Arterio venous malformation(avm)
- 2. ŌĆó DIRECT CONNECTION BETWEEN ARTERY AND VEIN BYPASSING THE CAPILLARY ŌĆó DECREASED O2 DELIVERY ŌĆó INCREASED O2 IN VENOUS BLOOD
- 3. AVM ŌĆó DEPENDING ON THE FLOW ŌĆó LOW FLOW ŌĆó HIGH FLOW ŌĆō PRIMARY ŌĆō SECONDARY(LOW FLOW PROGRESSES TO HIGH FLOW IN ADULT )
- 4. AVM ŌĆó CONGENITAL ŌĆó ACQUIRED ŌĆó THERE ARE ANGIOGRAPHICALLY OCCULT VASCULAR MALFORMATION ŌĆó OSLER-WEBER RENDU SYNDROME ŌĆō 15-20%
- 5. THIS NIDUS SITE IS PRONE FOR RUPTURE AS THE FLOW INCREASES THE THIN WALLED VEIN CANNOT HANDLE THE BLOOD
- 6. ŌĆó SINCE THERE IN NO DAMPENING OF FLOW IN THE BLOOD, AS THERE IS NO CAPILLARYŌĆ”.
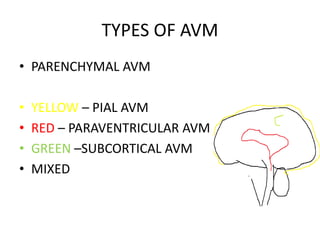
- 7. TYPES OF AVM ŌĆó PARENCHYMAL AVM ŌĆó YELLOW ŌĆō PIAL AVM ŌĆó RED ŌĆō PARAVENTRICULAR AVM ŌĆó GREEN ŌĆōSUBCORTICAL AVM ŌĆó MIXED
- 8. ŌĆó DURAL AVM ŌĆó MIXED (DURAL AND PARENCHYMAL AVM)
- 9. CLINICAL PRESENTATION ŌĆó HEMORRHAGE(INTRAPARENCHYMAL>INTRAVENTRICU LAR HEMORRHAGE >SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE ) ŌĆó MASS EFFECT IF ON TRIGEMINAL NERVE ŌĆō TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA(ALWAYS MRI) SEIZURES ISCHEMIA BY STEAL INCREASED ICP
- 11. INVESTIGATION ŌĆó CT ŌĆó MRI ANGIOGRAPHY
- 13. MANAGEMENT ŌĆó SURGICAL RESECTION ŌĆó EMBOLISATION ŌĆō Onyx-18, 34 ŌĆō AVM ŌĆō ONYX 500 - ANEURYSM ŌĆó STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY ŌĆō FOR DEEPER LESION OF LESS THAN 3 CM
- 14. POST OPERATIVE COMPLICATION ŌĆó NORMAL PERFUSION PRESSURE BREAKTHROUGH ŌĆō Swelling or hemorrhage due to loss of autoregulation - Patient pretreated with propanolol 20mg QID TO MINIMISE THIS EFFECT ŌĆó OCCLUSIVE HYPEREMIA. ŌĆō MAY BE DUE TO OCCLUSION OF DRAINING VEIN OR DUE TO THROMBOSIS (DELAYED EFFECT)
- 15. ŌĆó POST OPERATIVELY ŌĆō CATHETER ANGIOGRAPHY AT 1 YEAR AND AT 5 YEAR AFTER TREATMENT
- 16. THANK YOU