BADON, STARLETTE KAYE.pptx
- 1. THE CALL FOR EXCELLENCE THE PURPOSE OF EDUCATION
- 2. NATIONAL REPORTS CALL FOR REFORM Characterization of âexcellenceâ as symptomatic of the âAmericanizationâ of higher education. 1 By the early 1980âs national attention began to focus on the educational need for excellence and higher educational standards particularly the neglected â averageâ students â and not just the disadvantaged or the talented. OVERVIEW ON THE POLICY REPORT
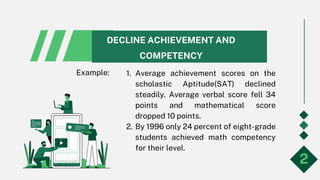
- 3. DECLINE ACHIEVEMENT AND COMPETENCY 1. Average achievement scores on the scholastic Aptitude(SAT) declined steadily. Average verbal score fell 34 points and mathematical score dropped 10 points. 2. By 1996 only 24 percent of eight-grade students achieved math competency for their level. 2 Example:
- 4. 1. Average Schools that do not have computer laboratories have an MPS of 79.3% 2. Schools that have adequate textbooks in Math have an MPS of 73.0% 3. Schools where teachers discuss the lesson the whole period (chalk-talk method), then ask questions if there is remaining time have an MPS of 67.7% 4. Schools where quizzes are regularly given have an MPS of 68.4% 3 Analysis "NAT Overview and 2012 Test Results". https://www.philippinesbasiceducation.us/2013/07/the-national-achievement-test-in.html
- 5. INTERNATIONAL COMPARISON International comparisons of statistical data on national elementary, secondary and higher education school systems provide feedback on how education systems have improved over time, how equitable they are, and students compare to their peers around the world. 4
- 6. FUNCTIONAL ILLITERACY In the Philippines , at least nine out of 10 children aged 10 struggle to read and write simple text, according to World Bankâs statistics on learning poverty in 2021. The country ranked lowest among 79 countries that participated in a 2018 international reading literacy assessment.(PISA) 5
- 7. STUDENT âTEACHER RATIOS These problem have occurred despite a relatively good student- techer ratio approximately 16 : 1 student per teacher in the U.S, ratios of over 25 : 1 in Japan and Korea. 45 : 1 in the Philippines. 6 For School Year 2017-2018, the teacher-student ratio in the Philippines is 1:31 for the elementary level, 1:36 for Junior High School level, and 1:31 for Senior High School level https://www.pna.gov.ph/articles/1029281
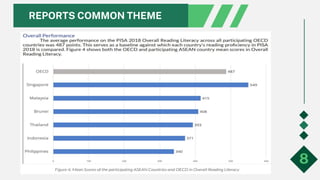
- 8. REPORTS COMMON THEME Statistical data in education summarized empahasize the need top strengthen the curriculum in the core subjects in English, math, science, Foreign language, social studies. 7
- 11. IMPORTANCE OF TECHNOLOGY Technology and computer courses are mentioned often and at the drawn of twenty-first century the need to improve studentâs technology skills and upgrade school technology is almost a mantra. 10 Based on a 2021 survey by the World Bank on low- income households, only 40 percent have access to the internet while 95.5 percent of the same study subjects used paper-based learning modules and materials. https://www.pna.gov.ph/articles/1191435
- 12. HIGHER STANDARDS, MORE RIGOROUS REQUIREMENTS Tougher standards and tougher courses, and a majority propose that colleges raises their admission requirements. Most of the reports talk about increasing homework, time in school, upgrading teachers certification. Overall the report stress academic achievement, not the whole child, and increased productivity not relevancy or humanism. 11
- 13. SCHOOL PLAY TOO MANY ROLES Schools are pressed with so many social roles; that the school cannot meet all these expectations; and that the schools are in danger of loosing its sight to their key purpose - teaching basic skills and core academic subjects, new skills for computer use, and higher-level cognitive skills for the world of work and technology. 12
- 14. RISING TIDE OF MEDIOCRITY Mediocrity is defined as a paralysis of an educational institution that maintains the status quo regardless of its effectiveness, is content with its limited capacity to produce excellence, believes that improvement is out of its reach, and masquerades mediocrity as excellence. 13
- 15. DEVELOPING NATIONAL STANDARDS In line with the new professional standards for teachers, the Department of Education (DepEd), through the Teacher Education Council (TEC), issues this DepEd Order entitled National Adoption and Implementation of the Philippine Professional Standards for Teachers (PPST) 14
- 16. PROGRESS REPORT ON NATIONAL EDUCATION GOALS Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) 15
- 17. PROGRESS REPORT ON NATIONAL EDUCATION GOALS 16 https://www.pids.gov.ph/details/policy-issue-at-a-glance-how-is-the-philippines-faring-in-sdg- achievement-goal-4-quality-educatio
- 18. 17
- 19. 18
- 20. 19
- 21. 20
- 22. PROGRESS REPORT ON NATIONAL EDUCATION GOALS 8
- 23. NATIONAL EDUCATIONAL REFORM âEducational Reform in the 21st Centuryâ identified the following global reforms in both the lower and higher education levels. The Philippines has finally embarked on its most ground-breaking change to the schooling system in decades, the K-12 reform. 22
- 24. What is your Educational Philosophy? Read the story of Amanda Scott 23 QUESTION
- 25. SUMMING UP 24 The concept of âexcellenceâ can be defined in many ways. It has to do with âeminenceâ(high value) but it is also linked to quality insurance and quality control. The purpose of education are influenced by changing social forces as well as by educational philosophies and theories. We expect the school to be the key instrument for solving our technological or social problems and preparing our work force for the future. Schools have been encouraged to provide a world-class quality education, with an emphasis on high achievement and the general improvement of outcomes for all.
- 26. Amanda Scott, a brand new eight-grade teacher at Oxford Middle School, just finished her first post observation conference with Ms. Renee, her principal. Although a positive and upbeat conference, Ms. Reneeâs comments keep ringing in Amandaâs head. âAmandaâ Ms. Renee said, â its clear that you enjoy your students and they responded well to the structure and expectations youâve created. I was pleased with the flow of the lessons and the students paid attention to you and to each other. But when you interview for this position, you describe yourself as âfacilitator of active learningâ and your portfolio showed that you understood that approach. Now, though, what I see in your class is mostly is teacher directed: lecture, vocabulary drills, worksheets, and so on. How are you building the studentâs capabilities for creativity, autonomy, and critical thinking? Whereâs the Amanda Scott we interviewed? Next time I visit, I would like to see that Amanda in action. â How could I get away from what I believe in? Amanda scold herself. The problem, she realizes, was that in her first few weeks as a teacher, feeling unsure of herself, she tried to be safe, to make sure her students were getting a basic foundation. Now it is the time to change them and herself. Late that day, while Amanda and several other teachers were eating lunch in the teacherâs lounge, someone picked up the local morning paper, which had a lead article about the result of a statewide assessment program administered to eight graders. Composite scores for every middle school in the metropolitan region were listed, and Oxford Middle was rank the bottom third. Amandaâs school made marginal improvement over the last yeaâs test in reading and math scores, but lost ground on the writing portion of the test. Everyone in the lounge lamented the newspaperâs remark that the schoolâs progress was ânot significantâ. They express pride in the advances of their students made. They argued that most schools with comparable populations of low- income and actually diverse students have not shown gains as great as Oxford Middle. Bill OâConneli pointed to another article in the newspaper. This one featured members of a Citizenâs Education Advisory Council complaining about schoolsâ performance on the assessment program. Their demand was for back-to-basic approach with more emphasis on factual knowledge and less on critical thinking and innovative and time-consuming teaching strategies Amanda asked herself, âWhat should I do?
- 27. 1. What philosophical orientation is being expresses by each party in this dilemma? 2. Which of the orientations above best reflects your own personal philosophy of education? 3. If none, does, can you think of someone who would represent your philosophy in this dilemma, such as a concerned parent or business leader in the community? 4. What will you do if you were a teacher at Oxford Middle School faced with this conflict in educational goals? Do you see any way to achieve both goals? 26 End of the Topic Questions
- 28. References Bell, J.A. âHigh-Performing, High-Poverty Schools,â Leadership (September-October 2001) 8-11. https://sdg-tracker.org/quality-education https://www.philippinesbasiceducation.us/2013/07/the-national- achievement-test-in.html https://www.pna.gov.ph/articles/1029281
- 29. I hope you learn somethingâĶ Thank you for listening to my report!
Editor's Notes
- Why is there a need to call for excellence in education
- Americanization Characterization of âexcellenceâ. An average student who performs at a level that is considered to be typical or typical for their age group or for the group of students to which they belong. Disadvantage students are those not having the standard of living conditions, education, etc. that most people have. Talented students â these are students who learn more quickly and independently than most students their own age. So there is a need for educational reforms based on the national reports this in order to transform educational structures with the aim of raising the quality of education in a country. Some of these report will be shown on the next slides.
- At this point, the 75% is not yet met. Our educational body needs to upgrade find ways on how to improve our test results. And after which k-12 was created. Nat target the performance of the children. But also the teachers, principals and administrators
- ASEAN integration. Can somebody give us short information of what is ASEAN integration? Trade liberation, regional economic integration, and free trade. These are the Key drivers. Here in the Philippines we need to ensure the strength of the Philippine country brand and that includes the people. align our branding initiatives with that of the ASEAN region
- Philippine International Student Assessment Functional illiterate - consists of reading and writing skills that are inadequate "to manage daily living and employment tasks that require reading skills beyond a basic level. For example, you instructed your studnts to bring picture and CAR issued during the assessment in claiming their Nc certs. Then 1 student ask. Unsay dal.on pagclaim sa cert. A SHS Students know how to read and write but when you ask questions about what he has read. He cannot answer. Meaning poor reading comprehension.
- The student-teacher ratio has been found to be one of the strongest indicators of student success and engagement in class. The fewer students each teacher works with, the more closely they're able to adapt their teaching to the specific learning styles. When the number of students decreases, teachers can allocate more time to cater to the individual learning needs of each pupil.
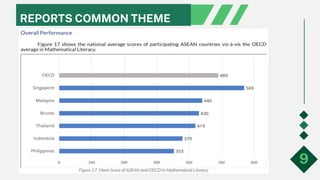
- Filipino students achieved an average of 353 points in Mathematical Literacy; this is significantly lower than the OECD average (489 points) and is classified as below Level 1 proficiency.
- Technology not only provides students with access to countless online resources, but also aids them in the learning process. Free Internet Access in Public Places Act
- In all walks of life, when quality really matters we put systems into place - with rules, practices, incentives, penalties, and supports - that help all of us to maintain high standards. We do so because we understand that individuals do their best, are the most productive, and reach higher goals when they are working in a system that supports their best efforts. Productivity without wellbeing is not sustainable. maintaining a balance between the call for excellence in education and the need of people. Education is not just about knowing a lot but also about being able to do something with that knowledge and skills, and feeling responsible for that.
- Many of the reports concern not only with academic productivity but also with national productivity, link human capital with economic capital. Investment to school would mean investment in the economy. âOur basic role is to develop our studentsâ qualifications. We also train good citizens, teach moral values âĶ .â Such as more time on Extra curricular activities, Taking part in one too many extra-curricular activities will cause your kid to lose focus and concentration on his studies
- Some signs of mediocrity in schools are the following. Misplaced and discouraged innovation The ânowâ is the limit. Unqualified staff Biased governance and leadership.
- The goal panel is proposing a tougher standards, comparable to the best in the world; aligning all components of education system with these standards; and strengthening teachersâ subject-matter knowledge and teaching skills. K-12 program promotes global competency by accelerating mutual recognition of Filipino graduates and professionals in other countries
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) (SDG) are a collection of 17 global goals aimed at improving the planet and the quality of human life around the world by the year 2030. Letâs focus on SGD 4
- The goal panel is proposing a tougher standards, comparable to the best in the world; aligning all components of education system with these standards; and strengthening teachersâ subject-matter knowledge and teaching skills.
- Target 4.b: By 2020, substantially expand globally the number of scholarships available to developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States and African countries, for enrolment in higher education, including vocational training and information and communications technology, technical, engineering and scientific programmes, in developed countries and other developing countrie
- Based on discussion paper â The Philippines Voluntary National Review on the Sustainability and Development Goals.
- The goal panel is proposing a tougher standards, comparable to the best in the world; aligning all components of education system with these standards; and strengthening teachersâ subject-matter knowledge and teaching skills.
- The concept of âexcellenceâ can be defined in many ways. It has to do with high value) but it is also linked to quality insurance and quality control. This is by benchmarking our educational institutions or educational systems, in order to gain efficiency in students educational education and in learning. The purpose of education are influenced by changing social forces as well as by educational philosophies and theories. We expect the school to be the key instrument for solving our technological or social problems and preparing our work force for the future. Thus, Schools have been encouraged to provide a world-class quality education, with an emphasis on high achievement and the general improvement of outcomes for all. Educational Reform is necessary to restructure the educational standards to reflect the ever-evolving contemporary ideals of social, economic, and our political political culture aswell. Revision of curriculum means to strengthen the curriculum that is capable of producing more âcompetent, job-ready, active and responsibleâ citizens.