Arterial supply to the shoulder and brachial plexus
- 1. university of Holy Karbala College of medicine Axilla, Arterial Supply to the shoulder and Brachial plexus By Mohammed Hasan Abed
- 2. axilla is a pyramid-shaped space between the upper part of the arm and the side of the chest. It forms an important passage for nerves, blood, and lymph vessels as they travel from the root of the neck to the upper limb.
- 3. Apex of the axilla • it is a narrow triangular gap which is bounded by the clavicle anteriorly, scapula posteriorly, and the first rib medially.
- 4. Apex of the axilla • The apex is also called the inlet since it allows the entrance to the axilla of nerves and vessels
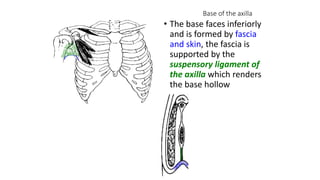
- 5. Base of the axilla • The base faces inferiorly and is formed by fascia and skin, the fascia is supported by the suspensory ligament of the axilla which renders the base hollow
- 6. Anterior wall of the axilla • This is formed by the clavicle, pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, subclavius, and the clavipectoral fascia Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor
- 7. Posterior wall of the axilla scapula subscapularis Latissimus dorsi
- 8. Medial wall of axilla • The medial wall is formed by the upper ribs and intercostal muscles covered by serratus anterior muscle
- 9. Lateral wall of axilla • The lateral wall is narrow and is formed by the floor of the intertubercular groove of the humerus to which is attached the tendon of latissimus dorsi and in which runs the tendon of the long head of biceps
- 10. Arterial Supply to the shoulder
- 11. Axillary artery • Begins at the outer border of the first rib as the continuation of the subclavian artery
- 12. Axillary artery • Ends by becoming the brachial artery at the lower border of teres major
- 13. Axillary artery • For descriptive purposes it is divided into three parts by pectoralis minor muscle
- 15. 1. Brachial artery 2. Subscapular artery 3. Posterior and anterior humeral circumflex artery 4. Axillary artery 5. Dorsal scapular artery 6. Suprascapular artery 7. Thyrocervical trunk 8. Subclavian artery 9. Thoracoacromial artery 10. Acromial branch 11. Deltoid branch 12. Pectoral branch
- 16. Branches of the 1st part of the axillary artery • Superior thoracic artery
- 17. Branches of the 2nd part of the axillary artery • Thoraco-acromial artery • lateral thoracic artery
- 18. Branches of the 3rd part of the axillary artery • Anterior circumflex humeral artery • posterior circumflex humeral artery • subscapular artery
- 19. Subscapular artery • descends along the lateral border of the scapula and ends as the circumflex scapular and thoracodorsal arteries Circumflex scapular Thoraco-dorsal
- 20. Subscapular artery • the circumflex scapular artery passes around the lateral border of the scapula to supply muscles on the dorsal aspect of the scapula. • The thoracodorsal artery is the continuation of the subscapular artery along the lateral border of the scapula
- 23. 1 Pectoralis minor muscle (reflected) 2 Anterior circumflex humeral artery 3 Musculocutaneous nerve (divided) 4 Axillary artery 5 Posterior circumflex humeral artery 6 Profunda brachii artery 7 Median nerve (var.) 8 Brachial artery 9 Biceps brachii muscle 10 Thoraco-acromial artery 11 Suprascapular artery 12 Descending scapular artery 13 Brachial plexus (middle trunk) 14 Transverse cervical artery 15 Anterior scalene muscle and phrenic nerve 16 Right internal carotid artery 17 Right external carotid artery 18 Carotid sinus 19 Superior thyroid artery 20 Right common carotid artery 21 Ascending cervical artery 22 Thyroid gland 23 Inferior thyroid artery 24 Internal thoracic artery 25 Right subclavian artery 26 Brachiocephalic trunk 27 Left brachiocephalic vein (divided) 28 Left vagus nerve 29 Superior vena cava (divided) 30 Ascending aorta 31 Median nerve (divided) 32 Phrenic nerve 33 Right lung (divided) and pulmonary pleura 34 Thoracodorsal artery 35 Subscapular artery 36 Lateral mammary branches (var.) 37 Lateral thoracic artery 38 Thyrocervical trunk 39 Supreme intercostal artery 40 Superior ulnar collateral artery 41 Inferior ulnar collateral artery 42 Middle collateral artery 43 Radial collateral artery 44 Radial recurrent artery 45 Radial artery 46 Anterior and posterior interosseous arteries 47 Princeps pollicis artery 48 Deep palmar arch 49 Common palmar digital arteries 50 Ulnar recurrent artery 51 Recurrent interosseous artery 52 Common interosseous artery 53 Ulnar artery 54 Superficial palmar arch 55 Median nerve and brachial artery 56 Biceps brachii muscle 57 Ulnar nerve 58 Flexor pollicis longus muscle 59 Proper palmar digital arteries 60 Anterior interosseous artery 61 Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle 62 Superficial palmar branch of radial artery
- 24. Brachial plexus
- 25. The nerves entering the upper limb provide the following important functions: 1- sensory innervation to the skin and deep structures, such as the joints; 2- motor innervation to the muscles; 3- influence over the diameters of the blood vessels by the sympathetic vasomotor nerves; 4- and sympathetic secretomotor supply to the sweat glands.
- 27. 1. Roots 2. Trunks 3. Superior trunk 4. Middle trunk 5. Inferior trunk 6. Divisions (posterior and anterior) 7. Cords 8. Lateral cord 9. Lateral pectoral nerve 10. Posterior cord 11. Upper, middle, and lower subscapular nerves 12. Medial cord 13. Medial pectoral nerve 14. Medial brachial cutaneous nerve 15. Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve 16. Terminal branches 17. Musculocutaneous nerve 18. Axillary nerve 19. Radial nerve 20. Median nerve 21. Ulnar nerve
- 29. Muscles or Skin Innervated root Dorsal scapular nerve (C5) Rhomboids and The levator scapulae Long thoracic nerve (C5, 6, and 7) Serratus anterior Upper trunk Nerve to subclavius (C5 and 6) Suprascapular nerve Supraspinatus, lnfraspinatus Lateral cord Lateral pectoral nerve Pectoralis major Musculocutaneous nerve All the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm Lateral root of median nerve Medial cord Medial pectoral nerve Pectoralis major and minor Medial cutaneous nerve of arm and medial cutaneous nerve of forearm Skin of medial arm and medial forearm Ulnar nerve Medial root of median nerve Posterior cord Upper subscapular nerve Subscapularis Middle subscapular (Thoracodorsal) nerve Latissimus dorsi lower subscapular nerve Subscapularis and teres major Axillary nerve (C5-6) Deltoid and teres minor Radial nerve (C5-T1) Posterior compartment muscles of the arm and forearm
- 31. 1 Accessory nerve 2 Dorsal scapular artery 3 Suprascapular nerve 4 Clavicle and pectoralis minor muscle 5 Lateral cord of brachial plexus 6 Musculocutaneous nerve 7 Axillary nerve 8 Median nerve 9 Brachial artery 10 Radial nerve 11 Cervical plexus 12 Common carotid artery 13 Roots of brachial plexus (C5–Th1) 14 Phrenic nerve 15 Transverse cervical artery 16 Subclavian artery 17 Posterior cord of brachial plexus 18 Medial cord of brachial plexus 19 Subscapular artery 20 Long thoracic nerve 21 Ulnar nerve 22 Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm 23 Thoracodorsal nerve 24 Intercostobrachial nerves 25 Medial cutaneous nerves of arm and forearm 26 Anterior scalene muscle 27 Middle scalene muscle 28 Intercostal nerve (Th3) 29 Axillary artery 30 Suprascapular artery
- 32. Thank you