Antipsychotics
- 1. Name:- Bhadani Smit Ramjibhai Roll No.:- 17BPH095 Program:- B.Pharm Sem.:- IV Subject:- Pharmacology
- 2. 1. Definition :- Psychosis:- 2. Dopamine Hypothesis:- 3. Classification of Antipsychotics:- 4. Pharmacological Profile of Each Category:- 5. Clinical Usage:-
- 3. âĒ A Symptom Of Mental illnesses. âĒ Characterised by Distorted or Non-Existent sense of Reality:- - Hallucination. - Delusions. - Disorganised Speech. - Disorganised or Agitated Behaviour.
- 4. ïĻ Mood Disorder (Major Depression or Mania With Psychotic Features). ïĻ Substance Induced Psychosis. ïĻ Dementia with Psychotic features. ïĻ Delirium with Psychotic features. ïĻ Schizophrenia.
- 5. ïĻ Put Forward by Arvid Carlsson. ïĻ âThe Clinical features Of Schizophrenia (Sometimes extended to psychosis in General) is related to over activity of dopaminergic function within the brain.â
- 6. ï Typical/First Generation Antipsychotics:- I. Phenothiazine Ex. :- Chlorpromazine II. Butyraphenones Ex. :- Haloperidol III. Thioxanthenes Ex. :-Flupentixol ï Atypical/Second Generation Antipsychotics:- Ex. :- Clozapine , Risperidone , Olanzapine , Quetiapine , Aripiprazole.
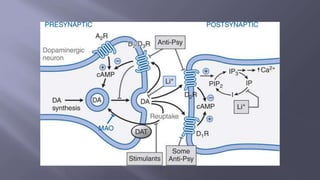
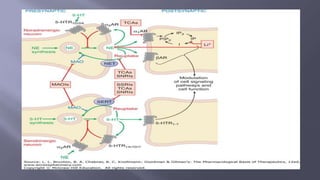
- 7. ïĻ Mode Of Action :- - Predominantly Act as antagonists at brain dopamine D2 receptors. - Also Blocks Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors Antihistamine receptors Îą adrenoceptors
- 9. ïĻ High rapid oral absorption. ïĻ Highly lipophilic with high apparent volumes of distribution. ïĻ Undergo extensive phase 1 metabolism by CYPs and subsequent phase 2 conjugations. ïĻ Excreted in the urine and to some extent in the bile.
- 10. ïĻ Extrapyramidal Motor Effects:- ïĻ Due to dopamine D2 receptor blockade in the nigrostriatal pathway (except tardive dyskinesia). A. Acute dystonia B. Akathisia C. Parkinsonism D. Tardive Dyskinesia
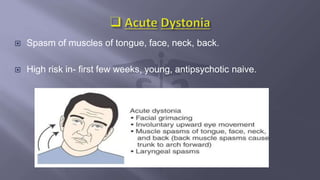
- 11. ïĻ Spasm of muscles of tongue, face, neck, back. ïĻ High risk in- first few weeks, young, antipsychotic naive.
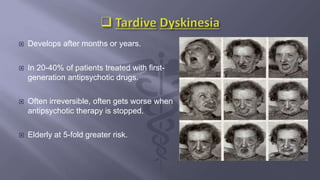
- 12. ïĻ Develops after months or years. ïĻ In 20-40% of patients treated with first- generation antipsychotic drugs. ïĻ Often irreversible, often gets worse when antipsychotic therapy is stopped. ïĻ Elderly at 5-fold greater risk.
- 13. ïĻ Endocrine effects:- Due to blockage of dopamine D2 receptors in tuberohypophyseal pathway ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ ïŪ Increased prolactin.:- ïĄ Gynaecomastia. ïĄ Agalactorrhea. ïĄ amenorrhea in women. ïĄ sexual dysfunction or infertility in men.
- 14. ïĻ Central antagonism of H1 receptors:- a) Sedation. b) Weight gain via appetite stimulation. ïĻ Muscarinic antagonism -anticholinergic effects. ïĻ ïĄ1 Adrenergic antagonism - orthostatic hypotension.
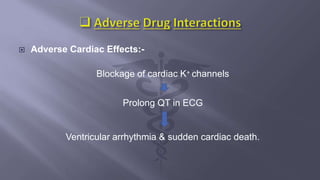
- 15. ïĻ Adverse Cardiac Effects:- Blockage of cardiac K+ channels Prolong QT in ECG Ventricular arrhythmia & sudden cardiac death.
- 16. ïĻ Increased risk for cerebrovascular events and all- cause mortality in dementia patients. ïĻ Lowers seizure threshold. ïĻ Increased triglycerides. ïĻ Hyperglycaemia.
- 17. ïĻ A fatal idiosyncratic ADR of antipsychotics. ïĻ Characterized by, 1. Mental status changes. 2. Muscle rigidity. 3. Hyperthermia. 4. Autonomic dysfunction.
- 18. A. Typical/First Generation Antipsychotics:- A. Phenothiazine e.g. chlorpromazine. B. Butyraphenones e.g. haloperidol. C. Thioxanthenes e.g. flupentixol. B. Atypical/Second Generation Antipsychotics:- e.g. Clozapine, Risperidone, Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Aripiprazole.
- 19. ïĻ Mode of Action:- Predominant antagonism of 5-HT2A receptors with a lesser degree antagonism of dopamine D2 receptors. ïĻ Has efficacy against negative symptoms esp. Clozapine.
- 21. ïĻ Extrapyramidal Motor Effects:- ïĄ Considerably less compared to typical antipsychotics. ïĄ Blockage of 5-HT2A receptors increase dopamine in striatum preventing extrapyramidal effects. ïĻ Cardiotoxicity:- ïĄ Less associated with QT prolongation at therapeutic doses.
- 22. ïĻ High risk of new onset diabetes and diabetes ketoacidosis esp. with clozapine and olanzapine. ïĻ Agranulocytosis common with clozapine esp. in first 6 months ï regular FBC monitoring essential.
- 26. ïĻ Various disorders treated with antipsychotics in the elderly â psychosis, bipolar affective disorder, delirium & dementia. ïĻ Use extreme caution because of side effect profile. ïĻ âStart low & go slowâ (Malone et al 2007) & titrate over longer periods of time to reach the required dose. ïĻ Avoid polypharmacy wherever possible.
- 27. ïĻ Avoid antipsychotics if possible. ïĻ Use the lowest effective dose. ïĻ Neonatal adverse effects observed include generalized hypertonicity and dystonic reactions.
- 28. ïĻ The safety of atypical agents is yet to be established but preliminary reports there to be no deleterious effects to the fetus. ïĻ Isolated cases of congenital abnormalities with the use of Clozapine. ïĻ No increased risk has emerged with the use of Olanzapine. ïĻ The conventional agents are generally preferred. ïĻ Supervised dose reduction and cessation 7-10 days prior to delivery should be considered.
- 29. ïĻ Remember that antidepressant medication is only part of the treatment for antenatal depression and anxiety. Also consider:- ïĻ Psychological therapies. ïĻ Exclude organic illness as a cause of mental health symptoms. ïĻ Address any alcohol and/or illicit substance abuse. ïĻ Assess the social situation. ïĻ General lifestyle measures: adequate rest/sleep, balanced diet, exercise. ïĻ The decision to treat should be made on an individual case basis.
- 30. ïĻ Conventional and atypical antipsychotics are used as the foundation for pharmacological management of schizophrenia and related psychosis. ïĻ All have equal efficacy, exception Clozapine. ïĻ Atypical generally better tolerated & have less EPSE. ïĻ Atypical first line treatment. ïĻ Start lowest effective possible dose & titrate upwards. ïĻ Ongoing monitoring & management of adverse effects. ïĻ Caution numerous drug interaction & potential for neuroleptic malignant syndrome.