Assam ppt
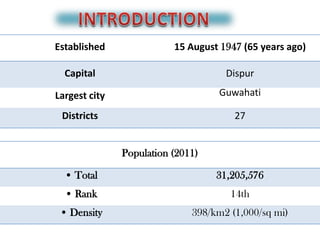
- 3. Established 15 August 1947 (65 years ago) Capital Dispur Largest city Guwahati Districts 27 Population (2011) • Total 31,205,576 • Rank 14th • Density 398/km2 (1,000/sq mi)
- 4. ÔÉò Total area of Assam is 78,438 square kilometers in census 2011. ÔÉò Total Population of Assam is 31,205,576 as per census 2011. 1.Male :- 15,939,443. 2.Female :- 15,266,133. ÔÉò Square Kilometer : Average density of Assam is 398 per sq. km. ÔÉò Female Sex ratio of Assam is 958 females per 1000 males. ÔÉò Population growth rate of Assam was 17.07 percent during the 2001-2011 period. ÔÉò Average literacy rate of Assam is 72.19 percent. 1.Male :- 77.85 percent. 2,Female :-63.00 percent.
- 5. Assam ‚Üí The state is a gateway to Northeast India. Guwahati is the largest city of the state. ‚Üí Assam is known for its tea, petroleum resources, diversity. and bio- Assam is becoming an increasingly popular destination for wildlife tourism. Kaziranga National Park and Manas National Park are registered as world-heritage sites. ‚Üí Assam is located in the Northeast of India. The state shares its borders with Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Tripura and West Bengal. ‚Üí The state shares international borders with Bangladesh and the Kingdom of Bhutan. ‚Üí ‚Üí Assamese and Bodo are the official languages.
- 6. Assam’s GSDP  At current prices, the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of Assam was US$ 24.0 billion in 2011-12.  The average annual GSDP growth rate was 10.6 per cent from 2004-05 to 2011-12. 2011-12 2010-11 2009-10 2008-09 2007-08 2006-07 2005-06 2004-05 24.0 22.8 19.5 17.6 17.6 14.2 CAGR 13.4 11.8 0 5 10 15 20 US$ billion 10.6% 25 30
- 10. Percentage Distribution of GSDP 100 80 46.9 48.8 40 18.8 17.0 20 34.3 34.2 2004-05 2011-12 60 0 Primary Sector Secondary Sector Tertiary Sector
- 11. Economic Snapshot – FDI Inflows & Investments Break up of Outstanding Investments by Sector (2011-12) 3.5% 0.2% Services 10.1% Manufacturing 36.0% 16.3% Electricity Mining Irrigation 33.9% Real Estate
- 12. Physical Infrastructure – Airports → Assam has an international airport at Guwahati known as Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport. Dibrugarh Lakhimpur → The Airport Authority of India plans to make Guwahati Airport as Jorhat one of the majorGuwahati Tezpur international airports of India, connecting Southeast Asia with India. → Silchar The state also has six domestic airports, at Guwahati, Tezpur, Jorhat, Dibrugarh, Silchar and North International airport Lakhimpur. Domestic airport → Guwahati Airport received 2.2 million passengers during 2011-12.
- 13. Physical Infrastructure – Inland Waterways → Assam’s major river routes are the Brahmaputra and the Barak rivers, with a combined navigable length of around 1,000 km. → Seven port locations are operational in the state for import and export to the Kolkata and Haldia ports. → The river Brahmaputra is known as the National Waterway No 2 (The Ganges is known as the National Waterway No 1). → The Directorate of Inland Water Transport (IWT) and Central Inland Waterways Corporation of Assam. Container Corporation of India Limited (CONCOR) operates an Inland Container Depot (ICD) at Amingaon, 10 km from Guwahati. Two bonded warehouses of CONCOR along with a private warehouse (total area of 6,400 sq m) operate from the ICD. →
- 14. Physical Infrastructure – Roads Road Type Road Length (km) Total Road Length 42,641 National Highways 2,836 State Highways 3,134 Major District Roads 4,413 Rural Roads 30,844
- 15. Physical Infrastructure – Telecom → According to Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), Assam had nearly 14.0 million wireless subscribers and 230,987 wire-line subscribers as of January 2012. Telecom Infrastructure (January 2012) → The state also had 90,245 broadband subscribers as of December 2011. As of December 2011, the state had 597 telephone exchanges. 14,009,48 3 Wire-line Subscribers 230,987 Broadband Subscribers* → Wireless Subscribers 90,245 Post Offices** 4,006 Telephone Exchanges* 597 Some of the Major Telecom Operators in Assam Reliance Communications Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) Bharti Airtel Aircel Limited Vodafone Essar IDEA Cellular Tata Teleservices
- 16. Education → Assam has a literacy rate of 73.2 per cent. . → The State Government is taking several steps to encourage setting up of various educational complexes for skill development. The State Government has formed a steering committee and 27 institute management committees, to facilitate close coordination between industry and academia. Premier Institutions in Assam • Gauhati University, Guwahati • Assam University, Silchar • Assam Agricultural University, Jorhat • Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati • National Institute of Technology, Silchar • Assam Medical College, Dibrugarh • Gauhati Medical College and Hospital, Guwahati
- 17. Social Infrastructure – Health Health Infrastructure • • • • • • State Level Hospital: 1 District Hospitals: 22 Sub Divisional Civil Hospitals: 13 Primary Health Centres: 844 Dispensaries: 261 Sub-Centres: 4,592
- 18. Key Industries Key industries in Assam → Assam produces over 50 per cent of the tea produced in India. → As of March 2011, there were 34,327 registered Small Scale Industrial (SSI) / Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) units in the state. • Tea • Coal, Oil and Gas • Limestone and Cement • Agriculture and Horticulture • Food Processing • Tourism • Traditional Cottage Industry • Sericulture
- 19. Assam → Key Industries – Tea Tea occupies an important place among all the agriculturebased industries in Assam. About 17 per cent of the workers of Assam are engaged in the tea industry. → Assam produces over 50 per cent of the tea produced in India and about one-sixth of the tea produced in the world. → In 2010-11, total tea production in the state was 525,000 tonnes. → Tea is grown both in the Brahmaputra and the Barak plains. Tea gardens are mostly found in the districts of Tinsukia, Dibrugarh, Sibsagar, Jorhat, Golaghat, Nagaon and Sonitpur. → → The Government has secured a Geographical Indication (GI) for the tea produced in the state. As a result ‘Assam Tea’ is known as ‘Assam Orthodox Tea’.
- 20. TEA INDUSTRIES Assam Tea Corp Ltd Williamson Magor Group Assam Company India Ltd Apeejay Tea Ltd
- 21. Energy: Coal, Oil and Gas. Indian Oil Corp Ltd (IOCL) Coal India Ltd (CIL) Oil and Natural Gas Corp Ltd (ONGC) Oil India Ltd (OIL)
- 22. CEMENT Cement Corp of India Ltd (CCI) Barak Valley Cements Ltd Jaypee Cements Ltd
- 23. Medicinal Herbs and Plants ‚Üí Assam, with its vast hills and forests, is home to a variety of medicinal herbs and plants. About 300 types of medicinal herbs and plants are found in abundance in the state with the Brahmaputra Valley, itself, having 150 varieties of herbs and plants of commercial value. ‚Üí Medicinal herbs and plants in the state are Sarpagandha (rauvolfia serpentine Benth.ex.Kur), Pippali (Piper longam Linn), Amlakhi (Emblica Officinalis Gaertn), Hilikha (Terinalia Chebula Retz.), Bhomora (Terminalia belerica), Arjuna (Terminalia arjuna Wight & Arn.) etc.
- 24. Assam Key Industries in Major Districts District Industries Barpeta Metal, Mastarted Oil Mill Bongaigaon Dibrugarh Jorhat Textiles, Dairy, Aluminium, Oil and Natural Gas Fertilizer, Petroleum and Natural Gas Tea, Cement, Pharmaceuticals, Aluminium and Food Products Karimganj Cement North Cachar Hills Cement Sivasagar Tea, Oil and Natural Gas Tinsukia Tea, Coal, Oil and Natural Gas
- 27. Cultural Infrastructure ‚Üí Assam is home to many ethnic groups and different cultures. The state is rich in folk music; different styles include regional folk music, ethnic folk music and bihu songs, among others. ‚Üí Assam has a rich tradition of performing arts. Ankiya Nat (Onkeeya Naat) is a traditional dance-drama (bhaona) form, popular since the 15th century A.D. ‚Üí The Bihu dance, Kushan Nritya, Sattriya and Banjar Kekan are some of the popular dance forms of Assam. ‚Üí Guwahati is the major centre for sporting facilities. The sports infrastructure
- 28. Food
- 29. Temples
- 30. Dress and Dance
- 31. THANK YOU