Artificial Intelligence, Data and Competition ŌĆō ─īORBA ŌĆō June 2024 OECD discussion
- 1. Governance of artificial intelligence and the interplay with competition policy OECD Competition Committee 12 June 2024 Juraj ─īorba Chair, OECD Working Party on Artificial Intelligence Governance (AIGO)
- 2. 1. Background: What is AI?
- 3. A variety of systems and policy implications Myriad of applications of AI systems
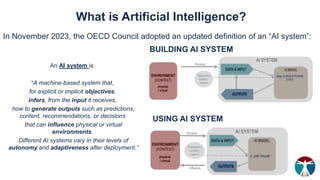
- 4. What is Artificial Intelligence? In November 2023, the OECD Council adopted an updated definition of an ŌĆ£AI systemŌĆØ: An AI system is: ŌĆ£A machine-based system that, for explicit or implicit objectives, infers, from the input it receives, how to generate outputs such as predictions, content, recommendations, or decisions that can influence physical or virtual environments. Different AI systems vary in their levels of autonomy and adaptiveness after deployment.ŌĆØ BUILDING AI SYSTEM USING AI SYSTEM
- 5. 2. The OECD AI Principles
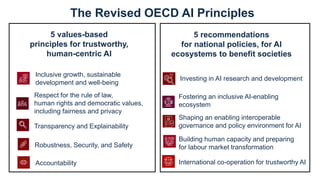
- 6. Respect for the rule of law, human rights and democratic values, including fairness and privacy Transparency and Explainability Robustness, Security, and Safety Accountability Inclusive growth, sustainable development and well-being 5 values-based principles for trustworthy, human-centric AI 5 recommendations for national policies, for AI ecosystems to benefit societies Investing in AI research and development Fostering an inclusive AI-enabling ecosystem Shaping an enabling interoperable governance and policy environment for AI Building human capacity and preparing for labour market transformation International co-operation for trustworthy AI The Revised OECD AI Principles
- 7. Shaping an enabling interoperable governance and policy environment for AI (Principle 2.3) [ŌĆ”] Governments should review and adapt, as appropriate, their policy and regulatory frameworks and assessment mechanisms as they apply to AI systems to encourage innovation and competition for trustworthy AI.
- 8. 3. Key parts of the value chain: what is required to successfully develop and deploy AI models?
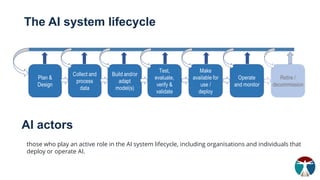
- 9. The AI system lifecycle AI actors those who play an active role in the AI system lifecycle, including organisations and individuals that deploy or operate AI.
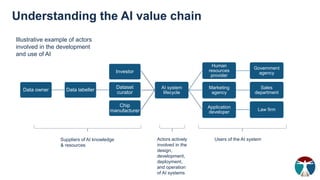
- 10. AI system lifecycle Human resources provider Government agency Marketing agency Sales department Application developer Law firm Data owner Data labeller Investor Dataset curator Chip manufacturer Illustrative example of actors involved in the development and use of AI Suppliers of AI knowledge & resources Actors actively involved in the design, development, deployment, and operation of AI systems Users of the AI system Understanding the AI value chain
- 11. Investment Key inputs to develop AI ŌĆō ŌĆ£AI enablersŌĆØ Research (Programming) skills / skilled labour
- 12. Research
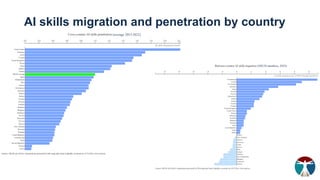
- 13. AI skills migration and penetration by country (OECD members, 2022) (average 2015-2022)
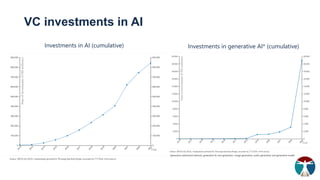
- 14. VC investments in AI *generative adversarial network, generative AI, text generation, image generation, audio generation and generative model. Investments in generative AI* (cumulative) Investments in AI (cumulative)
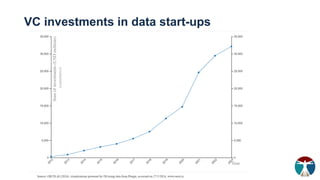
- 15. VC investments in data start-ups (cumulative)
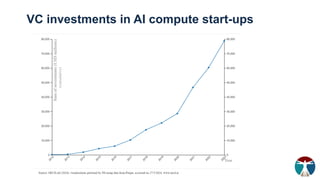
- 16. VC investments in AI compute start-ups (cumulative)
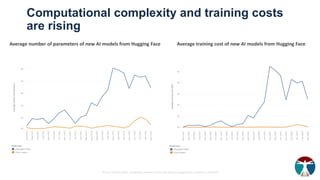
- 17. Computational complexity and training costs are rising Average number of parameters of new AI models from Hugging Face Average training cost of new AI models from Hugging Face Source: OECD.AI (2024), visualisations powered by JSU using data from Hugging Face, accessed on 22/4/2024
- 18. New models keep being developed Source: OECD.AI (2024), visualisations powered by JSU using data from Hugging Face, accessed on 22/4/2024
- 19. Next steps ŌĆóMore nuanced understanding of market dynamics and AI actors is needed ŌĆóMonitoring (market) developments in such AI enablers will be key to a comprehensive understanding of competition in AI ŌĆóCross-disciplinary exchanges can foster more targeted policy responses





![Shaping an enabling interoperable governance
and policy environment for AI (Principle 2.3)
[ŌĆ”]
Governments should review and adapt, as
appropriate, their policy and regulatory
frameworks and assessment mechanisms as they
apply to AI systems to encourage innovation and
competition for trustworthy AI.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oecd-ai-data-and-competition-oecd-wp-aigo-june2024-240612113054-c594594b/85/Artificial-Intelligence-Data-and-Competition-CORBA-June-2024-OECD-discussion-7-320.jpg)