Authentication: Cookies vs JWTs and why youŌĆÖre doing it wrong
- 1. Authentication Cookies vs JWTs and why youŌĆÖre doing it wrong
- 2. The power of an agency at your fingertips
- 4. HowYouŌĆÖreDoingItNow Cookies are so 20th century
- 5. CookieAuthentication Cookie Auth ŌĆó Stores a Session ID ŌĆó Looks up the user in a database ŌĆó All session information stored server side Concerns ŌĆó What do you do as your application scales? ŌĆó How do you route each request back to the same server that stored the session? ŌĆó As your app grows virally, how do you keep costs down?
- 6. WhatŌĆÖsaJWT? WhatŌĆÖs a JWT? JWT (pronounced jot) is a JSON Web Token
- 7. ThreePartsofaJWT ŌĆó Header ŌĆó Declares that it is a JWT ŌĆó Specifies the decoding algorithm ŌĆó Claims ŌĆó Plain text data (encoded with base64) ŌĆó Typically json object ŌĆó Signature ŌĆó Header + Claims encrypted using a server side secret key ŌĆó Only matches if header and claims arenŌĆÖt tampered with
- 8. SampleJWT Header Second Part / Payload Third Part / Signature Result
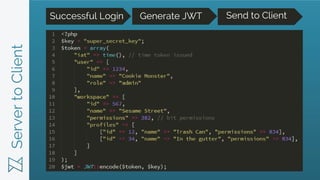
- 9. ServertoClient Successful Login Generate JWT Send to Client
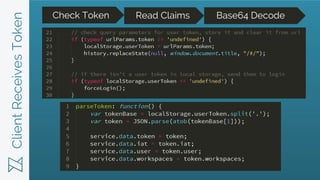
- 10. ClientReceivesToken Check Token Read Claims Base64 Decode
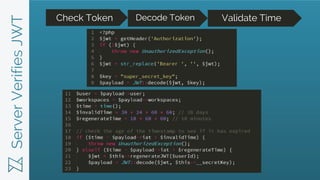
- 11. ServerVerifiesJWT Check Token Decode Token Validate Time
- 12. Implementation ŌĆó Generated on login and stored in the browser ŌĆó JWT is submitted with requests as an Authorization header or in a query string Authorization: Bearer {{full JWT}} ŌĆó Verification happens by regenerating the signature from the original plaintext ŌĆó After verification, check expiration timestamps ŌĆó Continue on your merry way ’üŖ
- 13. WhyshouldIcare?
- 15. AuthTransmission ŌĆó Typically very small (4k hard limit) ŌĆó Sent with every request to domain ŌĆō overhead ŌĆó Authorizing static files included ŌĆó Cookie specific storage ŌĆó Can get larger depending on info stored in token (8k soft limit) ŌĆó Only sent when necessary ŌĆó Uses signed requests, more cumbersome ŌĆó Stored in LocalStorage or SessionStorage Cookies JWT
- 17. Cross-domain/CORS ŌĆó Very difficult across domains ŌĆó Can be accessed from multiple subdomains ŌĆó Pre-flight request if using application/json ŌĆó Works from any domain ŌĆó Local storage only accessible from storing subdomain ŌĆó Pre-flight request Cookies JWT
- 18. Security
- 19. Security ŌĆó Subject to CSRF attacks ŌĆó HttpOnly makes XSS hard ŌĆó Secure flag forces SSL -- Man in the Middle (MITM) ŌĆó Taking cookie with browser access is easy ŌĆó Not subject to CSRF ŌĆó No XSS protection ŌĆó SSL managed in-app ŌĆó LocalStorage is no different Cookies JWT
- 20. Compatibility
- 21. Compatibility ŌĆó Less support for mobile ŌĆó Must be set by server ŌĆó CanŌĆÖt use for external API requests ŌĆó Standard for mobile auth ŌĆó Can be generated by anyone with secret key ŌĆó Easy to use for public API Cookies JWT
- 22. Stateless Apparently theyŌĆÖre a band
- 23. Stateless ŌĆó Contains a session id ŌĆó Requires a database lookup on every request ŌĆó Server-side sessions require subsequent requests to hit same server ŌĆó Scaling difficult ŌĆó Contains verified user information ŌĆó No db lookups required ŌĆó State is stored on client ŌĆó Scales easily Cookies JWT
- 25. ThingstoRemember ŌĆó Base64 is NOT secure, encrypt sensitive info ŌĆó DonŌĆÖt write your own server-side implementation ŌĆó There are some good SaaS companies that make this easier on you: ŌĆó Auth0* ŌĆó UserApp ŌĆó Firebase ŌĆó Keep your secret key SECRET Provided inspiration for this presentation: https://auth0.com/blog/2014/01/07/angularjs-authentication-with-cookies-vs-token/ *
- 26. FurtherInvestigation ŌĆó Angular httpAuthInterceptor ŌĆó Silently add userAgent to JWT ŌĆó Token heartbeat (refresh on each request) ŌĆó Two level authentication (GitHub style)