Augmented Reality
0 likes19 views
3D file formats are used to store 3D model information such as geometry, appearance, scene, and animations. Common 3D file formats include STL, OBJ, FBX, COLLADA, 3DS, IGES, STEP, and X3D. STL is one of the most important neutral formats and encodes surface geometry using triangular meshes. OBJ also supports surface geometry encoding and stores appearance separately. FBX supports geometry, appearance, and skeletal animations. COLLADA supports geometry, appearance properties, animation, and physics.
1 of 16
Download to read offline













Ad
Recommended
Solid modeling
Solid modelingDhruv Shah
Ėý
Solid modeling represents 3D objects on a computer by providing surfaces and filling in spaces to make objects appear solid. It allows for accurate mass property calculations, hidden surface removal, and shaded renderings. Solid models are the preferred format for CAD as they provide an unambiguous representation that can be used for simulation, analysis of properties like volume and inertia, and manufacturing. There are three main types - wireframe, surface, and solid - with solid models being the most complete representation. Solid modeling has applications in engineering, entertainment, medicine, and more.PPT s12-machine vision-s2
PPT s12-machine vision-s2Binus Online Learning
Ėý
This document provides an overview of machine vision applications including content-based image retrieval and face recognition. It discusses how content-based image retrieval systems work by extracting image features, calculating distances between images, and returning similar images from a database based on a query image. Examples of content-based image retrieval systems and the features they use are described. The document also covers face detection and recognition techniques, including the use of eigenfaces which represent faces as locations in a lower-dimensional space.Solidmodelling
Solidmodellingjntuhcej
Ėý
Solid modeling techniques have evolved from wireframe models, which only contained edges and vertices, to surface models, which added exterior surfaces, to solid models, which provide complete interior and exterior details. Solid modeling represents objects unambiguously and allows for engineering analysis. There are various representations of solid models, including boundary representations (B-reps), constructive solid geometry (CSG), and spatial partitioning. Boundary representations store topological data on how faces, edges, and vertices are connected, while CSG constructs solids using boolean operations on primitive shapes.PPT s01-machine vision-s2
PPT s01-machine vision-s2Binus Online Learning
Ėý
This document provides an overview of an introduction to machine vision course. The course introduces concepts of machine vision including image formation and filtering. It addresses machine vision techniques such as feature detection, extraction, and pattern recognition. Students will explore applications and learn about enabling technologies. The course involves assignments, midterm and final exams to assess learning outcomes including understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and designing approaches related to machine vision. Related fields, optical illusions, sample applications, software, and resources are also discussed.PPT s06-machine vision-s2
PPT s06-machine vision-s2Binus Online Learning
Ėý
This document provides an overview of feature detection techniques in machine vision, including edge detection, the Canny edge detector, interest points, and the Harris corner detector. It describes how edge detection works by finding discontinuities in images using masks and correlation. It explains that the Canny edge detector is an optimal method that uses Gaussian smoothing and non-maximum suppression. Interest points are localized features useful for applications like image alignment, and the Harris corner detector computes gradients to find locations with dominant directions, identifying corners.CSG
CSGselvakumar948
Ėý
This document discusses Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) which is a technique for generating complex 3D solid objects by combining primitive solid objects using set-theoretic operations like union, intersection, and difference. It describes how CSG trees represent objects and how ray tracing can be used to render CSG models by traversing the tree. It also covers calculating properties of CSG objects like volume and mass approximation through ray tracing.presentation on solid manipulation in computer aided design
presentation on solid manipulation in computer aided designRakshit vadi
Ėý
Solid manipulation involves evaluating and modifying 3D solids. It includes displaying solids as wireframes or shaded images, evaluating points and intersections on solids, trimming solids using boundary surfaces, splitting solids into sub-solids through segmentation, applying transformations like translation and rotation, and editing solids by changing their geometry or topology using their CSG trees. The document then describes each of these solid manipulation techniques in more detail.Solid modelling cg
Solid modelling cgNareek
Ėý
2D drawings are not ideal for representing 3D objects as they lack a Z axis. There are three main types of 3D models: wireframe, surface, and solid models. Wireframe models only contain edges and vertices and cannot represent complex surfaces. Surface models include edges, vertices and exterior surfaces but provide no interior details. Solid models are the current standard as they contain edges, vertices, exterior surfaces and interior details, providing an unambiguous representation of an object that can be used for engineering analysis.Solid Modeling Schemes CAM
Solid Modeling Schemes CAMCDO
Ėý
This document provides an overview of solid modeling schemes and techniques. It discusses six common solid modeling representations: spatial enumeration, cell decomposition, boundary representation, sweep methods, primitive instancing, and constructive solid geometry. It focuses on the last three techniques, which are most commonly used in modeling packages. Constructive solid geometry uses basic shapes combined with Boolean operations. Boundary representation describes a solid using its enclosing faces, edges and vertices. The document provides examples of both techniques and discusses how solid models allow designers to determine important properties and make design changes more easily compared to other modeling types.Solids[1]
Solids[1]Abhishek Kapoor
Ėý
Solid models in mechanical engineering are used for graphics, design, manufacturing, and assembly applications. There are three forms of solid model representation: wireframe, surface, and solid models. Solid models are the preferred form as they can calculate mass properties and perform other analyses. Solid models must be bounded, three-dimensional, and finite. They can be created using constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation (B-rep), or sweeping schemes. CSG combines primitives like blocks and cylinders using operations like union and subtraction. B-rep models surfaces and calculates volumetric properties. Sweeping extrudes a 2D sketch along a path.Introduction to solid modeling
Introduction to solid modeling*noT yeT workinG! !M stilL studyinG*
Ėý
This document discusses different methods of 3D modeling, including wireframe modeling, surface modeling, and solid modeling. It provides details on each modeling method, including their advantages and disadvantages. For example, wireframe modeling only contains edge information and cannot represent actual solids, while solid modeling defines enclosed volumes and allows simulation under real-life conditions. The document also covers specific solid modeling techniques like boundary representation and constructive solid geometry, as well as parametric modeling concepts.object 3d(1)
object 3d(1)HiteshJain007
Ėý
The document discusses several methods for solid modeling representation: voxels, quadtrees and octrees, binary space partitions (BSP), and constructive solid geometry (CSG). Voxels represent space as a 3D grid but require large storage. Quadtrees and octrees refine voxel resolution hierarchically. BSPs recursively partition space with planes into convex regions. CSG represents solids as a hierarchy of boolean operations on primitives. Each method has advantages and disadvantages for storage, acquisition, display, and boolean operations.ppt of solid modeling for cad
ppt of solid modeling for cadAyush Upadhyay
Ėý
This document discusses different types of 3D modeling including wireframe models, surface models, and solid models. It focuses on solid modeling which provides a complete, valid, and unambiguous geometric representation of physical objects. Solid models contain geometric and topological data and can be represented using constructive solid geometry (CSG) which constructs objects by combining simpler solid objects called primitives using Boolean set operations like union, intersection, and difference. CSG starts with basic primitives that are combined and recombined to model complex objects.Various object detection and tracking methods
Various object detection and tracking methodssujeeshkumarj
Ėý
This document provides an overview of various object detection and tracking methods. It discusses Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) for object detection, which extracts keypoints that are invariant to scale, orientation and illumination changes. It also covers You Only Look Once (YOLO) for real-time object detection using a single neural network, and Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) for human detection. For object tracking, it discusses point tracking using deterministic and statistical methods, kernel tracking using template matching, and silhouette tracking for complex object shapes. Applications mentioned include video surveillance, autonomous vehicles, and human-computer interaction.Object tracking presentation
Object tracking presentationMrsShwetaBanait1
Ėý
This presentation by Shweta Kanhere-Banait discusses object tracking in computer vision, including its definition, classifications, algorithms, challenges, applications, and future work. Object tracking is important in various fields such as security and human-computer interaction, while highlighting the roles of different tracking algorithms and their challenges, including appearance changes and occlusions. Future improvements in automatic feature selection and contextual information usage are suggested to enhance tracking accuracy.Image Segmentation using Otsu's Method - Computer Graphics (UCS505) Project R...
Image Segmentation using Otsu's Method - Computer Graphics (UCS505) Project R...Akshit Arora
Ėý
This project report describes the implementation of Otsu's method for image segmentation. Otsu's method is a global thresholding technique that automatically performs image thresholding. It finds the optimal threshold to separate foreground objects from the background by minimizing intra-class variance. The report provides an overview of image segmentation and thresholding techniques. It explains Otsu's algorithm and how it maximizes between-class variance. Results of applying Otsu's method on sample images using histogram analysis, the graythresh function, and adaptive thresholding are presented. The report concludes that Otsu's method is a simple and effective approach for automatic image thresholding and segmentation.PPT s11-machine vision-s2
PPT s11-machine vision-s2Binus Online Learning
Ėý
This document provides an overview of image matching techniques. It defines image matching as geometrically aligning two images so corresponding pixels represent the same scene region. Key aspects covered include detecting invariant local features, describing features in a scale and rotation invariant way using SIFT, and matching features between images. SIFT is highlighted as an extraordinarily robust technique that can handle various geometric and illumination changes. Feature matching is used in many computer vision applications such as image alignment, 3D reconstruction, and object recognition.LN s11-machine vision-s2
LN s11-machine vision-s2Binus Online Learning
Ėý
The document discusses machine vision and image matching. It begins with definitions of image matching as the process of geometrically positioning two images so their pixels represent the same physical areas. It describes extracting local invariant features from images using methods like Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) to find correspondences between images for tasks like object recognition and panorama creation despite variations in lighting, viewpoint and scale. SIFT extracts key points from images and represents each with a 128-element feature vector for robust matching between images.Object tracking final
Object tracking finalMrsShwetaBanait1
Ėý
This presentation provides an overview of object tracking, outlining its importance in computer vision and various applications, from security to interface development. It covers definitions, classifications, algorithms, challenges, and future directions for enhancing tracking accuracy through automatic feature selection. The discussion emphasizes the necessity to address issues like occlusion and re-identification in real-time tracking scenarios.Computer Vision Workshop
Computer Vision WorkshopHelen Tabunshchyk
Ėý
This document discusses computer vision using OpenCV. It provides examples of how computer vision is used today in applications like optical character recognition, machine inspection, retail, medical imaging, and surveillance. It also discusses consumer applications of computer vision like photo stitching, exposure bracketing, and face detection. The document gives a brief history of computer vision from early algorithms in the 1970s to modern algorithms and applications. It introduces OpenCV, an open source library for computer vision, and describes its features and community support. Finally, it discusses different approaches to motion detection in computer vision like optic, infrared, sound, and magnetic sensors.3D theory: geometry, extrusion, co-ordinate theory
3D theory: geometry, extrusion, co-ordinate theoryiain bruce
Ėý
This document provides information about 3D modeling and the software Blender. It discusses how 3D is used in games, animation, and film for assets, environments, characters, and visual effects. Blender is introduced as a free and open-source 3D modeling software with strengths in flexibility but weaknesses in documentation. Key features covered include add-ons, file formats, geometry elements like vertices and polygons, surfaces, primitives, and Cartesian coordinates. Box modeling is also defined. The next topic will be on rendering and the graphics pipeline.STL Format: 3D Printing & Modeling Standard"
STL Format: 3D Printing & Modeling Standard"IshanKakad1
Ėý
The STL file format is primarily used for 3D models, encoding surface geometry through tessellation without including color or texture. It is widely adopted in 3D printing and CAD programs due to its universal compatibility and efficiency in representing single-material designs. While it offers advantages like widespread support and a robust ecosystem, it has limitations such as large file sizes for high fidelity and inability to store metadata.3D Models and their Primary Characteristics
3D Models and their Primary CharacteristicsVeetil Digital Service
Ėý
3D modeling has become widely popular in various industries, including gaming, film, medicine, and engineering, with applications in creating and visualizing complex objects. The document outlines different types of 3D models, such as solid and shell models, and discusses modeling techniques like NURBS and polygonal modeling, which are essential for creating detailed 3D representations. It also emphasizes the importance of texturing and shading techniques to enhance the realism of 3D objects.abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstCGR_Unit-1.pptx
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstCGR_Unit-1.pptx220komal4002
Ėý
The document provides an overview of computer graphics, detailing its definition, applications, and basic terms such as images, objects, pixels, and resolutions. It discusses various coordinate systems used in 2D and 3D graphics, including Cartesian, polar, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Additionally, it covers file formats for graphics, their characteristics, and how they store digital images, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of formats like TIFF, BMP, JPEG, GIF, PNG, and PCX.A (very brief) Introduction to Image Processing and 3D Printing with ImageJ
A (very brief) Introduction to Image Processing and 3D Printing with ImageJPaul Mignone, Ph.D
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to image processing using ImageJ, focusing on digital images, their representation, and processing techniques. It covers essential concepts such as image resolution, sampling, quantization, image histograms, and various processing methods including image filtering and segmentation. Additionally, it outlines practical demonstrations using ImageJ and Meshmixer for analyzing and processing microstructural images.Game Programming Syllabus for B.Tech Final Year
Game Programming Syllabus for B.Tech Final YearAvinashAvuthu2
Ėý
The document outlines a game programming course led by Dr. A. Avinash at Vellore Institute of Technology, covering essential technologies and techniques used in the game industry, game design processes, and development mechanics. Course outcomes include the ability to design, develop, and document games using modern programming tools and methods. The curriculum encompasses various modules including game engine architecture, graphics and mathematics, lighting and texturing, game physics, artificial intelligence, and virtual and augmented reality applications.introduction_to_solid_modeling__1_.pptx
introduction_to_solid_modeling__1_.pptxKhalil Alhatab
Ėý
Geometric modeling involves creating mathematical representations of geometric objects using CAD software. There are three main types of geometric models: wireframe models using lines and curves, surface models representing an object's surface, and solid models representing the complete volumetric shape. Solid modeling is now the most common approach as it allows for properties like mass to be calculated and enables applications like finite element analysis. Geometric models can be created using set operations in constructive solid geometry or parametric modeling techniques.Introduction image features
Introduction image featurespayalshah14
Ėý
This document discusses image features and their representation. It defines image features as a reduced representation of input image data. The main types of features discussed are pixel-level, local, and global features. Local features include edge detection, corner detection, and color features. Color features can be represented using histograms that count the number of pixels for each color value. The document also discusses different techniques for representing detected edges, including simple representation, chain codes, slope representation and signatures. Histograms are described as a common method for color feature representation.2015 10-08 - additive manufacturing software 1
2015 10-08 - additive manufacturing software 1Biofabrication Group at University of Pisa
Ėý
The document discusses the advancements in additive manufacturing and its applications in medical fields such as orthodontics and tissue engineering. It outlines the process flow for additive manufacturing, including software used for CAD modeling, STL file generation, and image analysis for biofabrication. Additionally, it highlights the need for new file formats tailored to the additive manufacturing community to improve interoperability and functionality.Ciencias de la computaciÃģn, GrÃĄficos por computadora.
Ciencias de la computaciÃģn, GrÃĄficos por computadora.Watchsoft
Ėý
The document provides an overview of computer graphics, highlighting key textbooks and resources, introduction to graphics tools, and their applications in various fields such as film, web design, and simulation. It explains the types of graphics input devices and the functionalities of graphics software and libraries, with a focus on OpenGL as a widely used graphics library. Additionally, it discusses the hardware involved in graphics display including raster and line-drawing devices, along with the process of creating and manipulating graphical images.More Related Content
What's hot (12)
Solid Modeling Schemes CAM
Solid Modeling Schemes CAMCDO
Ėý
This document provides an overview of solid modeling schemes and techniques. It discusses six common solid modeling representations: spatial enumeration, cell decomposition, boundary representation, sweep methods, primitive instancing, and constructive solid geometry. It focuses on the last three techniques, which are most commonly used in modeling packages. Constructive solid geometry uses basic shapes combined with Boolean operations. Boundary representation describes a solid using its enclosing faces, edges and vertices. The document provides examples of both techniques and discusses how solid models allow designers to determine important properties and make design changes more easily compared to other modeling types.Solids[1]
Solids[1]Abhishek Kapoor
Ėý
Solid models in mechanical engineering are used for graphics, design, manufacturing, and assembly applications. There are three forms of solid model representation: wireframe, surface, and solid models. Solid models are the preferred form as they can calculate mass properties and perform other analyses. Solid models must be bounded, three-dimensional, and finite. They can be created using constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation (B-rep), or sweeping schemes. CSG combines primitives like blocks and cylinders using operations like union and subtraction. B-rep models surfaces and calculates volumetric properties. Sweeping extrudes a 2D sketch along a path.Introduction to solid modeling
Introduction to solid modeling*noT yeT workinG! !M stilL studyinG*
Ėý
This document discusses different methods of 3D modeling, including wireframe modeling, surface modeling, and solid modeling. It provides details on each modeling method, including their advantages and disadvantages. For example, wireframe modeling only contains edge information and cannot represent actual solids, while solid modeling defines enclosed volumes and allows simulation under real-life conditions. The document also covers specific solid modeling techniques like boundary representation and constructive solid geometry, as well as parametric modeling concepts.object 3d(1)
object 3d(1)HiteshJain007
Ėý
The document discusses several methods for solid modeling representation: voxels, quadtrees and octrees, binary space partitions (BSP), and constructive solid geometry (CSG). Voxels represent space as a 3D grid but require large storage. Quadtrees and octrees refine voxel resolution hierarchically. BSPs recursively partition space with planes into convex regions. CSG represents solids as a hierarchy of boolean operations on primitives. Each method has advantages and disadvantages for storage, acquisition, display, and boolean operations.ppt of solid modeling for cad
ppt of solid modeling for cadAyush Upadhyay
Ėý
This document discusses different types of 3D modeling including wireframe models, surface models, and solid models. It focuses on solid modeling which provides a complete, valid, and unambiguous geometric representation of physical objects. Solid models contain geometric and topological data and can be represented using constructive solid geometry (CSG) which constructs objects by combining simpler solid objects called primitives using Boolean set operations like union, intersection, and difference. CSG starts with basic primitives that are combined and recombined to model complex objects.Various object detection and tracking methods
Various object detection and tracking methodssujeeshkumarj
Ėý
This document provides an overview of various object detection and tracking methods. It discusses Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) for object detection, which extracts keypoints that are invariant to scale, orientation and illumination changes. It also covers You Only Look Once (YOLO) for real-time object detection using a single neural network, and Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) for human detection. For object tracking, it discusses point tracking using deterministic and statistical methods, kernel tracking using template matching, and silhouette tracking for complex object shapes. Applications mentioned include video surveillance, autonomous vehicles, and human-computer interaction.Object tracking presentation
Object tracking presentationMrsShwetaBanait1
Ėý
This presentation by Shweta Kanhere-Banait discusses object tracking in computer vision, including its definition, classifications, algorithms, challenges, applications, and future work. Object tracking is important in various fields such as security and human-computer interaction, while highlighting the roles of different tracking algorithms and their challenges, including appearance changes and occlusions. Future improvements in automatic feature selection and contextual information usage are suggested to enhance tracking accuracy.Image Segmentation using Otsu's Method - Computer Graphics (UCS505) Project R...
Image Segmentation using Otsu's Method - Computer Graphics (UCS505) Project R...Akshit Arora
Ėý
This project report describes the implementation of Otsu's method for image segmentation. Otsu's method is a global thresholding technique that automatically performs image thresholding. It finds the optimal threshold to separate foreground objects from the background by minimizing intra-class variance. The report provides an overview of image segmentation and thresholding techniques. It explains Otsu's algorithm and how it maximizes between-class variance. Results of applying Otsu's method on sample images using histogram analysis, the graythresh function, and adaptive thresholding are presented. The report concludes that Otsu's method is a simple and effective approach for automatic image thresholding and segmentation.PPT s11-machine vision-s2
PPT s11-machine vision-s2Binus Online Learning
Ėý
This document provides an overview of image matching techniques. It defines image matching as geometrically aligning two images so corresponding pixels represent the same scene region. Key aspects covered include detecting invariant local features, describing features in a scale and rotation invariant way using SIFT, and matching features between images. SIFT is highlighted as an extraordinarily robust technique that can handle various geometric and illumination changes. Feature matching is used in many computer vision applications such as image alignment, 3D reconstruction, and object recognition.LN s11-machine vision-s2
LN s11-machine vision-s2Binus Online Learning
Ėý
The document discusses machine vision and image matching. It begins with definitions of image matching as the process of geometrically positioning two images so their pixels represent the same physical areas. It describes extracting local invariant features from images using methods like Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) to find correspondences between images for tasks like object recognition and panorama creation despite variations in lighting, viewpoint and scale. SIFT extracts key points from images and represents each with a 128-element feature vector for robust matching between images.Object tracking final
Object tracking finalMrsShwetaBanait1
Ėý
This presentation provides an overview of object tracking, outlining its importance in computer vision and various applications, from security to interface development. It covers definitions, classifications, algorithms, challenges, and future directions for enhancing tracking accuracy through automatic feature selection. The discussion emphasizes the necessity to address issues like occlusion and re-identification in real-time tracking scenarios.Computer Vision Workshop
Computer Vision WorkshopHelen Tabunshchyk
Ėý
This document discusses computer vision using OpenCV. It provides examples of how computer vision is used today in applications like optical character recognition, machine inspection, retail, medical imaging, and surveillance. It also discusses consumer applications of computer vision like photo stitching, exposure bracketing, and face detection. The document gives a brief history of computer vision from early algorithms in the 1970s to modern algorithms and applications. It introduces OpenCV, an open source library for computer vision, and describes its features and community support. Finally, it discusses different approaches to motion detection in computer vision like optic, infrared, sound, and magnetic sensors.Similar to Augmented Reality (20)
3D theory: geometry, extrusion, co-ordinate theory
3D theory: geometry, extrusion, co-ordinate theoryiain bruce
Ėý
This document provides information about 3D modeling and the software Blender. It discusses how 3D is used in games, animation, and film for assets, environments, characters, and visual effects. Blender is introduced as a free and open-source 3D modeling software with strengths in flexibility but weaknesses in documentation. Key features covered include add-ons, file formats, geometry elements like vertices and polygons, surfaces, primitives, and Cartesian coordinates. Box modeling is also defined. The next topic will be on rendering and the graphics pipeline.STL Format: 3D Printing & Modeling Standard"
STL Format: 3D Printing & Modeling Standard"IshanKakad1
Ėý
The STL file format is primarily used for 3D models, encoding surface geometry through tessellation without including color or texture. It is widely adopted in 3D printing and CAD programs due to its universal compatibility and efficiency in representing single-material designs. While it offers advantages like widespread support and a robust ecosystem, it has limitations such as large file sizes for high fidelity and inability to store metadata.3D Models and their Primary Characteristics
3D Models and their Primary CharacteristicsVeetil Digital Service
Ėý
3D modeling has become widely popular in various industries, including gaming, film, medicine, and engineering, with applications in creating and visualizing complex objects. The document outlines different types of 3D models, such as solid and shell models, and discusses modeling techniques like NURBS and polygonal modeling, which are essential for creating detailed 3D representations. It also emphasizes the importance of texturing and shading techniques to enhance the realism of 3D objects.abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstCGR_Unit-1.pptx
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstCGR_Unit-1.pptx220komal4002
Ėý
The document provides an overview of computer graphics, detailing its definition, applications, and basic terms such as images, objects, pixels, and resolutions. It discusses various coordinate systems used in 2D and 3D graphics, including Cartesian, polar, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Additionally, it covers file formats for graphics, their characteristics, and how they store digital images, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of formats like TIFF, BMP, JPEG, GIF, PNG, and PCX.A (very brief) Introduction to Image Processing and 3D Printing with ImageJ
A (very brief) Introduction to Image Processing and 3D Printing with ImageJPaul Mignone, Ph.D
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to image processing using ImageJ, focusing on digital images, their representation, and processing techniques. It covers essential concepts such as image resolution, sampling, quantization, image histograms, and various processing methods including image filtering and segmentation. Additionally, it outlines practical demonstrations using ImageJ and Meshmixer for analyzing and processing microstructural images.Game Programming Syllabus for B.Tech Final Year
Game Programming Syllabus for B.Tech Final YearAvinashAvuthu2
Ėý
The document outlines a game programming course led by Dr. A. Avinash at Vellore Institute of Technology, covering essential technologies and techniques used in the game industry, game design processes, and development mechanics. Course outcomes include the ability to design, develop, and document games using modern programming tools and methods. The curriculum encompasses various modules including game engine architecture, graphics and mathematics, lighting and texturing, game physics, artificial intelligence, and virtual and augmented reality applications.introduction_to_solid_modeling__1_.pptx
introduction_to_solid_modeling__1_.pptxKhalil Alhatab
Ėý
Geometric modeling involves creating mathematical representations of geometric objects using CAD software. There are three main types of geometric models: wireframe models using lines and curves, surface models representing an object's surface, and solid models representing the complete volumetric shape. Solid modeling is now the most common approach as it allows for properties like mass to be calculated and enables applications like finite element analysis. Geometric models can be created using set operations in constructive solid geometry or parametric modeling techniques.Introduction image features
Introduction image featurespayalshah14
Ėý
This document discusses image features and their representation. It defines image features as a reduced representation of input image data. The main types of features discussed are pixel-level, local, and global features. Local features include edge detection, corner detection, and color features. Color features can be represented using histograms that count the number of pixels for each color value. The document also discusses different techniques for representing detected edges, including simple representation, chain codes, slope representation and signatures. Histograms are described as a common method for color feature representation.2015 10-08 - additive manufacturing software 1
2015 10-08 - additive manufacturing software 1Biofabrication Group at University of Pisa
Ėý
The document discusses the advancements in additive manufacturing and its applications in medical fields such as orthodontics and tissue engineering. It outlines the process flow for additive manufacturing, including software used for CAD modeling, STL file generation, and image analysis for biofabrication. Additionally, it highlights the need for new file formats tailored to the additive manufacturing community to improve interoperability and functionality.Ciencias de la computaciÃģn, GrÃĄficos por computadora.
Ciencias de la computaciÃģn, GrÃĄficos por computadora.Watchsoft
Ėý
The document provides an overview of computer graphics, highlighting key textbooks and resources, introduction to graphics tools, and their applications in various fields such as film, web design, and simulation. It explains the types of graphics input devices and the functionalities of graphics software and libraries, with a focus on OpenGL as a widely used graphics library. Additionally, it discusses the hardware involved in graphics display including raster and line-drawing devices, along with the process of creating and manipulating graphical images.Computer Vision UNit 3 Presentaion šÝšÝßĢ
Computer Vision UNit 3 Presentaion šÝšÝßĢMilanBhalodiya2
Ėý
The document outlines various feature detection techniques in image processing, including edge, corner, line detection, and active contours. It discusses methods such as Prewitt, Sobel, Laplacian, and Canny edge detection, as well as feature descriptors like SIFT and HOG. Additionally, it explains image segmentation techniques through active contours and discusses image matching challenges and techniques for identifying keypoints and their characteristics.Data structures
Data structuresAshish Kumar
Ėý
The document discusses different data structures used to represent image data at various levels of abstraction, from low-level pixel matrices to higher-level relational models. It describes iconic and segmented image representations, as well as geometric, relational, and hierarchical structures like matrices, chains, graphs, run-length coding, pyramids, and quadtrees. These data structures organize image information to facilitate image analysis algorithms.Building 3D content to last
Building 3D content to lastJISC Digital Media
Ėý
The document discusses the challenges and best practices in building and sharing 3D content, focusing on file formats, metadata, and the need for a culture of data reuse. It highlights the variety of 3D file formats in use, the importance of significant properties to be maintained in digital records, and the ongoing requirement for community-defined metadata standards. The conclusion emphasizes the complexity of sharing 3D content and the need for collaboration between content creators and repositories to ensure preservation.Lecture 1.1 - Terms & Concepts
Lecture 1.1 - Terms & Conceptsmgordon320
Ėý
This document provides an overview of key terms and concepts for an introductory 3D modeling class. It discusses the Cartesian coordinate system used in 3D modeling programs. It also defines different types of 3D modeling like polygon mesh modeling and NURBS. Additionally, it covers terminology around 3D files, image files, and rendering. Students are asked to install software and be prepared to ask questions in the next class.Chap_9_Representation_and_Description.pdf
Chap_9_Representation_and_Description.pdfssuser1ecccc
Ėý
The document discusses various concepts in digital image processing, focusing on image representation and description, including segmentation, boundary following, and polygonal approximations. Key methods depicted include low, mid, and high-level processing, as well as techniques for encoding contours such as chain codes and minimum-perimeter polygons. It highlights the importance of appropriate representation formats for effective image analysis and object recognition.Chap_9_Representation_and_Description.pdf
Chap_9_Representation_and_Description.pdfssuser1ecccc
Ėý
The document discusses various concepts in digital image processing, focusing on image representation and description, including segmentation, boundary following, and polygonal approximations. Key methods depicted include low, mid, and high-level processing, as well as techniques for encoding contours such as chain codes and minimum-perimeter polygons. It highlights the importance of appropriate representation formats for effective image analysis and object recognition.Digital Image Processing Unit 2 ppt.pptx
Digital Image Processing Unit 2 ppt.pptxen21cs301047
Ėý
This document covers various topics in digital image processing, including imaging geometry, image acquisition systems, and transformations like the Fourier Transform. It explains the importance of imaging parameters and geometric operations such as translation, scaling, and rotation in enhancing image quality. Moreover, it discusses types of digital images, including binary, grayscale, and color images, as well as the applications of Fourier Transform and Discrete Cosine Transform in image analysis and compression.Modelling - Third dimension.pptx
Modelling - Third dimension.pptxAliya Fathima Ilyas
Ėý
The document discusses a conceptual and logical model for 3D spatial analysis and visualization using a simplified spatial model (SSM) that incorporates geometric abstractions such as points, lines, surfaces, and bodies. It elaborates on the relationships and interactions between these spatial objects and presents a server-oriented prototype system that enables remote querying and visualization of 3D information. The model aims to support complex spatial queries and facilitate data collection and object reconstruction from aerial photographs and CAD formats.Solid Modelling in computer aided Design
Solid Modelling in computer aided Designrahulkatre9
Ėý
Solid models provide more complete representations of objects than surface or wireframe models by including topological information about connectivity in addition to geometric information. Solid models allow for accurate design and further automation in manufacturing. They represent objects fully using primitives that can be combined through Boolean operations. Major solid modeling schemes include boundary representation, constructive solid geometry, and sweeping which use primitives, instances, and operations on primitives to build valid solid models.Game development terminologies
Game development terminologiesAhmed Badr
Ėý
The document outlines various game terminologies and concepts related to computer graphics, including the RGB color model, pixel art, texture mapping, and rendering techniques. It covers essential terminology such as sprites, polygons, models, and animation methods like skeletal and procedural animation. Additionally, it discusses advanced topics like lightmaps, ray tracing, and the role of game engines in video game development.Ad
Augmented Reality
- 2. What is 3D File Format File that used to store information of about 3D Models in format of plain text or binary data. Like Geometry, appearance, scene and animations.
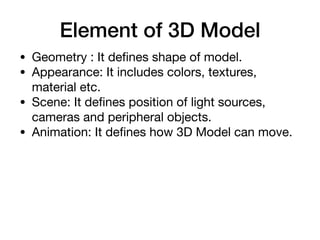
- 3. Element of 3D Model âĒ Geometry : It deïŽnes shape of model. âĒ Appearance: It includes colors, textures, material etc. âĒ Scene: It deïŽnes position of light sources, cameras and peripheral objects. âĒ Animation: It deïŽnes how 3D Model can move.
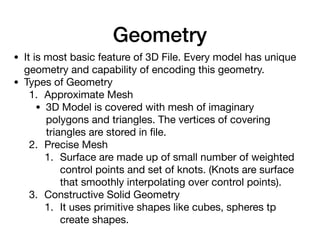
- 4. Geometry âĒ It is most basic feature of 3D File. Every model has unique geometry and capability of encoding this geometry. âĒ Types of Geometry 1. Approximate Mesh âĒ 3D Model is covered with mesh of imaginary polygons and triangles. The vertices of covering triangles are stored in ïŽle. 2. Precise Mesh 1. Surface are made up of small number of weighted control points and set of knots. (Knots are surface that smoothly interpolating over control points). 3. Constructive Solid Geometry 1. It uses primitive shapes like cubes, spheres tp create shapes.
- 5. Appearance Appearance describes surface properties like material type, texture, color etc. Appearance can be encoded in two ways 1. Texture Mapping âĒ Every point in 3D Modelâs surface is mapped into 2D image and 2D Image coordinates have attributes like texture, color etc. Rendering 3D Model, every surface point is assigned a coordinate in 2D Image. 2. Face Attributes âĒ It stores texture information by assigning each face of mesh attributes. Surface can have specular component indicating the color and intensity of true mirror reïŽections of light sources and other near surfaces. This component is encoded by transmissive component describing color and intensity of light that passing through surface.
- 6. Scene Information âĒ The scene describes layout of 3D Model in terms of cameras, light sources and other 3D Model. âĒ Camera is deïŽned by four parameters: magniïŽcation, principal point, location, direction. âĒ Light source means nature of light like location, color and intensity of it. âĒ Storing other nearby 3D Model is required when model is consist of diïŽerent parts and needs to certain way to make up the scene.
- 7. Animation Animation deïŽnes how 3D Model can move. 3D Animating ways 1. Skeletal Animation 1. Each model is associated with underlying skeleton. The skeleton is made out of hierarchy of virtual âbonesâ. Movement of bones higher in the hierarchy aïŽect the bones lower in hierarchy. Like Human body. Bones are connected by âjointsâ. Joints deïŽnes constraints in the possible transformations for bones, to restricting how bone can move in relation to its parent. 2. Techniques of Animation 1. To store animations of skeletal structures, diïŽerent techniques can be used. E.g. forward kinematics, inverse kinematics, keyframes etc.
- 8. File Types âĒ STL âĒ OBJ âĒ FBX âĒ COLLADA âĒ 3DS âĒ IGES âĒ STEP âĒ X3D
- 9. STL (STereoLithography) âĒ STL is one of most important neutral 3D ïŽle formats. âĒ One of oldest 3D ïŽle format. âĒ STL encodes surface geometry of 3D model using triangular mesh. âĒ STL speciïŽes both ASCII and binary representation. âĒ It ignores appearance, scene and animations. âĒ Used in 3D Printing, computer-aided manufacturing.
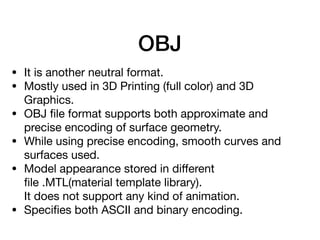
- 10. OBJ âĒ It is another neutral format. âĒ Mostly used in 3D Printing (full color) and 3D Graphics. âĒ OBJ ïŽle format supports both approximate and precise encoding of surface geometry. âĒ While using precise encoding, smooth curves and surfaces used. âĒ Model appearance stored in diïŽerent ïŽle .MTL(material template library). âĻ It does not support any kind of animation. âĒ SpeciïŽes both ASCII and binary encoding.
- 11. FBX âĒ It is proprietary ïŽle format. Used in AutoDesk softwares like 3DS Max, Maya. âĒ Widely used in ïŽlm industry and video games. âĒ It supports geometry and appearance.âĻ It also provides skeletal animations and morphs. âĒ Both binary and ASCII ïŽles supported.
- 12. COLLADA âĒ It is neutral ïŽle format. (.DAE) âĒ Used in video game and ïŽlm industry. âĒ Supports geometry, appearance related properties like color, material, textures and animation. âĻ It supports kinematics and physics. âĒ It stores data using XML.
- 13. 3DS âĒ 3DS ïŽle format using architecture, engineering, education and manufacturing. âĒ This format retains only basic information about geometry, appearance, scene and animation.âĻ Uses triangular mesh to encode the surface geometry. Limit for triangles is 65536. âĒ It doesnât support directional light sources. âĒ SpeciïŽes in binary encoding. âĒ It is standard storing format for 3D Models and interchanging between other 3D ïŽle formats.
- 14. IGES âĒ IGES is neutral ïŽle format.(.IGS, .IGES) âĒ Mostly used in defence industry (US Air Force) and engineering ïŽeld. âĒ It described in ASCII encoding. âĒ It is ïŽexible for surface geometry. âĒ It stores color but doesnât support properties like textures, material types. âĒ Animation is not supported.
- 15. STEP âĒ Standard for the exchange for product data or ISO 10303. (.STP)âĻ It is widely used in engineering related ïŽelds like automative and aeronautic engineering, building construction etc. âĒ Used to describing product data throughout life cycle of product, independent from any system. âĒ It supports feature like surface geometry, storing color.âĻ It supports additional encode topology, geometrical tolerances, material properties like textures, materials types and other product data.
- 16. VRML and X3D âĒ Virtual reality model language. âĒ Used in Internet and Web. âĒ Is uses polygonal mesh to encode surface geometry with NURBS encoding.âĻ Stores appearance related information like color, texture, transparency. âĒ It has capability of storing scene related information and support for animation.âĻ Integrated with HTML5.
