Armamentarium in implantology
- 2. Instruments to Incise Tissue ŌĆó Scalpel and Surgical Blades ŌĆó Most common: #3 Salpel and #15 or #15c Blade ŌĆó #15 blade- short, rounded cutting edge ŌĆó #12 blade- pointed and crescent shaped; mainly used around teeth or in difficult access areas
- 3. Instruments to Reflect Tissue ŌĆó Reflect mucosa and periosteum to expose bone after incision ŌĆó Molt periosteal elevator #9 ŌĆó 2/4 Molt elevator; more effficient instrument positioned in a dished out fashion. ŌĆó Tissue can be reflected three different ways: (1) prying motionŌĆö pointed end used in a prying motion to elevate the soft tissue; (2) push strokeŌĆö used after full thickness incision to slide underneath the flap; (3) pull or scrape strokeŌĆö used to remove tissue tags from the bone in a scraping motion
- 4. Instruments to Grasp Tissue ŌĆó Used to stabilize soft tissue flaps ŌĆó Adson forceps: have small teeth or serrations ŌĆó Used to grasp and stabilize soft tissue flaps during suturing ŌĆó Allison forceps: larger and more aggressive teeth used to hold heavy or high tension tissue; rarely used in implant dentistry
- 5. Instruments to remove Bone /Tissue ŌĆó Rongeur forceps ŌĆó Sharp edged, scoop shaped tip used for snipping away the bone ŌĆó Spring between the handles increases the magnitude of forces ŌĆó Double action rongeur generates more force then Single action rongeur
- 6. Surgical burs: ŌĆó Always used with irrigation ŌĆó Cross cut fissure burs : make pilot holes in bone ŌĆó Special reduction burs for Alveoloplasty ŌĆó Straight hand piece
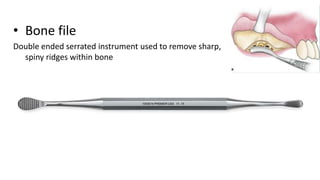
- 7. ŌĆó Bone file Double ended serrated instrument used to remove sharp, spiny ridges within bone
- 8. Instruments to remove tissue from extraction sockets or Bony defects ŌĆó Surgical currette: is spoon shaped and have sharp edges that allow scraping of the bony walls. Eg. Lucas 86 Currette ŌĆó scraping removes soft tissue, will also initiate the regional acceleratory phenomenon (RAP) ŌĆó Regional acceleratory phenomenon is a local response to noxious stimulus by which tissue forms faster than normal regional regeneration process.
- 9. Bone grafting instruments ŌĆó Bone scrapers: used to harvest autogenous bone from the oral cavity and deliver the collected bone particles to the surgical site. ŌĆó These instruments consist of a harvesting blade and collection chamber
- 10. ŌĆó Grafting spoon and condenser:
- 11. Surgical scissors ŌĆó Used to cut tissues or sutures and spread tissue ŌĆó Dean : angled blades that are 3cm from midscrew ŌĆó They have one serreted blade with slight curved handle ŌĆó Easy acess to cut sutures and remove diseased tisssue
- 12. ŌĆó Iris : very small, extremely sharp scissors with fine tip used for precision cutting ŌĆó Metzenbaum: for delicate tissue and blunt dissection
- 13. Hemostats ŌĆó Has serrated tips that allow for clamping of tissue or small materials ŌĆó Used to constrict blood vessels, retrieve loose objects in the oral cavity and securely hold small items
- 14. Instruments to Retract Tissue ŌĆó Used to hold back cheek, tongue or flap which permit visibility to the surgical site. ŌĆó Mouth mirror ŌĆó Weider tongue retractor: broad, heart shaped with grooves and perforations ŌĆó Seldin retractor: double ended with round blunt end; used to retract tissue flap after incision ŌĆó Minnesota retractor
- 15. ŌĆó Misch ŌĆ£SpoonŌĆØ cheek and tongue retractor: ergonomically designed to reduce hand fatigue ŌĆó Sinus graft cheek retractor: broad based flap retractor that reduces force to the infraorbital foramen area.
- 16. Instruments to hold mouth open ŌĆó Bite block ŌĆó Molt mouth prop: ratchet designed instrument that allows variation of opening ŌĆó Orringer retractor: spring loaded mouth prop which maintains upper and lower soft tissue retraction
- 17. Instruments to hold drapes ŌĆó Towel clamp: non perforating clamp used to secure instruments and surgical materials, such as suction tubing to the surgical drapes
- 18. Handpiece and Motors ŌĆó Surgical motor console: console, foot pedal, and motor cord
- 19. Handpiece ŌĆó 1:1 handpiece: usually straight handpiece ŌĆó 40,000 - 50,000 RPM ŌĆó Used for bone grafting procedures ŌĆó 20:1 handpiece: contraangle reduction implant handpiece to drill osteotomies and place implants
- 20. ŌĆó Piezosurgery units: selectively cuts mineralized tissue without damaging soft tissue ŌĆó Uses high frequency vibration 25-35 kHz ŌĆó Advantages: high precision accuracy, minimal thermal damage, increased healing and less soft tissue trauma. ŌĆó Uses: atraumatic extractions, removal of implants, bone grafting procedures and sinus augmentation procedures
- 21. Osteotomes ŌĆó Sinus osteotome: used to raise floor of maxillary sinus ŌĆó Offset osteotomes to increase osteotomy diameter ŌĆó Straight osteotome for bone spreading