many tissues âĒ Entry into CSF is poor âĒ tÂ― -70days Adverse effects: Skin: Reddish black discoloration, discoloration hair other body secretion, itching, phototoxicity, dry skin, conjunctival pigmentation and cosmetic problems GI: Enteritis,losesstool,nausea, abdominal pain, anorexia,weight loss Contraindications: Clofazimine contraindication with liver and kidney damage patients
- 8. Anti-TB Drugs âĒ Rifampin and Ethionamide (Refer anti TB chapter) OtherAntibiotic OFLOXACIN: âĒ Active against M.leprae Mode of action âĒ Ofloxacin inhibit topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase No DNAReplication Inhibit cell division âĒ Component of Multi-drug Therapy (MDT)
- 9. Adverse effects: âĒ Abdominal pain cramp, Dry mouth, Fatigue,GI intolerance, Visual Disturbance MINOCYCLINE âĒ Tetracycline derivatives active against M.leprae âĒ Dose:100mg/day âĒ Used as alternative MDT regimen Mode of action: Minocycline bind and inhibit protein synthesis by binding to 30S ribosomal subunit Interfere the binding and attachment of aminoacyl tRNA ribosomal complex Bacteriostatic effect
- 10. Adverse effects: âĒ Numbness âĒ Hair loss âĒ Dizziness âĒ Muscle/joint pain âĒ Rashes, itching âĒ Loss of appetite CLARITHROMYCIN âĒ Macrolide antibiotic having significant activity against M.leprae. âĒ Less bactericidal than Rifampin. âĒ Used as alternative MDT regimens.
- 11. Mode of action: Clarithromycin binding with 50S ribosomal subunit &Inhibit bacterial protein synthesis Interfere protein translocation Interfere protein synthesis Bactericidal effects Adverse effect : âĒ GI disturbance âĒ Nausea,vomoting âĒ Diarrhea âĒ Rashes, abdominal pain âĒ Elevated blood urea nitrogen
- 12. âĒ Chemotherapy of leprosy: âĒ The WHO recommends the use of MDT for all leprosy cases. âĒ Leprosy has been classified into two types multibacillary and paucibacillary leprosy. âĒ The objective and need for MDT are: 1. To make the patient non contagious as early as possible by killing the dividing bacilli. 2. To prevent the development of drugs resistant bacilli. 3.To prevent relapse by destroying the document bacilli (persisters) 4.To shorten the duration of effective therapy. TREATMENT SCHEDULES OFTHERAPY All drugs are administrated orally . 1.For multibacillary leprosy(LL,BL and BB) âĒ Rifampacin600mg.once monthly âĒ Clofazimine 300mg,once monthly âĒ Dapsone 100mg,daily âĒ Clofazimine 500mg Supervised Unsupervised (self-administrated)
- 13. âĒ Duration of treatment is 2yrs,and later the patient should be followed up for period of 5yrs. âĒ If clofazimine is unacceptable, the alternative drugs used is ethionamide 250mg daily. 2. For paucibacillary leprosy (TT,BT,AND I) âĒ Rifampicin 600mg once monthly: supervised. âĒ Dapsone 100mg daily: unsupervised Duration of treatment is 6 months, later the patient should be followed up for a period of minimum 2years. 3.Alternative regimens âĒ Clofazimine 50mg+ any two newer drugs(ofloxacin,minocycline,clarithromycin,etc..) daily for 6 months followed by clofazimine 50mg + any one newer drugs daily for another 18months. âĒ For single-lesion paucibacillary leprosy :(ROM regimens).
- 14. Rifampicin 600mg Ofloxacin 400mg Minocycline 100mg LEPRAREACTIONS âĒ âĒ These are immunologically mediated reaction that occur during the course of the disease. âĒ The exact cause of such reaction Is not clear and is usually precipitated by infection trauma, mental stress,etc. âĒ There are two types of reaction: 1. Type 1 lepra reaction(reversed reaction): It is a delayed type of hypersensitivity and is seen in borderline categories of leprosy. âĒ Characterized by neuropathy with painful tender nerves lesions. âĒ There are also cutaneous ulceration; when they occur after the initiation of therapy, they are known as reversal reaction. âĒ Type 1 lepra reaction is treated with oral prednisolone. As a single dose
- 15. 2. Type 2 lepra reaction (erythema modosum leprosum): âĒ It is a type 2 hypersensitivity reaction and is commonly seen in lepromatous leprosy. âĒ It is more severe than type 1 lepra reaction. âĒ It is characterized by tender,inflammed subcutaneous nodule with fever,lymphadenopathy,arthritis, indocyclitis,nerve pain,orhitis etc. âĒ The type 2 reaction maybe be due to release of antigen from the dying lepra bacilli. âĒ Severe from type 2 reaction is treated with thalidomide, but pregnancy is the absolute contraindication.. âĒ The other drugs used are aspirin,clofazimine, chloroquine and prednisolone.
- 16. REFERANCE KD Tripathi Essential of Medical Pharmacology 7th Edition Page no:765-779 ÂĐ2013,KD Tripathi