Asthma diagnosis
- 1. ProfessorProfessor Abdur-Rab KhanAbdur-Rab Khan MRCP- FRCP (UK)MRCP- FRCP (UK) Ayub Medical College AbbottabadAyub Medical College Abbottabad
- 2. Diagnosis of AsthmaDiagnosis of Asthma
- 5. Peak Expiratory Flow RatePeak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)(PEFR) ï Measures how fast a person can exhale air ï Requires a peak expiratory flow monitor OmronMini-Wright AM2 Plus
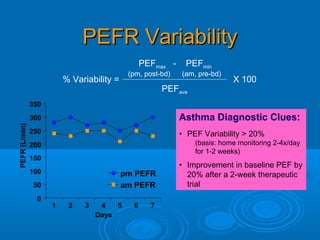
- 6. PEFR VariabilityPEFR Variability Asthma Diagnostic Clues: âĒ PEF Variability > 20% (basis: home monitoring 2-4x/day for 1-2 weeks) âĒ Improvement in baseline PEF by 20% after a 2-week therapeutic trial PEFmax - PEFmin PEFave (pm, post-bd) (am, pre-bd) % Variability = X 100 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Days PEFR(L/min) pm PEFR am PEFR
- 10. SpirometrySpirometry ï Recommended for the initial assessment of all asthma suspects!
- 13. > 15% increase in FEV1.0 after Ã-2 inhalation Hallmark of Asthma: Reversibility! Spirometry
- 15. Types of Flow Volume Curves Normal Obstructive Litersper second Concavity Asthma Concavity pre- bronchodilator Improved post-bronchodilator
- 16. Good MeasurementsGood Measurements are Essential!are Essential! Acceptable Loop Unacceptable Loop
- 17. Is it Asthma? Determine that the patient is experiencing episodic symptoms of airflow obstruction Demonstrate that the obstruction is at least partially reversible Exclude alternate diagnoses
- 18. Asthma wheezing Lung Disease Overlap Chronic Bronchitis cough+sputum Emphysema breathlessness Airway Remodeling in Asthma Denudation of the airway epithelium Collagen deposition beneath the basement membrane Edema Mast cell activation Inflammatory cell infiltration COPD
- 19. Classifying Severity: BASED ON SYMPTOMS & LUNG FUNCTION Daytime Symptoms Exacerbations Night attacks 11 22 33 44 IntermittentIntermittent âĒ <1x a week âĒ Brief MildMild persistentpersistent âĒ >1x a week but < 1x/day âĒ May affect activity & sleep ModerateModerate persistentpersistent âĒ Daily âĒ May affect activity & sleep SevereSevere persistentpersistent âĒ < 2x a month âĒ > 2x a month âĒ > once a week âĒ FrequentâĒ Daily âĒ Frequent âĒ Limits physical activity FEV1 or PEF âĒ > 80% predicted âĒ Variability < 20% âĒ > 80% predicted âĒ Variability 20-30% âĒ > 60-80% predicted âĒ Variability > 30% âĒ < 60% predicted âĒ Variability > 30%
Editor's Notes
- 06/15/13
- 06/15/13
- 06/15/13
- 06/15/13 Self explanatory.
- 06/15/13