Automobile engineering
- 1. AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING Group Leader : Syed Jarri Abbas Group Members : Syed Ahad Ali Noman Hussain
- 2. INTRODUCTION TO AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING • The automobile is a self propelled vehicle that travels on land – William H Crouse • An automobile is a wheeled vehicle carrying its motive power unit – Kirpal Sing. • Automobile is a vehicle driven by an internal combustion engine and it is used for transportation of passengers and goods on the ground. Automobile can also be defined as a vehicle which can move by itself. • Examples : Car, jeep, bus, truck, scooter, etc
- 3. HISTORY • The automobile has been around for more than 100 years • The first car was built by Joseph Cugnot in 1769. It was powered by a steam engine and was very slow. • Richard Trevithick improved the steam engine’s design by making them smaller and lighter. • In 1801 he put one on wheels. It was the 1st horseless carriage that could transport passengers. • Jean Joseph Lenoir was the first to build the one cylinder engine, internal combustion engine. • Nikolaus August Otto built the first four cylinder engine.
- 4. Joseph Cugnot Steam Car
- 5. Richard Trevithick Horseless Carriage
- 6. Jean Joseph Lenoir Engine
- 7. History • Karl Benz, known as one of the founders of Mercedes-Benz, is the first to build an automobile powered by an internal combustion engine in 1885. • In 1886 Gottlieb Daimler designed the first four wheeled automobile. They also created the first v-slanted engine. • After 1886, Benz also inveted accelerator for speed regulation, battery ignition system, spark plug, clutch, gear shift, and the radiator for cooling the engine. • With these improvements, he started with production of the automobile, the first in the world, in the year 1888. • However in the year 1893 that the first for wheeled automobile was introduced by him.
- 9. Present • Today, the automobile industry is one of the biggest in the world. • In recent years tremendous changes have taken place in the automobile industry. • Two powerful forces have been at work – The challenges of foreign automotive manufacturers – Federal laws made by the Government covering, • Automotive air pollution. • Automotive Safety. • Automotive fuel economy.
- 10. Present • These two forces have caused the manufacturers to develop new generations of • Light weight vehicles • Fuel efficient vehicles. • This is an ongoing revolutionary process. • Each year, automotive manufacturers bring out new models that improve on fuel efficiency and performance with less air pollution. • The competition among manufacturers has resulted in many innovations that are being widely adopted.
- 11. New Innovations • A few of these innovations include – Antilock braking system (ABS) – Traction- Control System (TCS) – Four- wheel steering – Four-wheel drive (4WD) – All- wheel drive (AWD) – Electronically- controlled and active suspension system – Supplemental restraint system ( air bags) – Sequential port fuel injection – And a host of other innovations
- 12. Design-Manufacturing-Automobile • Engineering design and manufacturing skill have made the modern motor car simple to operate and economical to maintain • To achieve utmost simplicity of operation, and thus ensure greatest utility, engineers have made many design improvements and have added devices from time to time. E.g. 1. Electric self starter 2. Automotive oil pressure and engine temperature gauges 3. Synchromesh transmission 4. Automatic gear shifting mechanism
- 13. Design-Manufacturing-Automobile • Manufacturing skill, combined with improved designs, has affected great savings so that economical transportation has been become available to many millions. • At the same time improvements in manufacturing method have made it possible to use better material and closer tolerances so that car life has been tremendously increased.
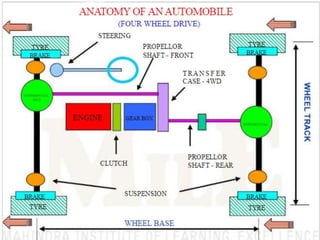
- 14. Components of a four wheeler Automobile • About 1500 separate parts are put together to make an automobile. • These parts are grouped into several systems. • Each system is made up of two or more parts that work together to perform a specific job. • The automotive vehicles are produced in large variety of sizes and shapes. • All have the same basic parts and systems.
- 16. Major Components • The major components of an automobile are. – An engine (power plant) – A power train (transmission system) – A suspension system – A steeing system – A braking system – An electrical system – A body
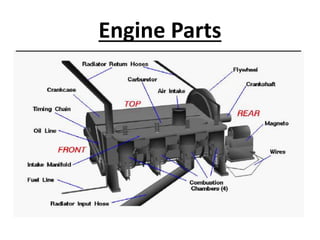
- 17. An engine • Power plant provides the motive power for all the various functions which the vehicle or any part of it may be called upon to perform. • The power plant generally consists of an I.C engine-spark ignition-compression ignition. • Gas turbines has also been used successfully. • Electric motors powered by batteries have also been used. • Combination of an I.C engine and electric motors have also been successfully employed in hybrid vehicles. • Solar energy powered systems have also been tried. • Most promising future power plant is the one based on fuel cells.
- 18. Engine Parts
- 20. An I.C Engine • The following sub systems supports the I.C engine for continuous running. • Fuel system • Ignition system • Lubricating and Cooling system • Exhaust system • Electrical and electronic system
- 21. Fuel System • Supplies fuel to the engine • Consists of – Storage tank, – Piping work,and, – An arrangement for mixing with air and spraying into the engine cylinder. • In conventional petrol engines a carburetor is used for mixing the fuel with air. • Present, electronic fuel injection (EFI) is used to spray fuel air mixture. • An electronic control module (ECM) control the functions of EFI.
- 22. Ignition System • Function is to supply high voltage surge at the desired instant and of adequate strength to produce a spark in the engine. • Earlier electro mechanical system were used. • Now days in modern engines electronic systems are used.
- 23. Lubrication System • The lubrication system keeps all moving parts inside the engine coated with layers of oil. • This reduces wears on the parts. • It also allows the parts move freely with little power lost in making them move. • Relatively less viscous lubricating oils are used in engines. • Where as heavier oils and greases are used in the transmission and wheel bearings.
- 24. Cooling System • The cooling system removes just enough heat so the engine runs smoothly at the proper temperature. • It maybe of water cooling or oil cooling. • A water pump circulates coolant between the engine and the radiator. • Cooler outside air flows through the radiator and picks up and carries away the excess heat. • A thermostat helps the coolant at the proper temperature • A fan helps keep air moving through the radiator.
- 25. Exhaust System • Exhaust system used to vent exhaust gases with least back pressure. • It also reduce the engine noise with the help of muffler. • Now a days converters are also fitted in the exhaust pipe to reduce the harmful constituents in the exhaust gases.
- 26. Electrical System • It consists of storage battery, charging system and starting system. • The battery supplies electricity for starting the engine, providing energy for spark, and for all electrical devices in the vehicle. • The charging system consists of mainly an alternator and is used to continually charge the battery. • The starting system consists of starting motor and is used to start the engine.
- 27. Power Train or Transmission System • The power train carries power from the engine to the drive wheels. • Major power train’s parts may include – Clutch – Transmission or transaxle – Transfer case – Driveshaft, and – differential
- 29. THANK YOU