Attachment
- 2. Maximum ABL calculation âĒ Definition âĒ EBV calculation: body wt (kg) x average blood volume (ml/kg) âĒ ABL= [EBV x (Hi-Hf)]/Hi âĒ Where: âĒ EBV=Estimated Blood Volume âĒ Hi= initial hemoglobin âĒ Hf= final hemoglobin
- 3. Average blood volumes ï Premature Neonates 95 mL/kg ï Full Term Neonates 85 mL/kg ï Infants 80 mL/kg ï Adult Men 75 mL/kg ï Adult Women 65 mL/kg Normal Hct Values ïķ Men 42-52% ïķ Women 37-47% âĒ If the patient is obese, using the IBW or ABW will give more accuracy than an actual weight.
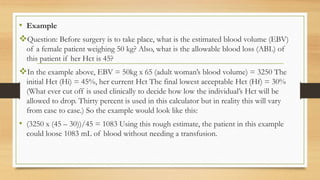
- 4. âĒ Example ïķQuestion: Before surgery is to take place, what is the estimated blood volume (EBV) of a female patient weighing 50 kg? Also, what is the allowable blood loss (ABL) of this patient if her Hct is 45? ïķIn the example above, EBV = 50kg x 65 (adult womanâs blood volume) = 3250 The initial Hct (Hi) = 45%, her current Hct The final lowest acceptable Hct (Hf) = 30% (What ever cut off is used clinically to decide how low the individualâs Hct will be allowed to drop. Thirty percent is used in this calculator but in reality this will vary from case to case.) So the example would look like this: âĒ (3250 x (45 â 30))/45 = 1083 Using this rough estimate, the patient in this example could loose 1083 mL of blood without needing a transfusion.
- 5. Replacing Blood Loss ïķIdeally, blood loss should be replaced with crystalloid or colloid solutions to maintain intravascular volume (normovolemia) until the danger of anemia outweighs the risks of transfusion. ïķ At that point, further blood loss is replaced with transfusions of red blood cells to maintain hemoglobin concentration (or hematocrit) at that level. ïķ For most patients, that point corresponds to a hemoglobin between 7 and 10 g/dL (or a hematocrit of 21-30%). ïķ Below a hemoglobin concentration of 7 g/dL, the resting cardiac output has to increase greatly to maintain normal oxygen deliveryâ
- 6. Estimating blood loss âĒ Dry sponges ïą4Ã4 hold ~ 10 mL blood ïąRay-techs ~ 10-20 mL blood ïąLap sponges ~ 50-100 mL blood
- 7. ïķPediatric cases should have sponges & gauze weighed for blood loss ïķBlood loss replacement âĒ Replace 1 mL blood with: i. 3 mL crystalloid (i.e. NS, Dextrose, LR) ii. 1 mL colloid (i.e. albumin**, HespanÂŪ, DextranÂŪ) iii. 1 mL whole blood iv. 1 mL PRBC
![Maximum ABL calculation
âĒ Definition
âĒ EBV calculation: body wt (kg) x average blood volume (ml/kg)
âĒ ABL= [EBV x (Hi-Hf)]/Hi
âĒ Where:
âĒ EBV=Estimated Blood Volume
âĒ Hi= initial hemoglobin
âĒ Hf= final hemoglobin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/attachment-190215174304/85/Attachment-2-320.jpg)