Assignment
- 2. COST ACCOUNTING  Cost accounting is the application of costing & cost accounting principle, methods & technique of the science, art and practice of the cost control ascertainment of profitability.  It also includes the presentation of information derived for the purpose of managerial decision making.  It is thus the science art & practice of a cost accountant  BY B.K. VASHISHTHA
- 3. COST ACCOUNTING - MEANING  Cost accounting is concerned with recording, classifying and summarizing costs for determination of costs of products or services, planning, controlling and reducing such costs and furnishing of information to management for decision making
- 4. COST ACCOUNTING - INTRODUCTION Accounting for determination and control of costs.  COST ACCOUNTING: The Institute of Cost and Management Accountant, England (ICMA) has defined Cost Accounting as – “the process of accounting for the costs from the point at which expenditure incurred, to the establishment of its ultimate relationship with cost centers and cost units. In its widest sense, it embraces the preparation of statistical data, the application of cost control methods and the ascertainment of the profitability of activities carried out or planned”. Cost Accounting = Costing + Cost Reporting + Cost Control. ahsanullah.mohsen
- 5. COST - MEANING Cost means the amount of expenditure (actual or notional) incurred on, or attributable to, a given thing. ahsanullah.mohsen
- 6. OBJECTIVES OF COST ACCOUNTING ÔÉò Ascertainment of costs ÔÉò Estimation of costs ÔÉò Cost control ÔÉò Cost reduction ÔÉò Determining selling price ÔÉò Facilitating preparation of financial and other statement ÔÉò Providing basis for operating policy ahsanullah.mohsen
- 7. COST TERMINOLOGY:  COST: Cost means the amount of expenditure incurred on a particular thing.  COSTING: Costing means the process of ascertainment of costs.  COST ACCOUNTING: The application of cost control methods and the ascertainment of the profitability of activities carried out or planned”.  COST CONTROL: Cost control means the control of costs by management. Following are the aspects or stages of cost control.  JOB COSTING: It helps in finding out the cost of production of every order and thus helps in ascertaining profit or loss made out on its execution. The management can judge the profitability of each job and decide its future courses of action.  BATCH COSTING: Batch costing production is done in batches and each batch consists of a number of units, the determination of optimum quantity to constitute an economical batch is all the more important. ahsanullah.mohsen
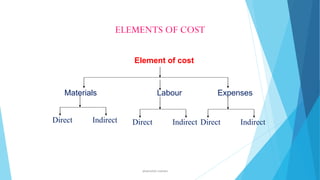
- 8. ELEMENTS OF COST Element of cost Materials Direct Indirect Labour Direct ahsanullah.mohsen Expenses Indirect Direct Indirect
- 9. MATERIAL: The substance from which the finished product is made is known as material. (a) DIRECT MATERIAL: is one which can be directly or easily identified in the product Eg: Timber in furniture, Cloth in dress, etc. (b) INDIRECT MATERIAL: one which cannot be easily identified in the product. ahsanullah.mohsen
- 10. EXAMPLES OF INDIRECT MATERIAL At factory level – lubricants, oil, consumables, etc. At office level – Printing & stationery, Brooms, Dusters, etc. At selling & dist. level – Packing materials, printing & stationery, etc. ahsanullah.mohsen
- 11. The human effort required to convert the materials into finished product is called labour. LABOUR: (a) DIRECT LABOUR: is one which can be conveniently identified or attributed wholly to a particular job, product or process. Eg:wages paid to carpenter, fees paid to tailor,etc. (b) INDIRECT LABOUR: is one which cannot be conveniently identified or attributed wholly to a particular job, product or process. ahsanullah.mohsen
- 12. EXAMPLES OF INDIRECT LABOUR At factory level – foremen’s salary, works manager’s salary, gate keeper’s salary,etc At office level – Accountant’s salary, GM’s salary, Manager’s salary, etc. At selling and dist.level – salesmen salaries, Logistics manager salary, etc. ahsanullah.mohsen
- 13. Advantages of cost sheet:  It shows the total cost amount and the cost per unit of production.  It is helpful for the purpose of cost  It facilities the fixation of the selling price of different products.   comparison. It helps in cost control by ascertaining the actual operational efficiency as compared to the standard or targeted competitors. KALPAN PATEL
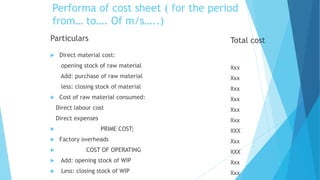
- 14. Performa of cost sheet ( for the period from… to…. Of m/s…..) Particulars  Total cost Direct material cost: opening stock of raw material Add: purchase of raw material Xxx less: closing stock of material  Xxx Xxx Cost of raw material consumed: Xxx Direct labour cost Direct expenses    Xxx Xxx PRIME COST; Factory overheads COST OF OPERATING XXX Xxx XXX  Add: opening stock of WIP Xxx  Less: closing stock of WIP Xxx
- 15. Conti……. particulars    Total cost FACTORY COST:       SALES REVENUE Kalpan Patel Xxx  Add: Profit/Loss XXX  TOTAL COST Xxx  Selling & distribution cost XXX  COST OF PRODUCTION OF GOODS FOR SALE Xxx  Less: closing stock of finished goods Xxx  Add: opening stock of finished goods XXX  OFFICE COST / COST OF PRODUCTION: Xxx  Office & Administration cost XXX XXX
- 16. EXPENSES:    Expenses are part of the cost which are not of the nature of material and labour but are incurred due to business activities. In short, the amount spend for running a business is termed as expenses. Direct expenses can be directly linked with a specific saleable product or service. The expenses that cannot be identified or linked or attributed or allocated directly to the finished saleable product or services are termed as INDIRECT expenses. Kalpan Patel
- 17. COST SHEET DIRECT MATERIAL DIRECT LABOUR DIRECT EXPENSES PRIME COST FACTORY OVERHEADS FACTORY COST OFFICE OVERHEADS COST OF PRODUCTION SELL & DIST OVERHEADS COST OF SALES PROFIT SALES ahsanullah.mohsen
- 18. COST SHEET - ADVANCED OPENING STOCK OF RAW MATERIALS +PURCHASES +CARRIAGE INWARDS -CLOSING STOCK OF RAW MATERIALS VALUE OF MATERIALS CONSUMED +DIRECT WAGES +DIRECT EXPENSES PRIME COST +FACTORY OVERHEADS +OPENING STOCK OF WIP -CLOSING STOCK OF WIP ahsanullah.mohsen FACTORY COST (CONT.)
- 19. FACTORY COST +ADMINISTRATIVE OVERHEADS COST OF PRODUCTION +OPENING STOCK OF FINISHED GOODS -CLOSING STOCK OF FINISHED GOODS COST OF GOODS SOLD +SELL. & DIST. OVERHEADS COST OF SALES +PROFIT SALES ahsanullah.mohsen
- 20. The concept of cost  Out lay cost  Opportunity cost  Cost and expenses  Expenses  Operating cost  Product cost  Period cost ahsanullah.mohsen
- 21. COST CLASSIFICATION – ON THE BASIS OF 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) Nature Function Direct & indirect Variability Controllability Normality Financial accounting classification Time Planning and control Managerial decision making ahsanullah.mohsen
- 22. ON THE BASIS OF NATURE ÔÉò Materials ÔÉò Labour ÔÉò Expenses ahsanullah.mohsen
- 23. ON THE BASIS OF VARIABILITY ÔÉò Fixed costs ÔÉò Variable costs ÔÉò Semi variable costs ahsanullah.mohsen
- 24. METHODS OF COSTING 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Job costing Contract costing Batch costing Process costing Unit costing Operating costing(uses for services) Operation costing(hybrid of job-order and process costing) Multiple costing ahsanullah.mohsen
- 25. TYPES OF COSTING 1. Uniform costing(number of firms in an industry) 2. Marginal costing 3. Standard costing 4. Historical costing(It is the ascertainment of costs after they have been incurred. This type of costing has limited utility.) 5. Absorption costing( both variable and fixed to operations, processes or product) ahsanullah.mohsen
- 26. Direct Materials Opening stock of materials Add Purchases of materials Less Closing stock of materials (a) Materials consumed Direct Wages Direct Expenses Calculation of various cost ------ ------ PRIME COST Add Factory Overheads Factory rent, rates, taxes Fuel-power and water Lighting and Heating Indirect wages Depreciation, Repairs Salaries of Works Manager etc. Indirect Materials Drawing office and works office expenses Depreciation on factory land and building Less Scrap value Defective work Add Work in progress (opening) Less Work in progress (closing) ------ WORKS COST Add Office/Administration overheads Office rent, insurance, lighting, cleaning Office salaries, telephone, law and audit expenses General Manager’s salary Printing and stationery Maintenance, repairs, upkeep of office bldg Bank charges and miscellaneous expenses ------ COST OF PRODUCTION Add Opening stock of finished goods Less Closing stock of finished goods ------ COST OF GOODS SOLD Add Selling and Distribution Overheads Showroom expenses, salesmen’s salaries & commission, bad debts, discounts, warehouse rent, carriage outwards, advertising, delivery expenses, samples and free gifts etc. COST OF SALES Add Net Profit or deduct net loss: ------ SALES ------
- 27. Audit Of Manufacturing Company  Adaptation  Scope Definition  Accounting Work  Letter of Engagement  Internal Control  Management Responsibilities  Evaluation of Evidence  Reporting
- 28. Special Items Considered in Auditing of Manufacturing Company Goods in Bonds  Loose-tools at Construction Site   Physical Verification Sheet  Financial Statement
- 29.  Work in Progress  Cost Sheets  Previous year financial Statements  General  Provisions of companies act
- 31. REFERENCES  Mohnes,A.Cost accounting  Professor,Joshi,D.(2012). Cost and management accountancy.  Patel,D, and Patel,K.(2012). Cost and management and accountancy.  Vashishtha,B.K.(2010). Cost of accounting.  Purushotham,V. Prabakaran. Audit of Manufacturing Company.