Autonomous Communities -A Spanish Phenomenon-
- 1. Autonomous Communities -A Spanish Phenomenon- Jaime Miguel Nieman Gonz├Ālez
- 2. ╠²
- 3. Theories of Nationalism Eduardo Lopez Aranguren: Nation: Objective Subjective Territory Collective Identity Language Conscience Culture Solidarity History Will Economy -Nations exist before we name them nations
- 4. Benedict Anderson Nations are ┬©Imagined political communities┬© They are constructed based on symbols such as: Flags, Hymns, National Heroes, and ŌĆ£ It is Nationalism which engenders nations and not the other way around ŌĆ£ Ernest Gellner
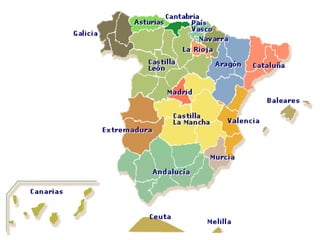
- 5. Forms to reach autonomy Fast track: Historic communities Slow Track: Must have parliamentary approval, and must wait 5 years. -Andalusia & Navarra- Autonomic fever! Cafe para todos Inter-Regional Compensation Fund
- 6. Historic Nationalisms Catalu├▒a Basque Country Galicia Organized pre-autonomic representative bodies Received statute of Autonomy through fast track
- 7. Division of Power Central government powers: Foreign Politics, Justice, Armed Forces, Legislation, Border control, Coordination of Economic Activity, Taxation, Social Security, Health Care, Fishing, Transportation and Road Works. Powers are transferrable - Devolution
- 8. Regional powers: -process of transference of powers All regions have: High court of Justice Regional Prime Minister Single Chamber Parliaments -Senate is not a Regional/Territotial body
- 9. Funding: Who pays? -most expensive responsibilities: Education and Healthcare 1980-81: Communities pay for the services received (ex. per student ) 1986: Changed to territorial size, total population, and existing services. 1993-94: Yearly Income Tax Division 15% to AC and 85% to Nation State 1996: Income Tax 33% to AC, 35% of VAT, and 40% of alcohol, tobacco, and petrol.
- 10. ╠²
- 11. Basque region and Navarra collect their own taxes (Income and Corporative taxes) Catalan tax grant for products Autonomous Police forces: Catalu├▒a: Mossos de Esquadra Basque Country: Ertzaintza Catalans and Basques are leaders and the rest follow.
- 12. Melian Debate - Comments on relations between states. "Well, then, we Athenians will use no fine words; we will not go out of our way to prove at length that we have a right to nile, because we overthrew the Persians; or that we attack you now because we are suffering any injury at your hands. We should not convince you if we did; nor must you expect to convince us by arguing that, although a colony of Sparta, you have taken no part in their expeditions, or that you have never done us any wrong. But you and we should say what we really think, and aim only at what is possible, for we both alike know that into the discussion of human affairs the question of justice only enters where there is equal power to enforce it, and that the powerful exact what they can, and the weak grant what they must."
- 13. INTERGOVERNMENTAL MODELS OF INTERACTION DUAL Division of responsibilities is clear between states/regions COOPERATIVE States/Regions cooperate with each other and work in the interest of all COMPETITIVE States/regions must compete with each other ASYMMETRICAL Treatment is not equal and some states/regions are favored