Bab 10 state diagram 2010
- 2. Statechart Diagram - Bersifat dinamis - Memperlihatkan state-state pada sistem; memuat state, transisi, event, serta aktivitas. - Memperlihatkan sifat dinamis dari antarmuka, kelas, kolaborasi dan terutama penting pada pemodelan sistem-sistem yang reaktif
- 3. SYSTEMS ANALYSYS AND DESIGN METHODS 5TH Edition Whitten Bentley Dittman Membuat model behavior dari objek-objek âĒ Setiap objek dapat dikatakan memiliki state --- nilai dari attributnya pada suatu saat tertentu. âĒ State diagram memodelkan daur hidup sebuah objek tunggal. Ia menggambarkan macam- macam state yang dimiliki sebuah objek, event yang mengakibatkan perubahan state selama waktu tertentu dan aturan-aturan yang mengatur transisi objek antara satu state dengan state lainnya. âĒ Perubahan terhadap state objek terjadi ketika ada suatu kejadian atau ketika nilai dari salah satu atributnya berubah. Perubahan state ini dipicu oleh adanya suatu event. Irwin/McGraw-Hill Copyrighth@2000 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies All Right reserved
- 4. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh âĒ Sebuah state diagram menunjukkan urut-urutan state dari sebuah objek selama masa hidupnya / lifetimenya, sekaligus dengan event-event yang menyebabkan perubahan dari state tersebut. âĒ Sebuah state diagram menjelaskan sebuah hypothetical machine (finite automaton) yang pada setiap waktu berada pada satu set finite state, yang terdiri dari: âĒ a finite, non-empty set of states; âĒ a finite, non-empty set of events; âĒ functions, yg menjelaskan transisi dari satu state ke state berikutnya; âĒ sebuah initial state; âĒ satu set final state. Addison-Wesley
- 5. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh Soal: âĒ On opening the flight, the initial state leads to the NoReservation state. When the state is entered, the Reset operation is executed. If a reservation is made for this flight, the object changes to the state PartiallyReserved. âĒ The Reserve event is associated to the homonymous Reserve action (implemented as an operation). âĒ In this operation, the actual reservation takes place, and the internal reservation counter is updated. After termination of this action, we will find the object in the PartiallyReserved state. âĒ Each additional reservation leads to the same action. As long as a free seats are available, the object remains in the PartiallyReserved state. If only one seat left, it changes into FullyBooked state. Cancellation of reserved seats is carried out in a similar way. Thus, the state diagram describes which actions are triggered by which events and under which conditions these (and together with the call of the corresponding operations) are permitted. Addison-Wesley
- 6. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh cancel() [reservedSeats>1] reserve() reserve() NoReservation [freeSeats>1] PartiallyReserved entry/reset() cancel() reserve() [ReservedSeats=1] [freeSeats=1] cancel() cancelFlight() close() openFlight() FullyBooked close() Closed Addison-Wesley
- 7. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh State âĒ Sebuah state dimiliki oleh satu buah Class dan merepresentasikan abstraksi atau kombinasi dari satu set nilai atribut yang mungkin terjadi pada objek tersebut dari class ini. âĒ Tidak setiap perubahan nilai atribut akan dianggap sebagai perubahan state. Hanya event tertentu yang sangat signifikan mengakibatkan perubahan behavior dari objek. âĒ Sebuah state oleh karena itu dapat dilihat juga sebagai rentang waktu (time span) antara dua event. âĒ Dua type khusus state yang ada adalah initial state dan final state. Addison-Wesley
- 8. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh âĒ Tidak ada transisi yang menuju initial state dan tidak ada event yang diperbolehkan meninggalkan final state. âĒ Transisi dari satu state ke state berikutnya di trigger / dipicu oleh event. Sebuah event terdiri dari nama event dan sejumlah argument. âĒ Event dapat memicu aksi didalam state yang dilakukan melalui operasi tertentu. Ada tiga trigger yang sudah predefine: âĒ entry, fires automatically when entering a state âĒ exit, fires automatically when leaving a state âĒ do, fires repeatedly as long as the state is active, that is, not left. Addison-Wesley
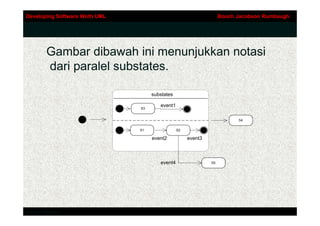
- 9. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh Substate âĒ Sebuah state dapat diuraikan lebih lanjut, baik sekuensial ataupun paralel substate. âĒ Gambar dibawah ini menunjukkan sebuah sequential nesting. Ketika kontrak asuransi ditetapkan, sebuah produk dipilih (sebagai contoh, content-nya), yang terdiri dari beberapa produk element (Pel), seperti furniture, gelas, dsb. Untuk setiap produk elemen, sebuah cover (istilah asuransi) harus dibuat. Ilustrasi dibawah ini menunjukkan Create covers state dari context ini. Create Covers covers:set=Empty set PElQuantity Define Reset cover addPEl [isComplete] addPEl Addison-Wesley
- 10. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh Gambar dibawah ini menunjukkan notasi dari paralel substates. substates event1 S3 S4 S1 S2 event2 event3 event4 S5 Addison-Wesley
- 11. Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh Event dan transition âĒ Sebuah event adalah sebuah kejadian yang memiliki pengaruh khusus dalam suatu context yang dibicarakan, karena ia men-trigger / memicu perubahan state. âĒ Kebalikan dari state, event bukan milik satu kelas tertentu. âĒ State transition (perubahan state) biasanya dipicu oleh adanya event yang digambarkan dengan anak panah yang menghubungkan state satu dengan state lainnya. Addison-Wesley
- 12. State Transition Diagram Add student[ count < 10 ] Add Student / Initialization Set count = 0 Open do: Initialize course entry: Register student exit: Increment count Cancel Cancel [ count = 10 ] Canceled do: Notify registered students Closed Cancel do: Finalize course Copyright ÂĐ 1997 by Rational Software Corporation
- 13. Transitions event [guard] | action x x y y The action that takes place when The event that Conditions that the transition is triggers the must be met for taken transition the transition to take place
- 14. Transitions event [guard] | action x x y y The action that takes place when The event that Conditions that the transition is triggers the must be met for taken transition the transition to take place
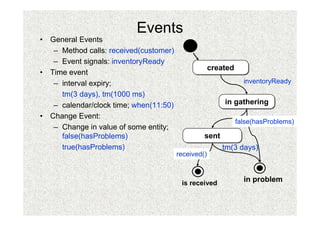
- 15. Events âĒ General Events â Method calls: received(customer) â Event signals: inventoryReady created created âĒ Time event â interval expiry; inventoryReady tm(3 days), tm(1000 ms) â calendar/clock time; when(11:50) in gathering in gathering âĒ Change Event: false(hasProblems) â Change in value of some entity; false(hasProblems) sent sent true(hasProblems) tm(3 days) received() is received in problem
- 16. Guards (Conditions) gatheringFinished [all items were gathered] sent sent in gathering in gathering in problem in problem gatheringFinished [items are not found] âĒ Boolean expressions. âĒ Evaluated when the transition is triggered âĒ Types of guards: â Simple predicate: [hasProblems], [x > 0] â Combined predicates: [ÂŽhasProblems âĻ (hasProblems ⧠order.sum < 100] â Guards on activities: [active(gatherItems)] â State related (weâll get back to it later)
- 17. Guards - Example bid [value < 100] bid [value >= 200] Selling Happy bid [(value >= 100) AND (value < 200)] Unhappy Intro | Building Blocks | Advanced
- 18. Static Conditional Branching âĒ A graphical shortcut for convenient rendering of decision trees Selling Happy bid [value >= 200] [value < 100] [(value >= 100) & (value < 200)] Unhappy
- 19. Empty Transitions âĒ A transition can have any combination (including none) of the events, guards and actions Empty âĒ When a transition does not have an event, Employee Transition it is taken after all the activities were rest[break] Cleaning ended Working do: put water do: put soap doing nothing do: shovel work do: wash soap do: drain work
- 20. Guards and Events âĒ Whatâs the difference between the two machines? E1 true(C) S1 S2 S3 E1 [C] S1 S2 S3 What happens if C changes to True before E1?
- 21. Actions âĒ An executable atomic computation âĒ Types of actions â Variable assignment: received() | status := received sent sent is received is received â Throwing a signal: received() | throw(InventoryUpdate) sent sent is received is received â Start, or stop activities (and concatenation of actions): | start(sendBill); stop(delivery); x := x+1 sent sent is received is received
- 22. Transitions - advanced âĒ Self-transitions: Transitions can be directed to the same state: / c=0 S2 E1 / c:=c+1 âĒ Un-deterministic states â when two transitions are taken in the same time, one of will be taken in an un- deterministic fashion: E1 S1 S2 [C1] S3
- 23. How does a Washing Machine Works? âĒ On / Off button. Start button âĒ (No stop button.) âĒ Feedback is given on the current stage (soaking, rinsing, draining, drying) âĒ Three plans: â Regular â Delicate (no soaking) â Super delicate (no soaking, no drying) âĒ Off can be clicked only before starting, or after finishing
- 24. Washing Machine off click(power) click(power) idle Tm(10 mins) | light(off) click(start) [plan=regular] soak click(start) [plan=delicate Do: light(soak) or super delicate] Do: pump(in) Tm(5 mins) [plan=super delicate] | light(off) tm(30 mins) rinse drain dry tm(5 mins) Do: light(rinse) tm(30 mins) Do: light(drain) [plan=not super Do: light(dry) Do: stir() Do: pump(out) delicate] Do: stir()
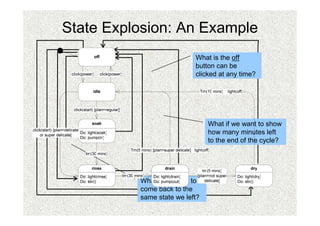
- 25. State Explosion: An Example What is the off button can be clicked at any time? What if we want to show how many minutes left to the end of the cycle? What if we want to come back to the same state we left?
- 26. Abstraction in Statechart Separating Independent Finding Common Regions Behavior Composite States Parallel States
- 27. The State Explosion Problem Class Class Class v1 : {t, f} v1 : {t, f} v1 : {t, f} v2 : {t, f} v2 : {t, f} v2 : {t, f} v3 : {t, f} ... v3 : {t, f} ... ... v3 : {t, f} ... âĒ Let â n: Num of Classes â m: Num of variables (assume equals among classes) âĒ Number of possible states = 2(nm) âĒ And... â What if the state space of each variable > 2 â What about association between objects?
- 28. Composite States
- 29. Composite + History off click(power) click(power) On H idle Tm(10 mins) | light(off) click(start) [plan=regular] soak click(start) [plan=delicate Do: light(soak) or super delicate] Do: pump(in) Tm(5 mins) [plan=super delicate] | light(off) tm(30 mins) rinse drain dry tm(5 mins) Do: light(rinse) tm(30 mins) Do: light(drain) [plan=not super Do: light(dry) Do: stir() Do: pump(out) delicate] Do: stir()
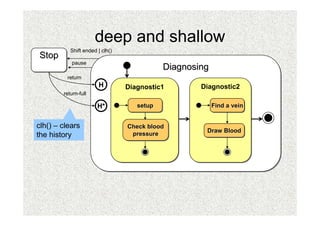
- 30. deep and shallow Shift ended | clh() Stop pause Diagnosing return H Diagnostic1 Diagnostic1 Diagnostic2 Diagnostic2 return-full H* setup setup Find a vein Find a vein clh() â clears Check blood Check blood Draw Blood Draw Blood the history pressure pressure
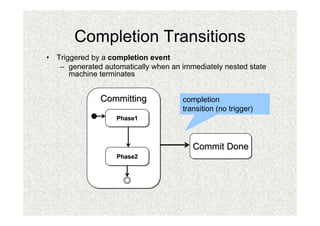
- 31. Completion Transitions âĒ Triggered by a completion event â generated automatically when an immediately nested state machine terminates Committing completion transition (no trigger) Phase1 Phase1 Commit Done Phase2 Phase2
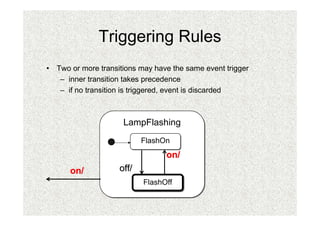
- 32. Triggering Rules âĒ Two or more transitions may have the same event trigger â inner transition takes precedence â if no transition is triggered, event is discarded LampFlashing FlashOn FlashOn on/ on/ off/ FlashOff FlashOff
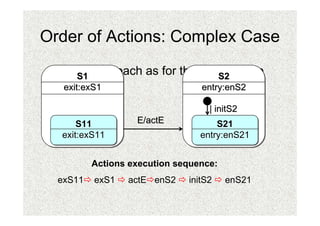
- 33. Order of Actions: Complex Case âĒ Same approach as for the simple case S1 S2 exit:exS1 entry:enS2 | initS2 S11 E/actE S21 exit:exS11 entry:enS21 Actions execution sequence: exS11 exS1 actE enS2 initS2 enS21
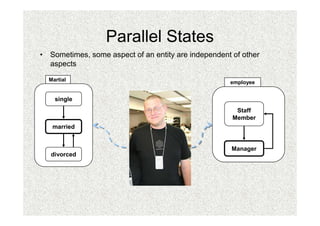
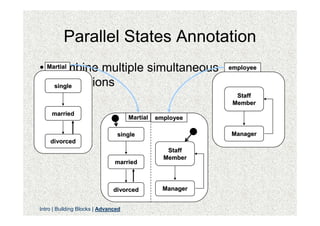
- 34. Parallel States âĒ Sometimes, some aspect of an entity are independent of other aspects Martial employee single Staff Member married Manager divorced
- 35. Parallel States Annotation âĒ Martial Combine multiple simultaneous employee descriptions single Staff Member married Martial employee single Manager divorced Staff Member married divorced Manager Intro | Building Blocks | Advanced
- 36. Interactions Between Parallel States off click(power) click(power) On H idle Spin Slow Do: spin(150rpm) click(start) idle [Plan in Regular] Regular Tm(entered(rinse),15) Tm(30) Exited(rinse) click(start) soak Entered(rinse) [Plan in [Plan not in Regular] click(plan) Super Delicate] Entered(rinse) [Plan not in Regular] idle out Tm(30) Tm(30) click(plan) Entered(soak) Do: pump out Delicate water Entered(drain) Exited(drain) rinse click(plan) in Tm(30) [Plan not in Super Delicate] Super Spin Fast Do: pump in Delicate water Do: spin(400rpm) drain Controller Pump Plan Rotor
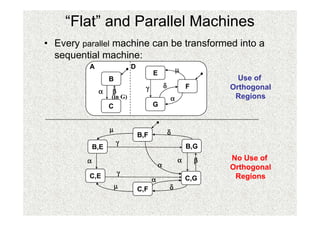
- 37. âFlatâ and Parallel Machines âĒ Every parallel machine can be transformed into a sequential machine: A D Âĩ E B Use of Îģ Îī F Orthogonal Îą Îē (in G) Îą Regions C G Âĩ Îī B,F Îģ B,E B,G Îą Îą Îē No Use of Îą Orthogonal Îģ C,E Îą C,G Regions Âĩ C,F Îī
- 38. Transition Forks and Joins âĒ For transitions into/out of orthogonal shipping regions: Processing Processing Sent Sent Confirmed Confirmed Credit Card Credit Card [ok] verification verification Receipt Sent Receipt Sent fork [not ok] charging Join In problem In problem




![Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh
cancel()
[reservedSeats>1]
reserve()
reserve()
NoReservation [freeSeats>1]
PartiallyReserved
entry/reset() cancel() reserve()
[ReservedSeats=1] [freeSeats=1]
cancel()
cancelFlight()
close()
openFlight()
FullyBooked
close()
Closed
Addison-Wesley](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-6-320.jpg)


![Developing Software Woth UML Booch Jacobson Rumbaugh
Substate
âĒ Sebuah state dapat diuraikan lebih lanjut, baik
sekuensial ataupun paralel substate.
âĒ Gambar dibawah ini menunjukkan sebuah sequential
nesting. Ketika kontrak asuransi ditetapkan, sebuah
produk dipilih (sebagai contoh, content-nya), yang terdiri
dari beberapa produk element (Pel), seperti furniture,
gelas, dsb. Untuk setiap produk elemen, sebuah cover
(istilah asuransi) harus dibuat. Ilustrasi dibawah ini
menunjukkan Create covers state dari context ini.
Create Covers
covers:set=Empty set
PElQuantity Define
Reset cover
addPEl [isComplete]
addPEl
Addison-Wesley](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-9-320.jpg)

![State Transition Diagram
Add student[ count < 10 ]
Add Student /
Initialization Set count = 0
Open
do: Initialize course
entry: Register student
exit: Increment count
Cancel
Cancel [ count = 10 ]
Canceled
do: Notify registered students
Closed
Cancel do: Finalize course
Copyright ÂĐ 1997 by Rational Software Corporation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-12-320.jpg)
![Transitions
event [guard] | action
x
x y
y
The action that
takes place when
The event that Conditions that the transition is
triggers the must be met for taken
transition the transition to
take place](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-13-320.jpg)
![Transitions
event [guard] | action
x
x y
y
The action that
takes place when
The event that Conditions that the transition is
triggers the must be met for taken
transition the transition to
take place](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-14-320.jpg)
![Guards (Conditions)
gatheringFinished [all items were gathered]
sent
sent
in gathering
in gathering
in problem
in problem
gatheringFinished [items are not found]
âĒ Boolean expressions.
âĒ Evaluated when the transition is triggered
âĒ Types of guards:
â Simple predicate: [hasProblems], [x > 0]
â Combined predicates:
[ÂŽhasProblems âĻ (hasProblems ⧠order.sum < 100]
â Guards on activities: [active(gatherItems)]
â State related (weâll get back to it later)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-16-320.jpg)
![Guards - Example
bid [value < 100]
bid [value >= 200]
Selling Happy
bid [(value >= 100) AND (value < 200)]
Unhappy
Intro | Building Blocks | Advanced](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-17-320.jpg)
![Static Conditional Branching
âĒ A graphical shortcut for convenient
rendering of decision trees
Selling Happy
bid
[value >= 200]
[value < 100]
[(value >= 100) & (value < 200)]
Unhappy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-18-320.jpg)
![Empty Transitions
âĒ A transition can have any combination
(including none) of the events, guards and
actions
Empty
âĒ When a transition does not have an event,
Employee Transition
it is taken after all the activities were
rest[break] Cleaning
ended
Working do: put water
do: put soap doing nothing
do: shovel work do: wash soap
do: drain
work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-19-320.jpg)
![Guards and Events
âĒ Whatâs the difference between the two
machines?
E1 true(C)
S1 S2 S3
E1 [C]
S1 S2 S3
What happens if C changes to True
before E1?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-20-320.jpg)

![Transitions - advanced
âĒ Self-transitions: Transitions can be directed to the same
state: / c=0
S2 E1 / c:=c+1
âĒ Un-deterministic states â when two transitions are taken
in the same time, one of will be taken in an un-
deterministic fashion:
E1
S1 S2
[C1]
S3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-22-320.jpg)

![Washing Machine
off
click(power) click(power)
idle Tm(10 mins) | light(off)
click(start) [plan=regular]
soak
click(start) [plan=delicate
Do: light(soak)
or super delicate]
Do: pump(in)
Tm(5 mins) [plan=super delicate] | light(off)
tm(30 mins)
rinse drain dry
tm(5 mins)
Do: light(rinse) tm(30 mins) Do: light(drain) [plan=not super Do: light(dry)
Do: stir() Do: pump(out) delicate] Do: stir()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-24-320.jpg)
![Composite + History
off
click(power)
click(power)
On
H
idle Tm(10 mins) | light(off)
click(start) [plan=regular]
soak
click(start) [plan=delicate
Do: light(soak)
or super delicate]
Do: pump(in)
Tm(5 mins) [plan=super delicate] | light(off)
tm(30 mins)
rinse drain dry
tm(5 mins)
Do: light(rinse) tm(30 mins) Do: light(drain) [plan=not super Do: light(dry)
Do: stir() Do: pump(out) delicate] Do: stir()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-29-320.jpg)
![Interactions Between Parallel
States off
click(power)
click(power)
On H
idle Spin Slow
Do: spin(150rpm)
click(start) idle
[Plan in Regular]
Regular
Tm(entered(rinse),15)
Tm(30) Exited(rinse)
click(start) soak Entered(rinse)
[Plan in
[Plan not in Regular] click(plan)
Super Delicate] Entered(rinse)
[Plan not in Regular] idle
out
Tm(30)
Tm(30) click(plan)
Entered(soak) Do: pump out Delicate
water Entered(drain)
Exited(drain)
rinse
click(plan)
in
Tm(30)
[Plan not in Super Delicate] Super Spin Fast
Do: pump in
Delicate
water
Do: spin(400rpm)
drain
Controller Pump Plan Rotor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-36-320.jpg)
![Transition Forks and Joins
âĒ For transitions into/out of orthogonal
shipping
regions:
Processing
Processing Sent
Sent Confirmed
Confirmed
Credit Card
Credit Card [ok]
verification
verification Receipt Sent
Receipt Sent
fork [not ok] charging Join
In problem
In problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bab10statediagram2010-110810023221-phpapp02/85/Bab-10-state-diagram-2010-38-320.jpg)

