Attitude & effects
- 1. Employee Attitude and Their Effects Presenter: Kevin Dhillon Human Resources Manager
- 2. ATTITUDES ï evaluative statements (either favorable or unfavorable) concerning objects, people, or events. ï reflect how one feels about something. example: âI like my job.â
- 3. Attitude can be characterized in three ways: âĒFirst, they tend to persist unless something is done to change them. âĒSecond, attitudes can fall anywhere along a continuum from very favorable to very unfavorable. âĒThird, attitudes are directed toward some object about which a person has feelings( sometimes called âaffectâ) and beliefs.
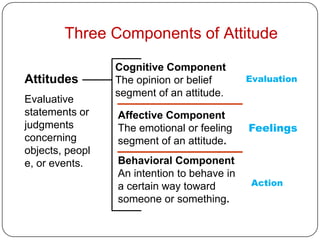
- 4. Three Components of Attitude Cognitive Component Attitudes The opinion or belief Evaluation segment of an attitude. Evaluative statements or Affective Component judgments The emotional or feeling Feelings concerning segment of an attitude. objects, peopl e, or events. Behavioral Component An intention to behave in a certain way toward Action someone or something.
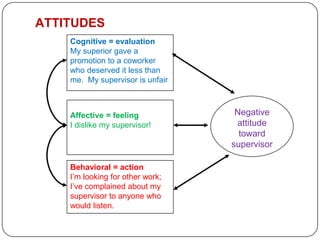
- 5. ATTITUDES Cognitive = evaluation My superior gave a promotion to a coworker who deserved it less than me. My supervisor is unfair. Affective = feeling Negative I dislike my supervisor! attitude toward supervisor Behavioral = action Iâm looking for other work; Iâve complained about my supervisor to anyone who would listen.
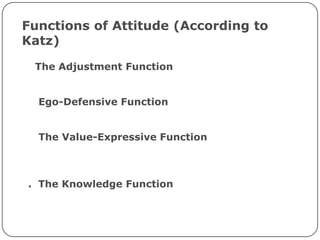
- 6. Functions of Attitude (According to Katz) 1. The Adjustment Function. Attitudes often help people to adjust to their work environment. 2. Ego-Defensive Function. Attitudes help people to retain their dignity and self- image. 3. The Value-Expressive Function. Attitudes provide individuals with a basis for expressing their values. 4. The Knowledge Function. Attitudes provide standards and frames of reference that allow people to understand and perceive the world around him.
- 7. Changing Attitudes Employeesâ attitudes can be changed and sometimes it is in the best interests of managements to try to do so. For example, if employees believe that their employer does not look after their welfare, the management should try to change their attitude and help develop a more positive attitude in them. However, the process of changing the attitude is not always easy.
- 8. Changing Attitudes Some of the possible ways of changing attitudes : ïž Providing New Information. ïž Use of Fear ïž Resolving Discrepancies ïž Influence of friends and peer ïž Co-opting
- 9. Important Attitudes Related to Organizations ï Job Satisfaction - Is a set of favorable or unfavorable feelings and emotions with which employees view their work. ï Job Involvement - The degree to which a person identifies with a job, actively participates in it, and considers performance important to self-worth. ï Organizational Commitment - The degree to which an employee identifies with a particular organization and its goals and wishes to maintain membership in the organization
- 10. Job Satisfaction ï A collection of positive and/or negative feelings that an individual holds toward his or her job âĒ A high level of job satisfaction equals positive attitudes toward the job and vice versa. âĒ Employee attitudes and job satisfaction are frequently used interchangeably. âĒ Often when people speak of âemployee attitudesâ they mean âemployee job satisfaction.â
- 11. Job Satisfaction ïž A pleasurable emotional state resulting from the appraisal of oneâs job or job experiences (Locke, 1976). ïž An employeeâs cognitive and affective evaluation of his or her job
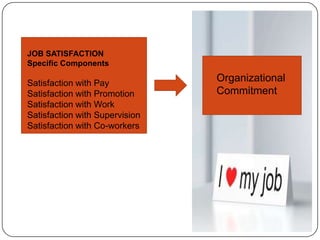
- 12. JOB SATISFACTION Specific Components Satisfaction with Pay Organizational Satisfaction with Promotion Commitment Satisfaction with Work Satisfaction with Supervision Satisfaction with Co-workers
- 13. How Are Employee Attitudes Measured? ï The most popular method for getting information about employee attitudes is through attitude surveys. ï Using attitude surveys on a regular basis provides managers with valuable feedback on how employees perceive their working conditions. Managers present the employee with set statements or questions to obtain specific information. Individual Responses are then combined and analyzed
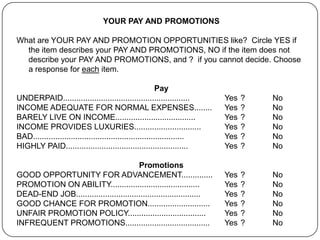
- 16. YOUR PAY AND PROMOTIONS What are YOUR PAY AND PROMOTION OPPORTUNITIES like? Circle YES if the item describes your PAY AND PROMOTIONS, NO if the item does not describe your PAY AND PROMOTIONS, and ? if you cannot decide. Choose a response for each item. Pay UNDERPAID......................................................... Yes ? No INCOME ADEQUATE FOR NORMAL EXPENSES........ Yes ? No BARELY LIVE ON INCOME.................................... Yes ? No INCOME PROVIDES LUXURIES.............................. Yes ? No BAD.................................................................... Yes ? No HIGHLY PAID....................................................... Yes ? No Promotions GOOD OPPORTUNITY FOR ADVANCEMENT.............. Yes ? No PROMOTION ON ABILITY........................................ Yes ? No DEAD-END JOB........................................................ Yes ? No GOOD CHANCE FOR PROMOTION............................ Yes ? No UNFAIR PROMOTION POLICY................................... Yes ? No INFREQUENT PROMOTIONS...................................... Yes ? No
- 17. Causes of Job Satisfaction ï Most people prefer work that is challenging and stimulating. ï Jobs with good compensation have average job satisfaction levels. Money may be a motivator, but may not stimulate job satisfaction. ï There is a link between a personâs personality and job satisfaction. Negative people are usually not satisfied with their jobs.
- 18. The Effect of Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance Satisfaction and Productivity ïžSatisfied workers are more productive AND more productive workers are more satisfied! ïžWorker productivity is higher in organizations with more satisfied workers. Satisfaction and Absenteeism ïžSatisfied employees have fewer avoidable absences.
- 19. Satisfaction and Turnover ïžSatisfied employees are less likely to quit. ïžOrganizations take actions to retain high performers and to weed out lower performers. Satisfaction and Customer Satisfaction ïžSatisfied workers provide better customer service.
- 20. Satisfied employees increase customer satisfaction because: ïž They are more friendly, upbeat, and responsive. ïž They are less likely to turnover, which helps build long-term customer relationships. Job satisfaction & organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) ïžSatisfied employees who feel fairly treated by and are trusting of the organization are more willing to engage in behaviors that go beyond the normal expectations of their job.
- 21. âPleasure in the Job puts perfection in the workâ - Aristotle âThe best way to appreciate your job is to imagine yourself without one.â - Oscar Wilde