Aquaponics
- 1. Aquaponics PRABHAKAR NIKUMBE
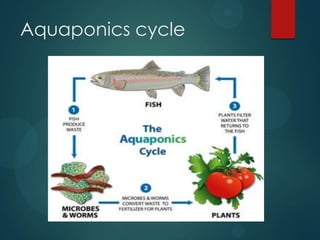
- 2. What is Aquaponics? Aquaponics is the farming of fish and plants in a single recirculating system. The waste from the fish becomes the nutrients for the plants, and the plants in turn remove these nutrients from the water, purifying it for the fish. In this way, the fish waste is used to grow a plant crop that becomes a second income stream for little extra cost. In fact, it works so well that the plants become the primary crop by volume and value.
- 4. Types of Aquaponics: There are three main types of Aquaponics: 1. Gravel Bed Culture (GBC) 2. Deep Water Culture (DWC) 3. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
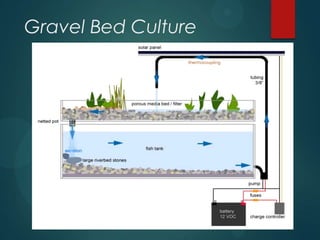
- 5. Gravel Bed Culture (GBC) ïĩ In this the plants are rooted in coarse gravel or aggregate media. ïĩ Bacteria grow on the media and convert the ammonia excreted by the fish to nitrate. ïĩ Plants within the grow beds remove the nitrate from the water, which then returns to the fish in a clean and healthy form. ïĩ No mechanical or biological filtration is required as the gravel beds suit both purposes. ïĩ This method is most variable in terms of the range of crops that can be grown and there is no waste water discharge.
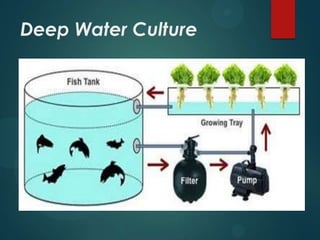
- 7. Deep Water Culture (DWC) ïĩ The water from the fish is filtered mechanically and biologically to remove the solids from suspension and convert the toxic ammonia to benign nitrate. ïĩ This clean water then travels down the length of a tank of water in which polystyrene rafts are floated. ïĩ Plants are rooted through the holes in the polystyrene sheets and into the water below, where the roots take up nutrients from the water. ïĩ DWC is most suited to leafy crops and there is some discharge of water during the filtration process.
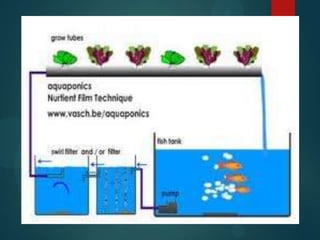
- 10. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) ïĩ As with DWC the water is filtered prior to going to the plants, but in this case the plants are rooted through holes in pipes. ïĩ The tip of the root touches the bottom surface of the pipe and absorbs nutrients from a thin film of water trickling down the length of the pipe. ïĩ NFT is very susceptible to heat uptake or loss as the air temperature changes, and the plants can be lost quickly through drying out during a power failure. ïĩ This method also results in the loss of water and nutrients during filter cleaning, and is also best suited to leafy crops.
- 12. Why Aquaponics ? Aquaponics is not only a most enjoyable way of producing high quality, wholesome crops as a business or for own use, but it also has several distinct advantages over both aquaculture and hydroponics.
- 13. Advantages of Aquaponics food production ïĩ Fish waste is utilised as plant feed rather than being wasted ïĩ Excellent crop quality - both in terms of taste and appearance ïĩ provides a truly organic form of nutrients for the plants ïĩ produces an organic product (no fertilizer or herbicides used) ïĩ no soil-borne disease as there is no soil ïĩ no water is wasted or consumed by weeds ïĩ Low electrical usage - commercial system (300m2) runs on <1kW of power !!!
- 14. ïĩ Systems do not require mechanical or biological filters - the processes all occur naturally, saving money and resulting in a natural, stable environment ïĩ Low labour requirement ïĩ relatively small spaces required as plant spacing can be intensive ïĩ plants grow and develop relatively quickly ïĩ Faster cash flow generation than aquaculture ïĩ Constant production throughout the year - markets love this ïĩ Ability to produce `out-of-season' crops
- 15. ïĩ Crop harvesting is quick and easy, regardless of the weather outside ïĩ Crops can be grown all year-round. In most climates a greenhouse is required ïĩ Higher yields than conventional farming ïĩ Faster growth to market size due to optimal conditions being maintained ïĩ Root temperature very stable resulting in fewer disease issues than hydroponics ïĩ No crop rotation needed & No weeds to pull out
- 16. Cultivable plants in Aquaponics ïĩ Bendi - Okra ïĩ Paku - Athyrium Esculentum ïĩ Cherry Tomato ïĩ Pudina - Mint ïĩ Daun Pandan - Pandanus ïĩ Sambung Nyawa - Gynura Amaryllifolius Procumbens ïĩ Kangkong - Water Spinach ïĩ Serai - Lemon Grass ïĩ Keladi - I Yam not Taro ïĩ Stevia Rebaudiana ïĩ Kesum - Knotweed Leaf ïĩ Ulam Raja - Cosmos Caudatus ïĩ Kunyit - Turmeric ïĩ Mengkudu Hutan - morinda elliptica
- 17. References ïĩ http://www.canna-uk.com/aquaponics ïĩ http://affnan-aquaponics.blogspot.in/ ïĩ http://www.aquaponic.be/en/aquaponics/permanent-watersysteem-nft/ ïĩ http://www.aquaponics.co.za/what-is-aquaponics ïĩ http://oneoftheengineers.blogspot.in/2012/11/what-is-aquaponic- gardening.html ïĩ http://truedemocracyparty.net/2012/02/aquaponics-1-million-pounds-of- food-on-3-acres-1-pump10000-fish-the-future-of-food/ ïĩ http://homeaquaponicsguide.blogspot.in/2012/04/aquaponics-systems- types.html
- 18. THANK YOU