Arabic mwe presentation 07
- 1. Automatic Extraction of Arabic Multiword Expressions *Mohammed Attia, Antonio Toral, Lamia Tounsi, Pavel Pecina and Josef van Genabith School of Computing, Dublin City University, Ireland
- 2. Outline ˇń Introduction ˇń Data Resources ˇń Methodology ˇń Crosslingual Correspondence Asymmetries ˇń Translation-Based Approach ˇń Corpus-Based Approach ˇń Discussion of experiments and results ˇń Conclusion
- 3. Introduction ˇń Criteria of MWEs ˇń Ubiquity ˇń Diversity ˇń Low polysemy ˇń Statistically significant co-occurrence ˇń Focus ˇń Arabic ˇń Nominal MWEs ˇń Purpose is building an MWE lexicon for Arabic
- 4. Data Resources ? Multilingual, bilingual and monolingual settings ? Availability of rich resources that have not been exploited in similar tasks before. ˇń Arabic Wikipedia (March 2010) ˇń 117,491 titles, of them 89,623 multiword titles ˇń Arabic is ranked 27th according to size (article count) and 17th according to usage ˇń Information helpful for linguistic processing
- 5. Data Resources ˇń Princeton WordNet 3.0 ˇń An electronic lexical database for English ˇń Arabic WordNet contains only 11,269 synsets (including 2,348 MWEs)
- 6. Data Resources ˇń Arabic Gigaword ˇń Unannotated corpus distributed by the Linguistic Data Consortium (LDC). ˇń Articles from news agencies and newspapers from different Arab regions, such as Al-Ahram in Egypt, An Nahar in Lebanon and Assabah in Tunisia. ˇń Largest publicly available corpus of Arabic to date. ˇń Contains 848 million words.
- 7. Methodology 3 different techniques for 3 different data sources Motivation for using different techniques ˇń The extraction of MWEs is a problem more complex than can be dealt with by one simple solution. ˇń The choice of technique depends on the nature of the task and the type of the resources used.
- 8. Pipeline
- 9. Technique 1: Crosslingual Asymmetries ˇń Data: Titles of Wikipedia Articles in Arabic and corresponding titles in 21 languages. ˇń Definition: We rely on many-to-one correspondence relations ˇń The non-compositionality of MWEs makes it unlikely to have a mirrored representation in the other languages. ˇń Compositionalily varies: ˇń highly compositional, "?" ,"????? ???????military base", ˇń with a degree of idiomaticity, such as, "?" ,"????? ???????amusement park", lit. "city of amusements". ˇń extremely opaque , "?" ,"??? ??????grasshopper", lit. "the horse of the Prophet".
- 10. Technique 1: Crosslingual Asymmetries ˇń Steps (1) Candidate Selection. All Arabic Wikipedia multiword titles are taken as candidates. (2) Filtering. We exclude titles of disambiguation and administrative pages. (3) Validation. We check if there is a single-word translation in any of 21 selected languages.
- 11. Technique 1: Crosslingual Asymmetries ˇń Evaluation: ˇń 1100 multiword titles are randomly selected from Arabic Wikipedia and manually tagged as: MWEs, non-MWEs, or NEs. ˇń Baseline: all multi-word titles are considered as MWEs ˇń Results
- 12. Example
- 13. Language Ranking How likely will each language give many-to-one correspondence?
- 14. Technique 2: Translation-Based ˇń Data: Princeton WordNet ˇń Assumption: MWEs in one language are likely to be translated as MWE in another language. ˇń Ontological advantage ˇń Steps ˇń Extracting the list of nominal MWEs from PWN 3.0. ˇń Translating the list into Arabic using Google Translate. ˇń Validating the results using pure frequency counts from three search engines: Al-Jazeera, BBC Arabic and AWK.
- 15. Technique 2: Translation-Based ˇń Evaluation (automatic) ˇń Gold Standard: PWN-MWEs found in English Wikipedia and have correspondence in Arabic: 6322 expressions. ˇń We test the Google translation without any filtering, and consider this as the baseline. ˇń Then we filter the output based on the number of combined hits from the search engines. ˇń Results
- 16. Technique 2: Translation-Based ˇń Evaluation (Manual) ˇń On 200 MWE candidates ˇń Precision ¨C Baseline (before validation): 45.5% ¨C After validation: 83%
- 17. Technique 2: Translation-Based ˇń Notes on Google Translate ˇń Word Order ¨C shark repellent => ?????? ????? ¨C accordion door => ?????????? ?????? ˇń Transferring source word to target ¨C acroclinium roseum => acroclinium roseum ¨C actitis hypoleucos => actitis hypoleucos
- 18. Technique 3: Corpus-Based ˇń Data: Arabic Gigaword corpus ˇń Association Measures used: ˇń Pointwise Mutual Information (PMI) ˇń PearsonˇŻs chi-square ˇń Steps (1) Compute the frequency of all the unigrams, bigrams, and trigrams (2) Computing the association measures for all bigrams and trigrams (threshold to 50) (3) Ranking bigrams and trigrams (4) Conducting lemmatization of Arabic words using MADA. (5) Filtering the list using the MADA POS-tagger. The patterns included for bigrams are: NN NA, and for trigrams: NNN NNA NAA
- 19. Technique 3: Corpus-Based ˇń Why is lemmatization important? ˇń Al>mm AlmtHdp (the-nations united) ˇ°the United Nationsˇ± Al>mm@>um~ap_1@N@1#AlmtHdp@mut~aHid_1@AJ@2# ˇń ll>mm AlmtHdp (to-the-nations united) ˇ°to the United Nationsˇ± ll>mm@>um~ap_1@N@3#AlmtHdp@mut~aHid_1@AJ@3# ˇń wAl>mm AlmtHdp (and-the-nations united) ˇ°and the United Nationsˇ± wAl>mm@>um~ap_1@c-N@3#AlmtHdp@mut~aHid_1@AJ@3# ˇń bAl>mm AlmtHdp (by-the-nations united) ˇ°by the United Nationsˇ± bAl>mm@>um~ap_1@N@3#AlmtHdp@mut~aHid_1@AJ@3#
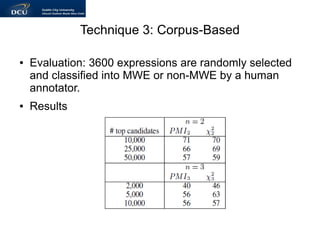
- 20. Technique 3: Corpus-Based ˇń Evaluation: 3600 expressions are randomly selected and classified into MWE or non-MWE by a human annotator. ˇń Results
- 21. Discussion results ˇń Combination of yields
- 22. Discussion of results ˇń Similarities and dissimilarities of output The set of collocations detected by the association measures may differ from the those which capture the interest of lexicographers and Wikipedians ˇń ?????? ?????? ˇ°Menachem Mazuzˇ± ˇń ??????? ?????? ˇ°fresh fruitsˇ± ˇń ??????? ??????? ˇ°Ladies and gentlemenˇ±
- 23. Conclusion ˇń Applicability to other languages ˇń the heterogeneity of the data sources helps to enrich the MWE lexicon. ˇń A lexical resource of: ˇń 33,000 MWEs ˇń 39,000 NEs
- 24. Thank you!