ARDS PPT EXPLANATION.pptx explanation in
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes43 views
Acute respiratory syndrome
1 of 22
Download to read offline





















Recommended
ARDS ppt



ARDS pptSanjay Peerapur
╠²
The document discusses acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a life-threatening lung condition that prevents sufficient oxygen from entering the blood. ARDS can result from direct or indirect lung injury and causes fluid buildup in the lungs, reduced lung compliance, and impaired gas exchange. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, low blood oxygen levels, and abnormal breath sounds. Treatment focuses on supportive care in the ICU, including mechanical ventilation, supplemental oxygen, medications, and positioning strategies to improve ventilation.ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME#MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING



ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME#MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSINGGAUTAMI TIRPUDE
╠²
The document presents information about a seminar on Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). The seminar aims to provide in-depth knowledge of ARDS including defining it, describing the pathophysiology and management. ARDS is a life-threatening condition that prevents enough oxygen from entering the blood. It occurs when the lungs become severely inflamed and fluid builds up in the tiny air sacs of the lungs. The seminar will discuss etiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, complications, and the nurse's role in management.Acute respiratory distress syndrome



Acute respiratory distress syndromeDr.Ashutosh Kumar Singh
╠²
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a sudden and progressive form of acute respiratory failure in which the alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and more permeable to intravascular fluid resulting in severe dyspnoea, hypoxemia and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates.
COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease )



COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease )Gargee karadkar
╠²
The document discusses chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD as a disease characterized by persistent airflow limitation that is usually caused by exposure to noxious particles or gases. The main causes of COPD are cigarette smoking and exposure to environmental pollutants. Symptoms include cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath. A diagnosis is made based on patient history and spirometry testing showing airflow limitation. Treatment focuses on bronchodilators, corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, and managing exacerbations. The goal of treatment is to improve lung function and quality of life.Pathology of Respiratory System Disorders



Pathology of Respiratory System DisordersShashidhar Venkatesh Murthy
╠²
The document discusses various respiratory pathologies including pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung cancer, and tuberculosis. It describes the signs, symptoms, etiology, pathogenesis and complications of these conditions. Smoking is identified as a major risk factor for developing COPD and lung cancer, with details provided on how cigarette smoke leads to inflammation and tissue destruction in the lungs over time.oxygenation.pptx



oxygenation.pptxziaullah884561
╠²
This document discusses oxygenation and its relationship to respiratory and cardiovascular function. It covers topics like the physiology of oxygenation, factors that affect oxygenation like age, environment, lifestyle, and health status. Common manifestations of altered respiratory and cardiovascular function are described, like dyspnea, tachypnea, and hypoxia. Life span changes and problems related to respiration and circulation at different ages are outlined. The document also discusses respiratory and cardiac emergencies, and the nursing process for assessment and care planning for patients with respiratory or cardiovascular issues.oxygenation.pptx



oxygenation.pptxMuhammadAbbasWali
╠²
This document discusses oxygenation and its relationship to respiratory and cardiovascular function. It covers topics like the physiology of oxygenation, factors that affect oxygenation like age, environment, lifestyle, and health status. Common manifestations of altered respiratory and cardiovascular function are described, like dyspnea, tachypnea, and hypoxia. Life span changes and problems related to respiration and circulation at different ages are outlined. The document also discusses respiratory and cardiac emergencies, and the nursing process for assessment and care planning for patients with respiratory or cardiovascular issues.Chronic Obstructive pulmonary diasese



Chronic Obstructive pulmonary diaseseMahesh Chand
╠²
The document discusses chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD as a progressive lung disease characterized by airflow obstruction caused by chronic bronchitis or emphysema. The document provides statistics on the prevalence and mortality of COPD worldwide and in India. It identifies the major risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluations, management including medications, oxygen therapy, surgery, and rehabilitation. It also discusses nursing care for patients with COPD.Pul edema



Pul edemaThomaskutty Saji
╠²
This document provides an overview of pulmonary edema through defining it, discussing anatomy and physiology, epidemiology, classification, pathogenesis, staging, causes, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, medical management, nursing diagnosis, interventions, complications, and expected outcomes. It summarizes the key points of pulmonary edema for medical professionals.COPD



COPDShubhrimaKhan
╠²
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis and emphysema that are characterized by persistent airflow limitation. The main causes of COPD are tobacco smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, and air pollution. Symptoms include cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath. Diagnosis involves assessing symptoms, lung function tests, and chest imaging. Treatment focuses on smoking cessation, medications to relieve symptoms and prevent exacerbations, pulmonary rehabilitation, and managing complications.Dyspnea.pptx



Dyspnea.pptxghadeereideh
╠²
Dyspnea or shortness of breath, is a subjective feeling of breathing discomfort.
Don't forget that dyspnea is a symptom not disease.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)



Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)Rattan Professional Education College, Sector 78, Mohali
╠²
This document discusses acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). It begins with an introduction and definition of ARDS. ARDS is an acute respiratory failure where the alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and more permeable, resulting in hypoxemia. The document then covers the etiology and risk factors of ARDS, which can be direct lung injury from things like pneumonia or indirect injury from sepsis. The pathophysiology of ARDS is explained through a schematic. Clinical manifestations like dyspnea and hypoxemia are outlined. Diagnostic evaluations and potential complications of ARDS are also reviewed. The document concludes with discussions of the medical management of ARDS including mechanical ventilation support, settings, modes of ventilation and use of PEECopd



CopdKHyati CHaudhari
╠²
This document provides an overview of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It defines COPD as a chronic lung disease causing obstructed airflow, usually caused by smoking. Common symptoms include chronic cough, dyspnea, wheezing, and excess sputum production. Diagnosis involves lung function tests, chest imaging, and blood gas analysis. Treatment focuses on bronchodilators, corticosteroids, oxygen therapy, smoking cessation, and surgery for severe cases. Nursing care addresses impaired gas exchange, ineffective breathing, anxiety, activity intolerance, sleep disturbances, and risk of infection.Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome



Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeNIKHIL DWIVEDI
╠²
This document provides an overview of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). It begins with an introduction defining ARDS as a life-threatening lung condition preventing enough oxygen from entering the blood. The document then covers the etiology, epidemiology, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, complications, risk factors, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and management of ARDS. It provides details on the causes, incidence rates, processes in the body, tests used for diagnosis, potential issues that can arise, and treatment approaches including medications, positioning techniques, and potential surgeries.COPD 



COPD Dipomala Asangbam
╠²
This document provides information on the care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD and lists its components. It describes the causes and risk factors, clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, diagnostic evaluation, medical management including pharmacotherapy, surgical options, pulmonary rehabilitation, and nursing management of COPD patients. The medical management focuses on assessing and monitoring the disease, reducing risk factors, managing stable COPD, and managing exacerbations according to WHO guidelines.lecture 3 CCNg Respiratory Part One 2023-2024.ppt



lecture 3 CCNg Respiratory Part One 2023-2024.pptArabAlkhadam
╠²
respiratory tract anatomy and function ARDS , RESPIRATORY FAILURE_085830.pptx



ARDS , RESPIRATORY FAILURE_085830.pptxShubhrimaKhan
╠²
1) Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening lung condition caused by direct or indirect injury to the lungs whereby the alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and permeable, resulting in pulmonary edema.
2) ARDS is characterized by hypoxemia, reduced lung compliance, and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates seen on chest imaging.
3) Treatment involves supportive care in an intensive care unit including mechanical ventilation, supplemental oxygen, and positioning therapies like prone positioning to improve oxygenation.Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 1.pptx



Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 1.pptxWakib Amin Mazumder
╠²
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include dyspnea, cough, and sputum production. COPD is caused by exposure to inhaled irritants, most often cigarette smoke, leading to chronic inflammation and structural changes in the lungs.
The predominant form of COPD is chronic bronchitis, which involves chronic cough and sputum production for at least 3 months per year for 2 consecutive years. This is associated with inflammation and eventual thickening of the bronchial tubes. Emphysema is another form of COPD characterized by permanent enlargement of airspaces and destruction of lung parenchyma.
The airflow limitation in COPD is due to a combination of parenchymal destruction (emphysema) and small airways disease (chronic bronchitis). The obstruction is generally progressive and irreversible. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, exposure history, and spirometry showing irreversible airflow limitation.
COPD treatment aims to reduce symptoms, improve exercise tolerance, prevent exacerbations, and slow disease progression. Smoking cessation is essential. Medications used include bronchodilators and inhaled steroids. Supplemental oxygen may be required in advanced disease. Exacerbations are treated with antibiotics, oral steroids, and other supportive therapies. Patients often have decreased quality of life and COPD is a leading cause of mortality worldwide.Chronic obstructive airways diseases



Chronic obstructive airways diseasesshivangimistry3
╠²
This document provides an overview of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by limited airflow. The two main types are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, wheezing and frequent respiratory infections. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exam, lung function tests and chest imaging. Treatment focuses on medications, oxygen therapy and managing symptoms. Quitting smoking can prevent further progression of COPD.COPD Presentation



COPD PresentationTarekRahman16
╠²
This presentation provides an overview of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It begins with an introduction and defines COPD as a group of lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and refractory asthma. It describes the pathophysiology of each condition and explains how chronic inflammation in the lungs leads to structural changes over time. Risk factors and clinical manifestations of COPD are outlined. The presentation reviews methods for diagnosing COPD including spirometry and pulse oximetry. It discusses treatment options and medications to manage COPD as well as potential complications. The presentation concludes with references used.Oxygenation, respiratory function and cardiovascular system



Oxygenation, respiratory function and cardiovascular systemNeeru Maher
╠²
oxygenation and respiration are the major functions of gaseous
exchange process in this slide share all the important description is presentChronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)- Preeti sharma



Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)- Preeti sharmaEducate with smile
╠²
COPD is a type of obstructive lung disease and related conditions. it is very helpful presentation to you about information of COPD.
It includes all things that is definition, causes, symptoms, pathophysiology, diagnostic evaluation, types, treatment and role of nurses for COPD patient.Case presentation of COPD ( Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease )



Case presentation of COPD ( Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease )Dr.Hashim Syed Ali (Dr.Foster)
╠²
This document contains information about a case study of a 65-year-old male patient presenting with fever, cough, abdominal pain, chest pain, body pain and weight loss. He was diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on his symptoms and investigation results. He was treated according to the standard COPD treatment protocol with antibiotics, bronchodilators, mucolytics and lifestyle modifications. The pharmacist found the prescription to be rational and counselled the patient about his disease, medications and lifestyle changes.Oxygen insufficeincy and sensory deprivation



Oxygen insufficeincy and sensory deprivationParbh Jot
╠²
The document discusses oxygen insufficiency and sensory deprivation. It defines oxygen insufficiency as a condition where the body or a region is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Causes include decreased hemoglobin, altitude, tissue oxygen extraction issues, and impaired ventilation. Symptoms include cyanosis, altered breathing, and fatigue. Nursing assessments focus on respiratory status and signs of hypoxia. Oxygen therapy is the primary treatment. Sensory deprivation occurs when a person experiences decreased meaningful stimuli and can affect physical, cognitive, and emotional functioning. At-risk groups include those with sensory impairments or in long-term care. Preventing deprivation involves promoting healthy sensory stimulation.Ckd chief (2)



Ckd chief (2)Rajiv Lal
╠²
This document discusses chronic kidney disease and its management. It defines chronic kidney disease as kidney damage and decreased kidney function for over 3 months. It then discusses the pathophysiology of chronic renal failure, noting the loss of nephrons and failure of kidney roles in fluid balance, waste excretion, and hormone regulation. Common causes of chronic kidney disease are listed, and the progression from initial insult to end stage renal disease is described. Diagnosis involves history, exam, and blood and urine tests to assess kidney function and check for underlying etiologies. Treatment focuses on slowing progression, managing complications, and preparing for renal replacement therapies like dialysis and transplantation.More Related Content
Similar to ARDS PPT EXPLANATION.pptx explanation in (20)
Chronic Obstructive pulmonary diasese



Chronic Obstructive pulmonary diaseseMahesh Chand
╠²
The document discusses chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD as a progressive lung disease characterized by airflow obstruction caused by chronic bronchitis or emphysema. The document provides statistics on the prevalence and mortality of COPD worldwide and in India. It identifies the major risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluations, management including medications, oxygen therapy, surgery, and rehabilitation. It also discusses nursing care for patients with COPD.Pul edema



Pul edemaThomaskutty Saji
╠²
This document provides an overview of pulmonary edema through defining it, discussing anatomy and physiology, epidemiology, classification, pathogenesis, staging, causes, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, medical management, nursing diagnosis, interventions, complications, and expected outcomes. It summarizes the key points of pulmonary edema for medical professionals.COPD



COPDShubhrimaKhan
╠²
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to a group of lung diseases including chronic bronchitis and emphysema that are characterized by persistent airflow limitation. The main causes of COPD are tobacco smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, and air pollution. Symptoms include cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath. Diagnosis involves assessing symptoms, lung function tests, and chest imaging. Treatment focuses on smoking cessation, medications to relieve symptoms and prevent exacerbations, pulmonary rehabilitation, and managing complications.Dyspnea.pptx



Dyspnea.pptxghadeereideh
╠²
Dyspnea or shortness of breath, is a subjective feeling of breathing discomfort.
Don't forget that dyspnea is a symptom not disease.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)



Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)Rattan Professional Education College, Sector 78, Mohali
╠²
This document discusses acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). It begins with an introduction and definition of ARDS. ARDS is an acute respiratory failure where the alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and more permeable, resulting in hypoxemia. The document then covers the etiology and risk factors of ARDS, which can be direct lung injury from things like pneumonia or indirect injury from sepsis. The pathophysiology of ARDS is explained through a schematic. Clinical manifestations like dyspnea and hypoxemia are outlined. Diagnostic evaluations and potential complications of ARDS are also reviewed. The document concludes with discussions of the medical management of ARDS including mechanical ventilation support, settings, modes of ventilation and use of PEECopd



CopdKHyati CHaudhari
╠²
This document provides an overview of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It defines COPD as a chronic lung disease causing obstructed airflow, usually caused by smoking. Common symptoms include chronic cough, dyspnea, wheezing, and excess sputum production. Diagnosis involves lung function tests, chest imaging, and blood gas analysis. Treatment focuses on bronchodilators, corticosteroids, oxygen therapy, smoking cessation, and surgery for severe cases. Nursing care addresses impaired gas exchange, ineffective breathing, anxiety, activity intolerance, sleep disturbances, and risk of infection.Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome



Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeNIKHIL DWIVEDI
╠²
This document provides an overview of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). It begins with an introduction defining ARDS as a life-threatening lung condition preventing enough oxygen from entering the blood. The document then covers the etiology, epidemiology, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, complications, risk factors, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and management of ARDS. It provides details on the causes, incidence rates, processes in the body, tests used for diagnosis, potential issues that can arise, and treatment approaches including medications, positioning techniques, and potential surgeries.COPD 



COPD Dipomala Asangbam
╠²
This document provides information on the care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD and lists its components. It describes the causes and risk factors, clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, diagnostic evaluation, medical management including pharmacotherapy, surgical options, pulmonary rehabilitation, and nursing management of COPD patients. The medical management focuses on assessing and monitoring the disease, reducing risk factors, managing stable COPD, and managing exacerbations according to WHO guidelines.lecture 3 CCNg Respiratory Part One 2023-2024.ppt



lecture 3 CCNg Respiratory Part One 2023-2024.pptArabAlkhadam
╠²
respiratory tract anatomy and function ARDS , RESPIRATORY FAILURE_085830.pptx



ARDS , RESPIRATORY FAILURE_085830.pptxShubhrimaKhan
╠²
1) Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening lung condition caused by direct or indirect injury to the lungs whereby the alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and permeable, resulting in pulmonary edema.
2) ARDS is characterized by hypoxemia, reduced lung compliance, and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates seen on chest imaging.
3) Treatment involves supportive care in an intensive care unit including mechanical ventilation, supplemental oxygen, and positioning therapies like prone positioning to improve oxygenation.Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 1.pptx



Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 1.pptxWakib Amin Mazumder
╠²
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include dyspnea, cough, and sputum production. COPD is caused by exposure to inhaled irritants, most often cigarette smoke, leading to chronic inflammation and structural changes in the lungs.
The predominant form of COPD is chronic bronchitis, which involves chronic cough and sputum production for at least 3 months per year for 2 consecutive years. This is associated with inflammation and eventual thickening of the bronchial tubes. Emphysema is another form of COPD characterized by permanent enlargement of airspaces and destruction of lung parenchyma.
The airflow limitation in COPD is due to a combination of parenchymal destruction (emphysema) and small airways disease (chronic bronchitis). The obstruction is generally progressive and irreversible. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, exposure history, and spirometry showing irreversible airflow limitation.
COPD treatment aims to reduce symptoms, improve exercise tolerance, prevent exacerbations, and slow disease progression. Smoking cessation is essential. Medications used include bronchodilators and inhaled steroids. Supplemental oxygen may be required in advanced disease. Exacerbations are treated with antibiotics, oral steroids, and other supportive therapies. Patients often have decreased quality of life and COPD is a leading cause of mortality worldwide.Chronic obstructive airways diseases



Chronic obstructive airways diseasesshivangimistry3
╠²
This document provides an overview of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by limited airflow. The two main types are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, wheezing and frequent respiratory infections. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exam, lung function tests and chest imaging. Treatment focuses on medications, oxygen therapy and managing symptoms. Quitting smoking can prevent further progression of COPD.COPD Presentation



COPD PresentationTarekRahman16
╠²
This presentation provides an overview of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It begins with an introduction and defines COPD as a group of lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and refractory asthma. It describes the pathophysiology of each condition and explains how chronic inflammation in the lungs leads to structural changes over time. Risk factors and clinical manifestations of COPD are outlined. The presentation reviews methods for diagnosing COPD including spirometry and pulse oximetry. It discusses treatment options and medications to manage COPD as well as potential complications. The presentation concludes with references used.Oxygenation, respiratory function and cardiovascular system



Oxygenation, respiratory function and cardiovascular systemNeeru Maher
╠²
oxygenation and respiration are the major functions of gaseous
exchange process in this slide share all the important description is presentChronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)- Preeti sharma



Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)- Preeti sharmaEducate with smile
╠²
COPD is a type of obstructive lung disease and related conditions. it is very helpful presentation to you about information of COPD.
It includes all things that is definition, causes, symptoms, pathophysiology, diagnostic evaluation, types, treatment and role of nurses for COPD patient.Case presentation of COPD ( Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease )



Case presentation of COPD ( Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease )Dr.Hashim Syed Ali (Dr.Foster)
╠²
This document contains information about a case study of a 65-year-old male patient presenting with fever, cough, abdominal pain, chest pain, body pain and weight loss. He was diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on his symptoms and investigation results. He was treated according to the standard COPD treatment protocol with antibiotics, bronchodilators, mucolytics and lifestyle modifications. The pharmacist found the prescription to be rational and counselled the patient about his disease, medications and lifestyle changes.Oxygen insufficeincy and sensory deprivation



Oxygen insufficeincy and sensory deprivationParbh Jot
╠²
The document discusses oxygen insufficiency and sensory deprivation. It defines oxygen insufficiency as a condition where the body or a region is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Causes include decreased hemoglobin, altitude, tissue oxygen extraction issues, and impaired ventilation. Symptoms include cyanosis, altered breathing, and fatigue. Nursing assessments focus on respiratory status and signs of hypoxia. Oxygen therapy is the primary treatment. Sensory deprivation occurs when a person experiences decreased meaningful stimuli and can affect physical, cognitive, and emotional functioning. At-risk groups include those with sensory impairments or in long-term care. Preventing deprivation involves promoting healthy sensory stimulation.Ckd chief (2)



Ckd chief (2)Rajiv Lal
╠²
This document discusses chronic kidney disease and its management. It defines chronic kidney disease as kidney damage and decreased kidney function for over 3 months. It then discusses the pathophysiology of chronic renal failure, noting the loss of nephrons and failure of kidney roles in fluid balance, waste excretion, and hormone regulation. Common causes of chronic kidney disease are listed, and the progression from initial insult to end stage renal disease is described. Diagnosis involves history, exam, and blood and urine tests to assess kidney function and check for underlying etiologies. Treatment focuses on slowing progression, managing complications, and preparing for renal replacement therapies like dialysis and transplantation.Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)



Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)Rattan Professional Education College, Sector 78, Mohali
╠²
More from Soum Geo (20)
Recently uploaded (20)
How to create security group category in Odoo 17



How to create security group category in Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
This slide will represent the creation of security group category in odoo 17. Security groups are essential for managing user access and permissions across different modules. Creating a security group category helps to organize related user groups and streamline permission settings within a specific module or functionality.Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
╠²
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
Ō£ģ Soft Tissue Therapy ŌĆō The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
Ō£ģ Sports Taping Techniques ŌĆō Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
Ō£ģ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia ŌĆō A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comAdministrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
╠²
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatMeeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠²
NAPD Annual Symposium
ŌĆ£Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ŌĆØBlind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde
╠²
¤ōó Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
¤ö¼ Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
¤ōī What YouŌĆÖll Learn in This Presentation
Ō£ģ History & Evolution of Antibiotics
Ō£ģ Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
Ō£ģ Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
Ō£ģ Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
Ō£ģ Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
Ō£ģ Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
Ō£ģ Clinical Applications & Challenges.
¤ÜĆ Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
¤æē Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
¤öö Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
╠²
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
╠²
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory App



Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory AppCeline George
╠²
This slide will helps us to efficiently create detailed reports of different records defined in its modules, both analytical and quantitative, with Odoo 17 ERP.RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)



RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)SONU HEETSON
╠²
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper. MMV MCQ PDF Free Download for Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Exam.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
ARDS PPT EXPLANATION.pptx explanation in
- 1. 1 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 2. 2 INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 3. 3 INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORY SYSTEM contdŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 4. 4 INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORY SYSTEM contdŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 5. 5 INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORY SYSTEM contdŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 6. 6 RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) ŌĆó Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening lung condition that prevents enough oxygen from getting into the blood. ŌĆó Acute respiratory distress syndrome was first described in 1967 by Ashbaugh and colleagues. ŌĆó ARDS is also referred with variety of terms like ŌĆó Stiff Lung ŌĆó Shock lung ŌĆó Wet lung ŌĆó Post traumatic lung ŌĆó Adult respiratory distress syndrome ŌĆó Adult hyaline membrane disease ŌĆó Capillary leak syndrome & ŌĆó Congestive atelectasis. Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 7. 7 DEFINITION ŌĆó Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a sudden and progressive form of acute respiratory failure in which the alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and more permeable to intravascular fluid resulting in severe dyspnea, hypoxemia and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates. Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 8. Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Insti tute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli 8 STAGES OF ODEMA FORMATION IN ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
- 9. 9 ETIOLOGY & RISK FACTORS ŌĆó Direct Lung Injury ŌĆō Common causes ŌĆó Aspiration of gastric contents or other substances. ŌĆó Viral/bacterial pneumonia ŌĆō Less Common causes ŌĆó Chest trauma ŌĆó Embolism: fat, air, amniotic fluid ŌĆó Inhalation of toxic substances ŌĆó Near-drowning ŌĆó O2 toxicity ŌĆó Radiation pneumonitis Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 10. 10 ETIOLOGY & RISK FACTORS contdŌĆ”ŌĆ”. ŌĆó Indirect Lung Injury ŌĆō Common causes ŌĆó Sepsis ŌĆó Severe traumatic injury ŌĆō Less common causes ŌĆó Acute pancreatitis ŌĆó Anaphylaxis ŌĆó Prolonged Cardiopulmonary bypass surgery ŌĆó Disseminated intravascular coagulation ŌĆó Multiple blood transfusions ŌĆó Narcotic drug overdose (e.g., heroin) ŌĆó Nonpulmonary systemic diseases ŌĆó Severe head injury ŌĆó Shock ŌĆó Massive blood transfusion. Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
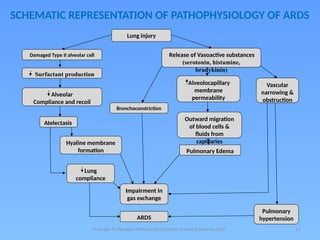
- 11. 11 SCHEMATIC REPRESENTATION OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ARDS Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli Lung injury Release of Vasoactive substances (serotonin, histamine, bradykinin) Damaged Type II alveolar cell Surfactant production Alveolocapillary membrane permeability Vascular narrowing & obstruction Alveolar Compliance and recoil Bronchoconstriction Outward migration of blood cells & fluids from capillaries Atelectasis Pulmonary Edema Hyaline membrane formation Lung compliance Impairment in gas exchange ARDS Pulmonary hypertension
- 12. 12 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS ŌĆó Early signs/symptoms ŌĆō Restlessness ŌĆō Dyspnea ŌĆō Low blood pressure ŌĆō Confusion ŌĆō Extreme tiredness ŌĆō Change in patientŌĆÖs behavior ŌĆó Mood swing ŌĆó Disorientation ŌĆó Change in LOC ŌĆō If pneumonia is causing ARDS then client may have ŌĆó Cough ŌĆó Fever Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 13. 13 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS CONTDŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” Late signs & symptoms ŌĆō Severe difficulty in breathing i.e., labored, rapid breathing. ŌĆō Shortness of breath. ŌĆō Tachycardia ŌĆō Cyanosis (blue skin, lips and nails) ŌĆō Think frothy sputum ŌĆō Metabolic acidosis ŌĆō Abnormal breath sounds, like crackles ŌĆō PaCo2 with respiratory alkalosis. ŌĆō PaO2 Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 14. 14 DIAGNOSITC EVALUATION ŌĆó History of above symptoms ŌĆó On physical examination ŌĆō Auscultation reveals abnormal breath sounds ŌĆó The first tests done are : ŌĆō Arterial blood gas analysis ŌĆō Bood tests ŌĆō Chest x-ray ŌĆō Bronchoscopy ŌĆō Sputum cultures and analysis ŌĆó Other tests are : ŌĆō Chest CT Scan ŌĆō Echocardiogram Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 15. 15 COMPLICATIONS ŌĆó Common complications are; ŌĆō Nosocomial pneumonia: ŌĆō Barotrauma ŌĆō Renal failure ŌĆó Other complications are : ŌĆō O2 toxicity, ŌĆō stress ulcers, ŌĆō Tracheal ulceration, ŌĆō Blood clots leading to deep vein thrombosis & ŌĆō pulmonary embolism. Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 16. 16 MEDICAL MANAGEMENT ŌĆó Persons with ARDS are hospitalized and require treatment in an intensive care unit. ŌĆó No specific therapy for ARDS exists. ŌĆó Supportive measures : ŌĆō Supplemental oxygen ŌĆō Mechanical respirator ŌĆō Positioning strategies ŌĆó Turn the patient from supine to prone. ŌĆó Another position is lateral rotation therapy ŌĆó Fluid therapy Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 17. 17 TURNING PATIENT PRONE ON VOLLMAN PRONE POSITIONER Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 18. 18 PATIENT LYING PRONE ON VOLLMAN PRONE POSITIONER Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 19. 19 LATERAL ROTATION THERAPY BED Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 20. 20 MEDICAL MANAGEMENT contdŌĆ”ŌĆ”. ŌĆó Medications : ŌĆō Antibiotics ŌĆō Anti-inflammatory drugs; such as corticosteroids ŌĆō Diuretics ŌĆō Drugs to raise blood pressure ŌĆō Anti-anxiety ŌĆō Muscle relaxers ŌĆō Inhaled drugs (Bronchodilators) Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 21. 21 NURSING DIAGNOSIS 1. Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung compliance, decreased energy as characterized by dyspnea, abnormal ABGs, cyanoisis & use of accessory muscles. 2. Impaired gas exchange related to diffusion defect as characterized by hypoxia (restlessness, irritability & fear of suffocation), hypercapnia, tachycardia & cyanosis. 3. Risk for decreased Cardiac output related to positive pressure ventilation 4. Ineffective protection related to positive pressure ventilation, decreased pulmonary compliance & increased secretions as characterized by crepitus, altered chest excursion, abnormal ABGs & restlessness. Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli
- 22. NURSING DIAGNOSIS CONTDŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. 5. Impaired physical mobility related to monitoring devices, mechanical ventilation & medications as characterized by imposed restrictions of movement, decreased muscle strength & limited range of motion. 6. Risk for impaired skin integrity related to prolonged bed rest, prolonged intubation & immobility. 7. Knowledge deficit related to health condition, new equipment & hospitalization as characterized by increased frequency of questions posed by patient and significant others. Mr sanjay. M. Peerapur, Principal, KLES Institute of Nursing Sciences, Hubli 22





























