Arabic Morphology Using Only Finite State Operations -Review
- 1. Arabic Morphology Using Only Finite-State OperationsSupervisor: Dr. A. R. WeerasingheSivaneasharajahLushanthan2006/CS/154
- 2. ?
- 3. ?
- 4. Author ŌĆō Kenneth R Beesley
- 5. Introducing MorphologyMorphology ŌĆśStructure of wordsŌĆÖ and ŌĆśhow words are formedŌĆÖMorphemeThe smallest linguistic unit within a word that can carry a meaning, such as "un-", "break", and "-able" in the word "unbreakableŌĆ£Morphotactics The ordering restrictions in place on the ordering of morphemesOrthographic/Variation Rule Models the changes that occur in a word usually when two morphemes combine (Spelling Rules)
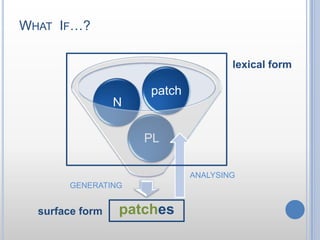
- 6. What IfŌĆ”?lexical formANALYSINGGENERATINGsurface form
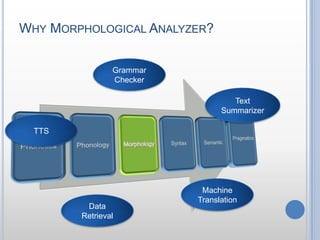
- 7. Why Morphological Analyzer?Grammar CheckerText Summarizer TTSMachine TranslationData Retrieval
- 8. To Do A Morphological ParsingLexiconList of Morphemes (stem+ affixes)POS information of morphemesMorphotacticsOrthographic Rules
- 9. A Finite State Transducer ŌĆō Cola MachineALPHABET - {F},{T}WORDS - {FFF}, {FT}, {TF} LANGUAGE - {FFF, FT, TF} FFF051015TT
- 10. FS Languages & Natural LanguagesA Network that accepts One-Word LanguageA two level transducerbaelttbael+Noun+ Pltbael╬Ąs
- 11. Writing Regular Expressions - Lexicon[ {kick} | {try} | {bore} ][%+Verb:0][ %+Bare:0 | %+Pres3PSg :s | %+Past: {ed} ];a:a = a{kick} = [ k:k i:i c:c k:k ] = [ k i c k ]word+Verb+ Caseword╬Ąsuffix
- 12. Possible wordsSolution?[ {kick} | {try} | {bore} ][%+Verb:0][ %+Bare:0 | %+Pres3PSg :s | %+Past: {ed} ];Another layer!
- 13. Writing Regular Expressions - Rules╬▒ -> ╬▓ || ╬│ _ ╬┤ is read as ŌĆ£╬▒ is rewritten as ╬▓ between ╬│ and ╬┤ŌĆØ [y -> i e || Cons _ s .#.,, y -> i || Cons _ e d .#. ] .o.e -> 0 || Cons _ e d .#. ;
- 14. In The Paper,Discontiguous dependencies between morphemes in a word ŌĆō FilteringNon-concatinativemorphotacticsReduplicationSemitic interdigitationVariation rules
- 15. Filtering Out Over-GenerationArt+word+Noun+Indef+Case?* %+ Art %+ ?* %+ Indef ?*$ [ %+ Art %+ ?* %+ Indef ]Prep+word+Noun+Def/Indef+Nom/Acc$ [%+ Prep %+ ?* [%+Acc | %+Nom]] $ [ %+ Art %+ ?* %+ Indef ] $ [%+ Prep %+ ?* [%+Acc | %+Nom]] ~[|]
- 16. Non- ConcatenativeMorphotacticsSemitic stem interdigitation Root ŌĆō ktb, drs Template - CVCVC Vocalization ŌĆō ui, a*K t bCV C V Cu iK u t i b^[{ktb}.m>.{CVCVC}.<m.[u*i]^]Root tierTemplate tierVocalization tierStem tier
- 17. The Current System4930 words72,000,000 abstract fully-voweled wordsSixty six finite state variation rulesNew-words added easily into the lexical database
- 19. Discussion
- 20. Thought For The DayNever say No for Education!









![Writing Regular Expressions - Lexicon[ {kick} | {try} | {bore} ][%+Verb:0][ %+Bare:0 | %+Pres3PSg :s | %+Past: {ed} ];a:a = a{kick} = [ k:k i:i c:c k:k ] = [ k i c k ]word+Verb+ Caseword╬Ąsuffix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/27lushanthandr-ruvanarabicmorphologyusingonlyfinite-stateoperations-100429081537-phpapp02/85/Arabic-Morphology-Using-Only-Finite-State-Operations-Review-11-320.jpg)
![Possible wordsSolution?[ {kick} | {try} | {bore} ][%+Verb:0][ %+Bare:0 | %+Pres3PSg :s | %+Past: {ed} ];Another layer!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/27lushanthandr-ruvanarabicmorphologyusingonlyfinite-stateoperations-100429081537-phpapp02/85/Arabic-Morphology-Using-Only-Finite-State-Operations-Review-12-320.jpg)
![Writing Regular Expressions - Rules╬▒ -> ╬▓ || ╬│ _ ╬┤ is read as ŌĆ£╬▒ is rewritten as ╬▓ between ╬│ and ╬┤ŌĆØ [y -> i e || Cons _ s .#.,, y -> i || Cons _ e d .#. ] .o.e -> 0 || Cons _ e d .#. ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/27lushanthandr-ruvanarabicmorphologyusingonlyfinite-stateoperations-100429081537-phpapp02/85/Arabic-Morphology-Using-Only-Finite-State-Operations-Review-13-320.jpg)

![Filtering Out Over-GenerationArt+word+Noun+Indef+Case?* %+ Art %+ ?* %+ Indef ?*$ [ %+ Art %+ ?* %+ Indef ]Prep+word+Noun+Def/Indef+Nom/Acc$ [%+ Prep %+ ?* [%+Acc | %+Nom]] $ [ %+ Art %+ ?* %+ Indef ] $ [%+ Prep %+ ?* [%+Acc | %+Nom]] ~[|]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/27lushanthandr-ruvanarabicmorphologyusingonlyfinite-stateoperations-100429081537-phpapp02/85/Arabic-Morphology-Using-Only-Finite-State-Operations-Review-15-320.jpg)
![Non- ConcatenativeMorphotacticsSemitic stem interdigitation Root ŌĆō ktb, drs Template - CVCVC Vocalization ŌĆō ui, a*K t bCV C V Cu iK u t i b^[{ktb}.m>.{CVCVC}.<m.[u*i]^]Root tierTemplate tierVocalization tierStem tier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/27lushanthandr-ruvanarabicmorphologyusingonlyfinite-stateoperations-100429081537-phpapp02/85/Arabic-Morphology-Using-Only-Finite-State-Operations-Review-16-320.jpg)



