Artificial intelligence
- 2. Presented by, 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 2
- 4. Intelligence Behavior the ability to learn from experiences and apply knowledge acquired from experience, handle complex situations, solve problems when important information is missing, determine what is important, react quickly and correctly to a new situation, understand visual images, process and manipulate symbols, be creative and imaginative, and use heuristics.
- 5. 4 Views of AI Think like humans Think rationally Act like humans Act rationally 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 5
- 6. Turing Test (developed by Alan Turing, a British Mathematician) attempts to determine whether the responses from a computer with intelligent behavior are indistinguishable from responses from a human.
- 7. Specific characteristics of intelligent behavior: – Learn from experience and apply the knowledge acquired from experience. – Handle complex situations. – Solve problems when important information is missing. – Determine what is important. – React quickly and correctly to a new situation. – Understand visual images. – Process and manipulate symbols. – Be creative and imaginative. – Use heuristics. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 7
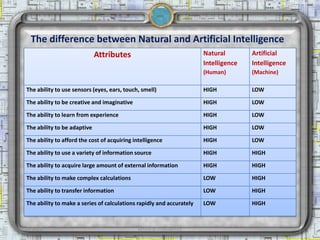
- 8. The difference between Natural and Artificial Intelligence Attributes Natural Artificial Intelligence Intelligence (Human) (Machine) The ability to use sensors (eyes, ears, touch, smell) HIGH LOW The ability to be creative and imaginative HIGH LOW The ability to learn from experience HIGH LOW The ability to be adaptive HIGH LOW The ability to afford the cost of acquiring intelligence HIGH LOW The ability to use a variety of information source HIGH HIGH The ability to acquire large amount of external information HIGH HIGH The ability to make complex calculations LOW HIGH The ability to transfer information LOW HIGH The ability to make a series of calculations rapidly and accurately LOW HIGH 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 8
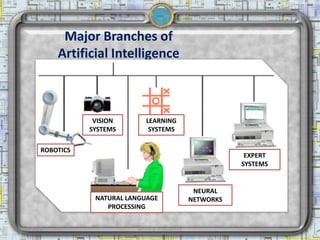
- 9. Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence VISION LEARNING SYSTEMS SYSTEMS ROBOTICS EXPERT SYSTEMS NEURAL NATURAL LANGUAGE NETWORKS PROCESSING 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 9
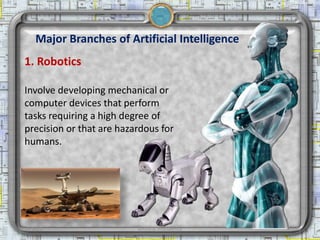
- 10. Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence 1. Robotics Involve developing mechanical or computer devices that perform tasks requiring a high degree of precision or that are hazardous for humans. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 10
- 11. 2. Vision Systems Include hardware and software that permit computers to capture, store, and manipulate visual images and pictures. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 11
- 12. 3. Natural language processing Computers understand and react to statements and commands made in a “natural” language, such as English. 4. Learning system Computer changes how it functions or reacts to situations based on feedback. 5. Neural network Computer system that can act like or simulate the functioning of the human brain. 6. Expert Systems Consists of hardware and software that stores knowledge and makes inferences, similar to a human expert. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 12
- 13. Ethics of AI – People might lose their jobs to automation. – People might lose their sense of being unique. – People might lose some of their privacy rights. – The use of AI systems might result in a loss of accountability. – The success of AI might mean the end of the human race. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 13
- 14. AI Applications AI techniques are used in many common applications; just a sample – Intelligent user interfaces – Search Engines – Spell/grammar checkers – Context sensitive help systems – Medical diagnosis systems – Regulating/Controlling hardware devices and processes (e.g, in automobiles) – Voice/image recognition (more generally, pattern recognition) – Scheduling systems (airlines, hotels, manufacturing) – Error detection/correction in electronic communication – Program verification / compiler and programming language design – Web search engines / Web spiders – Web personalization and Recommender systems (collaborative/content filtering) – Personal agents – Customer relationship management – Credit card verification in e-commerce / fraud detection – Data mining and knowledge discovery in databases – Computer games 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 14
- 15. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 15
- 16. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 16
- 17. 2/18/2013 Artificial Intelligence 17