Aromatic amines
- 1. âAROMATIC AMINESâ UNIT - II ROLL NO. 105 TO 114 Continuous Assessment No. :- 02 GESâS SIR DR.M.S.GOSAVI COLLEGE OF PHARMACEUTICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH , NASHIK
- 2. PARTICIPANTS SR.NO. ROLL NO. NAME 1. 105 Vedika Shivale 2. 106 Prajwal Sinkar 3. 107 Sourav Suryawanshi 4. 108 Shreya Tapse 5. 109 Prasad Wadghule 6. 110 Chinmay Wagh 7. 111 Harsh Wagh 8. 112 Pragati Wagh 9. 113 Sudarshan Wagh 10. 114 Yash Borse
- 3. ï Aromatic amines represent a category of chemical agents of considerable importance as witnessed by their widespread use as intermediates in the manufacture of drugs, pesticides and plastics, as antioxidants in the preparation of rubber for the manufacture of tires and cables and as curing agents in the preparation of various plastics. ï In addition, they are widely used as intermediates in the preparation of dyes and pigments extensively employed to color textiles, leathers, rubber, printing inks, paints, lacquers, metal finishes, plastic and paper products, as well as in semi-permanent coloring products. AANILINE
- 7. PREPARATIONS OF AROMATIC AMINES 1. 2. 3.
- 8. 1.
- 9. 2.
- 10. 3.
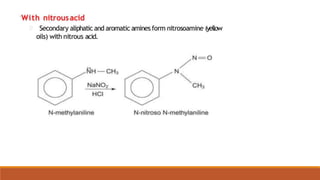
- 11. REACTIONS OF AROMATIC AMINES 1.Reaction With Nitrous Acid [Nitrosation Reaction]
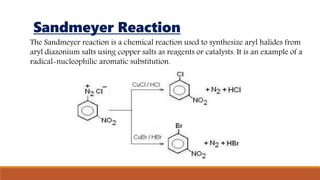
- 15. Sandmeyer Reaction The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts using copper salts as reagents or catalysts. It is an example of a radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
- 16. Coupling reaction The process of conversion of primary aromatic amines into its diazonium salt is called diazotization. Diazonium salts are important synthetic intermediates that can undergo coupling reactions to form azo dyes and electrophilic substitution reactions to introduce functional groups.
- 17. ï Hinsberg Test The Hinsberg test, which can distinguish primary, secondary, and tertiary amines, is based upon sulfonamide formation. In the Hinsberg test, an amine is reacted with benzene sulfonyl chloride.
- 20. ï EFFECT OF SUBSTITUENT ON BASICITY AMINE : Electronic effects : Owing to inductive effects, the basicity of an amine might be expected to increase with the number of alkyl groups on the amine. Correlations are complicated owing to the effects of solvation which are opposite the trends for inductive effects. Solvation effects also dominate the basicity of aromatic amines (anilines). For anilines, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen delocalizes into the ring, resulting in decreased basicity. Substituents on the aromatic ring, and their positions relative to the amino group, also affect basicity .
- 21. Solvation effects : Solvation significantly affects the basicity of amines. N-H groups strongly interact with water, especially in ammonium ions. Consequently, the basicity of ammonia is enhanced by solvation. The intrinsic basicity of amines, i.e. the situation where solvation is unimportant, has been evaluated in the gas phase. In the gas phase, amines exhibit the basicities predicted from the electron-releasing effects of the organic substituents. Thus tertiary amines are more basic than secondary amines, which are more basic than primary amines, and finally ammonia is least basic.
- 22. ï Diazonium compounds are standard reagents used in organic compound synthesis, especially of aryl derivatives. ï Diazonium salts are sensitive to light and break down under Ultraviolet or violet light nearby. This wealth contributed to their use in the copying of papers. For this process a diazonium salt is used to paint paper or film. ï Synthetic uses of Aryl Diazonium Salts ï The use of diazonium salts was to produce water-fast dyed fabrics by immersing the fabric in an aqueous solution of the diazonium compound, followed by immersion in a solution of the coupler









![REACTIONS OF AROMATIC AMINES
1.Reaction With Nitrous Acid [Nitrosation Reaction]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aromaticaminesfinal-1-211022044325/85/Aromatic-amines-11-320.jpg)