Artificial Lift Selection Criterion
- 1. Artificial Lift Selection Criteria for Optimum Efficiency Reservoir Types & Limitations Aditya Kumar Director ŌĆō Petroleum Engineering aditya@telestoenergy.com
- 2. Outline ŌĆó Nodal Analysis / Well Performance ŌĆó Reservoir Inflow Capability ŌĆó Reservoir Drive Mechanisms ŌĆó Reservoir Trends and Recovery ŌĆó Reservoir Relevant Consideration in Selecting an Artificial Lift Method
- 3. Nodal Analysis / Well Performance 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 4500 Production rate, STB/D Flowingbottomholepressure,psi Inflow (Reservoir) Curve Outflow (Tubing) Curve 2111 STB/D 1957 psi
- 4. Reservoir Inflow Capability ’Ć© ’Ć® ’āĘ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½’ĆŁ’āĘ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ĆŁ’é┤ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ s r r B pphk q w e oo wf 4 3 ln 1008.7 3 ’üŁ wfpp q J ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’āĘ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½’ĆŁ’āĘ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’üŁ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ s r r B kh J w e oo 4 3 ln 1008.7 3
- 5. Solution Gas Drive Reservoir
- 6. Gas Cap Drive Reservoir
- 8. Gravity Drainage Drive Reservoir Oil Oil Oil Point A Point B Point C Gas Gas Gas
- 9. Recovery Factors for Oil Reservoirs Drive Mechanism Average Recovery Range (% of OOIP) Average Recovery Factor (% of OOIP) Solution Gas Drive 5-30 15 Gas Cap Drive 15-50 30 Water Drive 30-60 40 Gravity Drainage Drive 16-85 50
- 10. Reservoir Changes and AL selection ŌĆó Reservoir behavior changes over the period of time for different drive mechanisms ŌĆó Rate of decrease of reservoir pressure ŌĆó Rate of increase in water cut ŌĆó Behavior of GOR with time ŌĆó Selection of an appropriate artificial lift method should take account of ŌĆó Inflow performance of the well based upon type of reservoir ŌĆó Variation of reservoir and fluid properties over time ŌĆó Capacity and operation of the lift systems
- 11. Liquid production rate The anticipated production rate is a controlling factor in selecting a lift method Water cut High water cuts require a lift method that can move large volumes of fluid Gas-liquid ratio A high GOR generally lowers the efficiency of pump-assisted lift Viscosity High-viscosity fluids can cause difficulty, particularly in sucker rod pumping Formation volume factor Ratio of reservoir volume to surface volume determines how much total fluid must be lifted to achieve the desired surface production rate Reservoir drive mechanism Depletion drive reservoirs: Late-stage production may require pumping to produce low fluid volumes or injected water. Water drive reservoirs : High water cuts may cause problems for lifting systems Gas cap drive reservoirs : Increasing gas-liquid ratios may affect lift efficiency. Other reservoir problems Sand, paraffin, or scale can cause plugging and/or abrasion. Presence of H2S, CO2 or salt water can cause corrosion. Downhole emulsions can increase backpressure and reduce lifting efficiency. High bottomhole temperatures can affect downhole equipment. Reservoir Relevant Consideration in Selecting an Artificial Lift Method
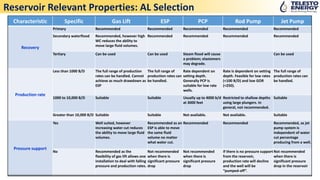
- 12. Reservoir Relevant Properties: AL Selection Characteristic Specific Gas Lift ESP PCP Rod Pump Jet Pump Recovery Primary Recommended Recommended Recommended Recommended Recommended Secondary waterflood Recommended, however high WC reduces the ability to move large fluid volumes. Recommended Recommended Recommended Recommended Tertiary Can be used Can be used Steam flood will cause a problem; elastomers may degrade. Can be used Production rate Less than 1000 B/D The full range of production rates can be handled. Cannot achieve as much drawdown as ESP The full range of production rates can be handled. Rate dependent on setting depth. Generally PCP is suitable for low rate wells. Rate is dependent on setting depth. Feasible for low rates (<100 B/D) and low GOR (<250). The full range of production rates can be handled. 1000 to 10,000 B/D Suitable Suitable Usually up to 4000 b/d at 3000 feet Restricted to shallow depths using large plungers. In general, not recommended. Suitable Greater than 10,000 B/D Suitable Suitable Not available. Not available. Suitable Pressure support Yes Well suited, however increasing water cut reduces the ability to move large fluid volumes. Recommended as an ESP is able to move the same fluid volume no matter what water cut. Recommended Recommended Recommended, as jet pump system is independent of water cut percentage producing from a well. No Recommended as the flexibility of gas lift allows one installation to deal with falling pressure and production rates. Not recommended when there is significant pressure drop Not recommended when there is significant pressure drop If there is no pressure support from the reservoir, production rate will decline and the well will be ŌĆ£pumped-offŌĆØ. Not recommended when there is significant pressure drop in the reservoir
- 13. Characteristic Specific Gas Lift ESP PCP Rod Pump Jet Pump Gas/oil ratio Less than 500 scf/STB Recommended Recommended. Recommended. Feasible for low rate and low GOR Recommended. 500 to 2000 scf/STB Recommended The achievable pump rate will be limited by the amount of gas breaking out of solution. The achievable pump rate will be limited by the amount of gas breaking out of solution. Gassy wells usually have lower volumetric efficiency. Target design is less than 1000 GLR. Greater than 2000 scf/STBRecommended. Gas lift would be only expected to be of benefit at higher GOR. FBHP will need to stay above the bubble point pressure to avoid gas cavitation. Not recommended. Not recommended Not recommended. Gas above 2000 SCF/STB substantially reduces efficiency but helps lift. Bubble point High Recommended for all bubble points. Not recommended. Not recommended. Not highly recommended. Not recommended. Low Recommended for all bubble points. Recommended. Recommended. Recommended. Recommended. Fluid viscosity (at reservoir temperature) Less than 100 cp Recommended Recommended Recommended Recommended Recommended 100 to 500 cp Recommended Efficiency of ESP will be reduced. Recommended. Pump efficiency will increase as viscosity increases. Good for < 200 cp fluids and low rate. Recommended Greater than 500 cp Has been used with success up to 1000 cp but problems with very high viscosity. Not recommended. Recommended for all high viscosity crude. Up to 80,000 cp. Not recommended, as pump efficiency will reduce. The system is capable of handling high-viscosity fluid. Production with up to 800 cp possible. Reservoir Relevant Properties: AL Selection
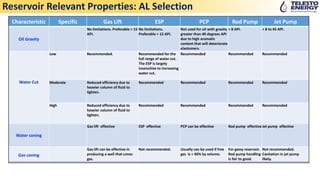
- 14. Reservoir Relevant Properties: AL Selection Characteristic Specific Gas Lift ESP PCP Rod Pump Jet Pump Oil Gravity No limitations. Preferable > 15 API. No limitations. Preferable > 12 API. Not used for oil with gravity greater than 40 degrees API due to high aromatic content that will deteriorate elastomers. > 8 API. > 8 to 45 API. Water Cut Low Recommended. Recommended for the full range of water cut. The ESP is largely insensitive to increasing water cut. Recommended Recommended Recommended Moderate Reduced efficiency due to heavier column of fluid to lighten. Recommended Recommended Recommended Recommended High Reduced efficiency due to heavier column of fluid to lighten. Recommended Recommended Recommended Recommended Water coning Gas lift effective ESP effective PCP can be effective Rod pump effectiveJet pump effective Gas coning Gas lift can be effective in producing a well that cones gas. Not recommended. Usually can be used if free gas is < 40% by volume. For gassy reservoir. Rod pump handling is fair to good. Not recommended. Cavitation in jet pump likely.
- 15. THANK YOU Telesto Energy Pte Ltd 30 Cecil Street, #19-08, Prudential Towers, Singapore 049712 Email: contact@telestoenergy.com | Website: www.telestoenergy.com Global Presence: India | Perth | Algiers Telestoenergy #telestoenergy Telestoenergy