Atoms & molecules
- 2. Laws of chemical combination
- 3. 1. Law of conservation of mass Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed.
- 4. 2. Law of constant proportions A pure chemical compound always contains same elements combined together in the same definite proportion by weight.
- 5. Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory All matter is composed of a very large number of very small particles called atoms. Atoms are indivisible particles,which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties. Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties. Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds. The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
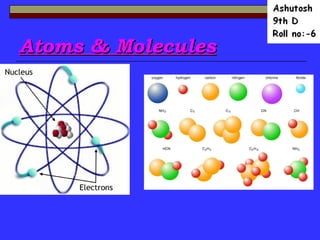
- 6. Atom An atom is the smallest unit that maintains the charateristics of an element. -Nucleus- The center of the atom,contains protons and neutrons -Electron Cloud-Region surroundings the nucleus containing the electrons.
- 7. Ã˝
- 8. Ã˝
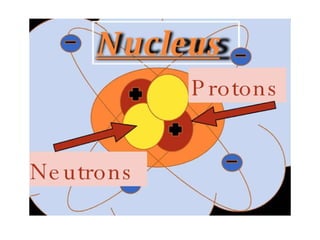
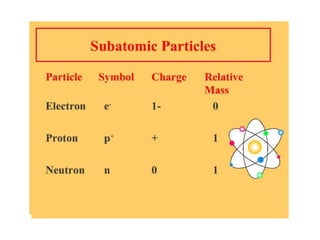
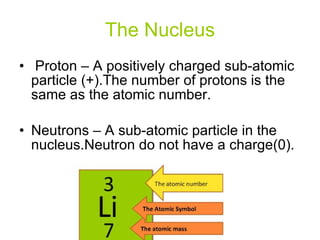
- 9. The Nucleus Proton – A positively charged sub-atomic particle (+).The number of protons is the same as the atomic number. Neutrons – A sub-atomic particle in the nucleus.Neutron do not have a charge(0).
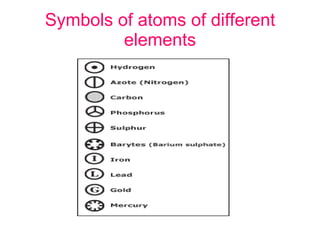
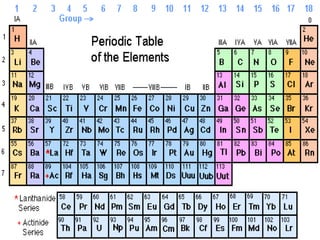
- 10. Symbols of atoms of different elements
- 12. Ã˝
- 13. Molecules
- 14. Molecules A molecule is defined as a stable neutral group of at least two atoms in a definite arrangement held together by very strong chemical bonds. It can also be defined as a unit of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
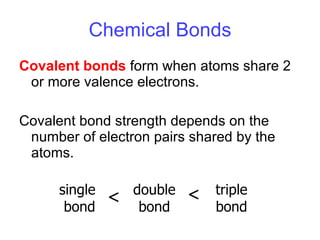
- 15. Chemical Bonds Covalent bonds form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons. Covalent bond strength depends on the number of electron pairs shared by the atoms. single bond double bond triple bond < <
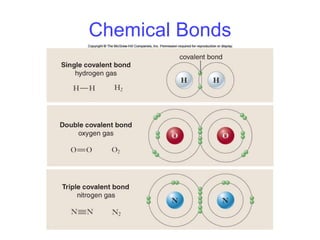
- 16. Chemical Bonds
- 17. Types of Bond
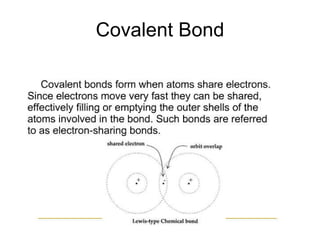
- 18. Covalent Bond